Unlock Efficiency: The Ultimate bm06 3D Sensor Guide (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for bm06 3d sensor
Navigating the global market for the bm06 3D sensor can be a daunting task for international B2B buyers, especially those located in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. As businesses increasingly rely on advanced sensing technologies for enhanced operational efficiency, understanding the nuances of sourcing the right bm06 3D sensor becomes essential. This guide is designed to equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed purchasing decisions, from exploring the various types of bm06 sensors available to assessing their specific applications across industries such as manufacturing, robotics, and healthcare.
In this comprehensive resource, we will delve into critical aspects of the bm06 3D sensor market, including supplier vetting processes, cost considerations, and potential pitfalls to avoid. By providing detailed insights into the key players in the market and the technologies that underpin the bm06 3D sensor, this guide empowers you to navigate your sourcing journey with confidence. Whether you are a procurement officer in Germany looking for reliable suppliers or a business leader in South America seeking innovative solutions, our aim is to streamline your decision-making process.
Ultimately, this guide serves as a vital tool for international B2B buyers, addressing their unique challenges and ensuring they can effectively harness the benefits of bm06 3D sensors in their operations. By understanding market dynamics and leveraging actionable insights, you can position your business for success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Understanding bm06 3d sensor Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Triangulation | High precision, uses laser beams for depth measurement | Robotics, Manufacturing, Quality Control | Pros: High accuracy; Cons: Higher cost than other types. |
| Time-of-Flight (ToF) | Measures distance by calculating time taken for light to return | Automotive, Security, 3D Mapping | Pros: Fast processing; Cons: Affected by ambient light. |
| Structured Light | Projects a known pattern onto the surface for depth capture | Medical Imaging, Scanning, Inspection | Pros: Good resolution; Cons: Limited range in outdoor settings. |
| Stereo Vision | Utilizes two or more cameras to capture depth information | Robotics, Augmented Reality, Drones | Pros: Cost-effective; Cons: Requires complex algorithms. |
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Uses sound waves to measure distance and create 3D profiles | Industrial Automation, Proximity Sensing | Pros: Affordable; Cons: Lower resolution compared to laser systems. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Laser Triangulation Sensors?
Laser triangulation sensors are known for their high precision and ability to measure small distances with accuracy. They work by projecting a laser beam onto a target and measuring the angle of the reflected beam. This makes them ideal for applications in robotics, manufacturing, and quality control where precision is critical. B2B buyers should consider the investment cost and calibration needs when purchasing, as these sensors typically come at a higher price point but deliver superior accuracy.
How Do Time-of-Flight Sensors Work and Their Suitability?
Time-of-Flight (ToF) sensors measure the time it takes for a light pulse to travel to an object and back. This technology is particularly suitable for automotive applications, security systems, and 3D mapping due to its quick response time. However, buyers should be aware that ToF sensors can be affected by ambient light conditions, which may impact performance in certain environments. Evaluating the operational environment is crucial when considering this type of sensor.
What Are the Advantages of Using Structured Light Sensors?
Structured light sensors operate by projecting a known pattern onto a surface and analyzing the deformation of that pattern to determine depth. They are widely used in medical imaging, scanning, and inspection tasks. Their ability to provide high-resolution images makes them advantageous for detailed applications. However, their performance can be limited in outdoor settings or highly reflective environments, which buyers should factor into their purchasing decisions.
Why Choose Stereo Vision Sensors for B2B Applications?
Stereo vision sensors rely on two or more cameras to capture images from different angles, enabling depth perception similar to human vision. They are particularly useful in robotics, augmented reality, and drone technology. While they are cost-effective compared to other methods, buyers should be aware that implementing stereo vision requires complex algorithms and processing capabilities, which may necessitate additional resources or expertise.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Ultrasonic Sensors?
Ultrasonic sensors use sound waves to measure distance and create 3D profiles. They are often employed in industrial automation and proximity sensing due to their affordability. While they provide a budget-friendly option, ultrasonic sensors typically offer lower resolution compared to laser systems. B2B buyers should assess their specific application needs to determine if the trade-off in resolution is acceptable for their operational requirements.
Related Video: What is a Sensor? Different Types of Sensors, Applications
Key Industrial Applications of bm06 3d sensor
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of bm06 3d sensor | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Automated Quality Control in Production Lines | Enhances product quality, reduces waste, and improves efficiency. | Compatibility with existing machinery and integration capabilities. |
| Logistics and Warehousing | Real-time Inventory Management | Streamlines operations, reduces stock discrepancies, and improves order accuracy. | Sensor range and data integration with warehouse management systems. |
| Automotive | Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) | Increases vehicle safety and compliance with regulations. | Compliance with industry standards and environmental conditions. |
| Construction | Site Monitoring and Safety Management | Enhances site safety, reduces accidents, and ensures regulatory compliance. | Durability in harsh environments and data accuracy under variable conditions. |
| Robotics and Automation | Precision Navigation for Autonomous Robots | Boosts operational efficiency and reduces human error in repetitive tasks. | Robustness in dynamic environments and ease of programming. |
How is the bm06 3D Sensor Used in Manufacturing for Quality Control?
In the manufacturing sector, the bm06 3D sensor is pivotal for automated quality control on production lines. It captures precise measurements of products, ensuring they meet design specifications. By identifying defects early in the production process, businesses can significantly reduce waste and rework costs. International buyers should consider compatibility with their existing machinery and the sensor’s ability to integrate seamlessly into their quality management systems to maximize efficiency.
What Role Does the bm06 3D Sensor Play in Logistics and Warehousing?
The bm06 3D sensor is instrumental in real-time inventory management within logistics and warehousing. By providing accurate spatial data, it helps businesses track inventory levels and optimize storage layouts. This capability reduces stock discrepancies and enhances order accuracy, ultimately improving customer satisfaction. For international buyers, it is essential to assess the sensor’s range and its data integration capabilities with existing warehouse management systems to ensure a smooth transition and operational efficiency.
How is the bm06 3D Sensor Enhancing Automotive Safety?
In the automotive industry, the bm06 3D sensor is integral to the development of Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS). It enables vehicles to perceive their surroundings with high precision, enhancing safety features such as collision avoidance and lane-keeping assistance. This technology not only boosts vehicle safety but also ensures compliance with stringent regulations. Buyers from regions like Europe, known for their strict automotive standards, should prioritize sensors that meet industry compliance and can withstand various environmental conditions.
How Does the bm06 3D Sensor Improve Construction Site Safety?
In construction, the bm06 3D sensor is used for site monitoring and safety management. It provides real-time data on site conditions, helping to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with safety regulations. By enhancing site safety and reducing the likelihood of accidents, businesses can protect their workforce and reduce liability. Buyers should focus on the sensor’s durability in harsh environments and its ability to deliver accurate data under variable conditions to ensure reliability.
What Benefits Does the bm06 3D Sensor Offer in Robotics and Automation?
The bm06 3D sensor significantly improves precision navigation for autonomous robots in various applications, from manufacturing to logistics. By providing detailed spatial awareness, it reduces human error in repetitive tasks and enhances overall operational efficiency. For international buyers, it is crucial to consider the sensor’s robustness in dynamic environments and ease of programming to ensure it fits seamlessly into their automation strategies.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘bm06 3d sensor’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Difficulty in Integration with Existing Systems
The Problem:
International B2B buyers often face challenges when integrating the BM06 3D sensor into their existing systems. This is particularly true for companies operating in diverse regions such as Africa and South America, where infrastructure may vary significantly. Buyers may encounter compatibility issues with software, hardware, and communication protocols, leading to downtime and increased costs. These integration headaches can also stem from insufficient technical documentation or varying standards across regions, making it difficult for teams to implement the sensor effectively.
The Solution:
To mitigate integration challenges, buyers should prioritize sourcing the BM06 3D sensor from reputable suppliers that provide comprehensive technical support and detailed documentation. Before purchasing, engage with the vendor to discuss your current systems and ask for case studies or references from similar companies that have successfully integrated the sensor. Additionally, consider investing in training sessions for your technical team to familiarize them with the sensor’s capabilities and integration methods. Utilizing middleware solutions can also bridge compatibility gaps, allowing seamless communication between the BM06 sensor and your existing systems.
Scenario 2: Concerns Over Sensor Accuracy and Reliability
The Problem:
One of the primary concerns for B2B buyers is the accuracy and reliability of the BM06 3D sensor, especially in critical applications such as manufacturing and logistics. In regions like the Middle East, where environmental factors can fluctuate significantly, buyers may worry that the sensor may not perform consistently under varying conditions. Inaccurate readings can lead to costly errors, such as misalignment in assembly lines or incorrect inventory tracking, ultimately affecting productivity and profitability.
The Solution:
To ensure the accuracy and reliability of the BM06 3D sensor, it is essential to conduct thorough testing before full-scale implementation. Buyers should request samples for pilot projects, allowing them to assess the sensor’s performance in their specific environment. Additionally, consider establishing a routine calibration schedule to maintain optimal sensor performance. Collaborating with the manufacturer for ongoing technical support can also help address any accuracy issues promptly. Lastly, integrating redundancy measures—such as using multiple sensors for critical applications—can enhance reliability and provide fallback options in case of sensor failure.
Scenario 3: Limited Support and Maintenance Options
The Problem:
B2B buyers in Europe and beyond often express frustration over limited support and maintenance options for the BM06 3D sensor. This issue can be exacerbated for companies operating in remote areas or countries with less established tech support networks. When problems arise, such as sensor malfunctions or software glitches, the inability to access timely support can lead to significant operational disruptions and financial losses.
The Solution:
To address support and maintenance challenges, buyers should select suppliers that offer robust after-sales support, including remote assistance and on-site service options. Prior to purchase, verify the availability of local service centers or authorized representatives in your region. Establishing a service-level agreement (SLA) with the vendor can ensure that you receive timely responses to support inquiries. Furthermore, consider investing in a local technician training program to empower your team with troubleshooting and maintenance skills, which can reduce dependency on external support and minimize downtime. Engaging in a proactive maintenance strategy, including regular updates and health checks of the sensor, can also help preemptively address potential issues.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for bm06 3d sensor
When selecting materials for the bm06 3D sensor, it is crucial to consider properties that directly impact performance, durability, and application suitability. The following analysis delves into four common materials used in the production of these sensors, providing actionable insights for international B2B buyers.
Which Metals Are Suitable for bm06 3D Sensors?
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance and high strength, making it suitable for various environments. It typically withstands temperatures up to 800°C and pressures exceeding 2000 psi.
Pros & Cons: The durability of stainless steel is a significant advantage, as it can endure harsh conditions without degrading. However, it is relatively expensive compared to other metals and can complicate manufacturing processes due to its toughness.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is compatible with a wide range of media, including water, oils, and gases, making it versatile for diverse applications.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from Europe, particularly Germany and the UK, should ensure compliance with standards such as DIN and ASTM for quality assurance. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing stainless steel from local suppliers can mitigate import costs.
Aluminum
Key Properties: Aluminum is lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and has good thermal conductivity. It generally performs well in temperatures up to 150°C and moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of aluminum is its low weight, which can reduce shipping costs and ease installation. However, it is less durable than stainless steel and may not perform well in high-pressure environments.
Impact on Application: Aluminum is suitable for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in portable devices or systems requiring frequent movement.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the availability of aluminum alloys that meet local standards in their regions. In the Middle East, for instance, specific grades may be preferred for their heat resistance in high-temperature applications.
Polycarbonate
Key Properties: Polycarbonate is a high-performance plastic known for its impact resistance and transparency. It can operate effectively at temperatures up to 120°C.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of polycarbonate is its lightweight nature and ease of molding, which simplifies manufacturing. However, it has a lower temperature and pressure tolerance compared to metals, limiting its use in extreme conditions.
Impact on Application: Polycarbonate is ideal for applications requiring transparency, such as visual monitoring systems, but may not be suitable for high-pressure environments.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with international safety standards is crucial, especially for buyers in Europe, where regulations on plastics can be stringent. Buyers in Africa and South America should ensure that the polycarbonate used is UV-stabilized for outdoor applications.
Glass-Filled Nylon
Key Properties: Glass-filled nylon is a composite material that offers enhanced strength and stiffness compared to standard nylon. It can withstand temperatures up to 150°C and moderate pressures.
Pros & Cons: This material is cost-effective and provides good mechanical properties, making it suitable for various applications. However, it can be more brittle than metals, which may lead to failure under certain stress conditions.
Impact on Application: Glass-filled nylon is often used in applications where weight and cost are critical, such as in consumer electronics.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must consider the environmental regulations regarding plastics in their regions. In Europe, compliance with REACH regulations is essential, while buyers in the Middle East may need to assess local chemical compatibility.
Summary Table of Material Selection for bm06 3D Sensor
| Material | Typical Use Case for bm06 3D sensor | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | Industrial automation, robotics | Excellent corrosion resistance | Higher cost and manufacturing complexity | High |
| Aluminum | Portable devices, lightweight sensors | Lightweight and easy to fabricate | Lower durability in high-pressure environments | Medium |
| Polycarbonate | Visual monitoring systems | Lightweight and impact-resistant | Limited temperature and pressure tolerance | Low |
| Glass-Filled Nylon | Consumer electronics | Cost-effective with good strength | Brittle under stress conditions | Medium |
This guide provides a comprehensive look at material selection for the bm06 3D sensor, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on specific application needs and regional considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for bm06 3d sensor
What are the Key Manufacturing Processes for the bm06 3D Sensor?
The manufacturing process for the bm06 3D sensor involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets high standards of precision and reliability. For B2B buyers, understanding these processes can aid in selecting the right suppliers and ensuring quality.
Material Preparation: What Materials are Used?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation. The bm06 3D sensor typically utilizes high-grade materials such as specialized plastics, metals, and semiconductors. These materials are chosen for their durability and ability to withstand various environmental conditions. Suppliers often perform extensive material testing to ensure that they meet specific industry standards.
Forming Techniques: How is the Sensor Shaped?
Once materials are prepared, the next step is forming. This includes techniques such as injection molding for plastics and machining for metal components. For the bm06 3D sensor, precision is paramount, and manufacturers often employ advanced CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining to achieve intricate designs and tight tolerances. This process is crucial for ensuring that all components fit together seamlessly.
Assembly: What Does the Assembly Process Involve?
The assembly phase is where the various components of the bm06 3D sensor come together. This can involve manual assembly as well as automated processes. For instance, robotic arms may be used for repetitive tasks, ensuring consistency and speed. Quality control measures are integrated into this stage, with checks at various points to confirm that components are assembled correctly.
Finishing: How is Quality Achieved in the Final Touches?
Finally, the finishing stage includes surface treatment, calibration, and packaging. Surface treatments may involve coatings that enhance durability or improve performance in specific environments. Calibration is critical for sensors, as it ensures that they provide accurate readings. The final packaging must also protect the sensor during transport while providing relevant product information for end-users.
What International Quality Standards Apply to the bm06 3D Sensor?
Quality assurance is a vital part of the manufacturing process, especially for international B2B buyers. The bm06 3D sensor must comply with various international standards to ensure safety, reliability, and performance.
Which ISO Standards are Relevant?
One of the primary quality standards is ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. Compliance with ISO 9001 indicates that a manufacturer has established processes that enhance customer satisfaction through consistent quality. B2B buyers should verify if their suppliers are certified and can provide documentation of compliance.
Are There Industry-Specific Certifications to Consider?
In addition to ISO standards, the bm06 3D sensor may require compliance with industry-specific certifications such as CE marking for European markets or API standards for certain applications. These certifications ensure that the product meets regulatory requirements and safety standards pertinent to specific industries. Buyers should inquire about these certifications when evaluating suppliers.
What are the Critical Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) is integral to ensuring that the bm06 3D sensor meets both manufacturing and regulatory standards. Understanding the QC checkpoints can help B2B buyers assess supplier reliability.
What are the Stages of Quality Control?
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial stage involves inspecting raw materials and components before they enter the production line. Suppliers should have strict criteria for accepting materials to ensure they meet specifications.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, IPQC checks are conducted at various stages to monitor the production process. This includes dimensional checks and functional tests to confirm that components are being produced correctly.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): After assembly, the final product undergoes comprehensive testing, including performance evaluations and environmental stress testing. This ensures that the bm06 3D sensor operates as intended before it is shipped to customers.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Assurance Processes?
For international B2B buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality assurance processes is essential. Here are several methods to ensure that suppliers adhere to high standards.
What are Effective Verification Methods?
-
Supplier Audits: Conducting audits of potential suppliers can provide insights into their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Audits should focus on compliance with ISO standards, as well as industry-specific certifications.
-
Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask suppliers for detailed quality reports that outline their manufacturing and QC processes. These reports should include data on defect rates, testing methods, and compliance with standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality processes. These inspections can be particularly valuable for buyers from regions like Africa and South America, where local regulations may differ.
What are the Quality Control Nuances for International B2B Buyers?
Navigating quality control nuances can be complex for international B2B buyers. Understanding these aspects can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
How Do Regional Regulations Impact Quality Assurance?
Different regions may have specific regulations that impact the quality assurance processes for the bm06 3D sensor. For instance, European markets may require CE marking, while Middle Eastern countries might have different compliance criteria. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local regulations and ensure that their suppliers are compliant.
What Should Buyers Consider Regarding Language and Communication?
Effective communication is crucial in verifying quality assurance processes. Language barriers can lead to misunderstandings regarding quality standards and specifications. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers can provide documentation and support in a language they understand, ideally English, German, or other relevant languages.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for the bm06 3D sensor is vital for international B2B buyers. By focusing on the key stages of manufacturing, relevant standards, critical quality checkpoints, and effective verification methods, buyers can make informed decisions and establish reliable partnerships with suppliers.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘bm06 3d sensor’
In the fast-evolving landscape of industrial technology, sourcing the right equipment, such as the bm06 3D sensor, is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and ensuring competitive advantage. This guide provides a structured checklist to assist international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, in making informed procurement decisions.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Understanding your specific needs is the first step in sourcing the bm06 3D sensor. Identify the technical requirements such as resolution, range, and environmental conditions where the sensor will operate. This clarity helps streamline the selection process and ensures compatibility with your existing systems.
- Considerations:
- Application type (e.g., manufacturing, robotics, quality control).
- Integration capabilities with current technologies.
Step 2: Research Market Trends and Innovations
Staying updated on the latest trends in 3D sensing technology can provide insights into the best products available. Investigate emerging features and improvements in sensor technology that could enhance performance and reduce costs.
- Key Areas to Explore:
- Advances in sensor accuracy and speed.
- Adoption of new materials or technologies that improve sensor durability.
Step 3: Evaluate Potential Suppliers
Before committing to a supplier, thorough vetting is essential. Request detailed company profiles, product catalogs, and case studies to understand their market position and reliability. Engaging with references from other buyers in your industry can provide valuable insights into the supplier’s performance.
- What to Look For:
- Customer reviews and testimonials.
- Industry certifications and compliance with international standards.
Step 4: Verify Supplier Certifications
Ensure that the suppliers you consider have the necessary certifications for quality and safety, especially if you operate in regulated industries. Certifications like ISO 9001 can indicate a commitment to quality management.
- Why This Matters:
- Helps mitigate risks associated with substandard products.
- Ensures the supplier meets international quality benchmarks.
Step 5: Request Samples or Demonstrations
Before finalizing your order, request samples or product demonstrations. This step allows you to evaluate the sensor’s performance in real-world conditions relevant to your application.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- Accuracy and speed of data processing.
- Ease of integration and user interface.
Step 6: Understand Warranty and Support Options
Review the warranty terms and after-sales support offered by the supplier. A robust support system can significantly reduce downtime and maintenance costs in the long term.
- Key Aspects to Check:
- Length and coverage of the warranty.
- Availability of technical support and training resources.
Step 7: Negotiate Pricing and Payment Terms
Finally, engage in negotiations regarding pricing and payment terms. Consider bulk purchasing discounts or long-term partnership agreements that could offer financial benefits.
- Negotiation Tips:
- Be clear about your budget and expectations.
- Explore flexible payment options that suit your cash flow.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing the bm06 3D sensor effectively, ensuring they select a product that meets their operational needs and enhances their business capabilities.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for bm06 3d sensor Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in bm06 3D Sensor Manufacturing?
When sourcing bm06 3D sensors, understanding the cost structure is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The selection of materials directly impacts both performance and cost. High-quality components such as semiconductors and optical lenses can significantly increase the overall price. Buyers should evaluate the trade-off between material quality and long-term reliability.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, manufacturers in Europe may have higher labor costs than those in Africa or South America. This factor can influence the final price, especially in labor-intensive production processes.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Buyers should inquire about how these costs are factored into the pricing.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling can be a significant upfront cost, particularly for unique sensor designs. Understanding the tooling requirements and their impact on pricing is essential for budget planning.
-
Quality Control (QC): Robust QC measures ensure product reliability but can also add to the overall cost. Buyers should weigh the importance of certifications and testing standards against the potential price increase.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on location and chosen shipping methods. Factors such as distance, weight, and dimensions of the shipment play a role in logistics costs.
-
Margin: Supplier profit margins will vary based on market conditions and competition. Understanding the typical margins in the industry can help buyers assess whether pricing is reasonable.
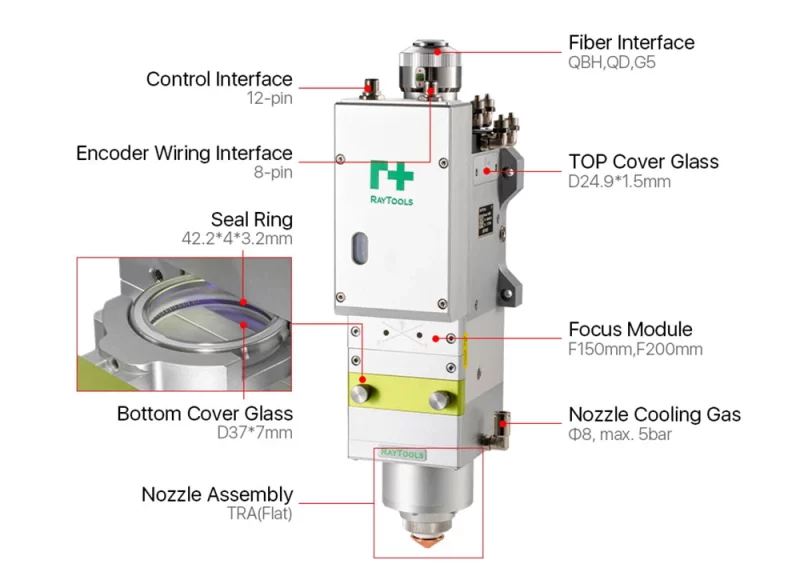
A stock image related to bm06 3d sensor.
How Do Price Influencers Affect bm06 3D Sensor Costs?
Several key influencers can impact the pricing of bm06 3D sensors:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly affect pricing. Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate volume discounts whenever possible.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom specifications can lead to increased costs. Buyers should clearly define their requirements to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Materials and Quality: Higher quality materials and certifications (e.g., ISO standards) can justify a higher price. It’s vital to balance quality with budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, reliability, and production capabilities can influence price. Established suppliers may charge a premium for their experience and quality assurance.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms affects shipping costs and risk allocation. Buyers should carefully consider which terms are most favorable for their operations.
What Are the Best Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing of bm06 3D Sensors?
To maximize cost efficiency when sourcing bm06 3D sensors, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in price negotiations with suppliers. Leverage your purchasing power, especially if you are considering larger orders, to secure better pricing or additional services.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Look beyond the initial purchase price. Evaluate maintenance, warranty, and potential downtime costs to understand the complete financial impact of your sourcing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of regional pricing variations and currency fluctuations. For instance, while European suppliers may offer high-quality sensors, their prices could be higher than those from emerging markets.
-
Research and Compare: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and offerings from different suppliers. Use this data to inform your negotiations and sourcing strategy.
-
Stay Informed on Market Trends: Understanding industry trends can provide insights into pricing fluctuations and help you make timely purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Please note that the prices for bm06 3D sensors can vary significantly based on the factors discussed above. It is advisable to conduct a thorough market analysis and request quotes from multiple suppliers to obtain the most accurate pricing information tailored to your specific needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing bm06 3d sensor With Other Solutions
Understanding the Importance of Alternatives in 3D Sensor Technology
In the rapidly evolving landscape of 3D sensing technology, choosing the right solution is critical for businesses aiming to enhance operational efficiency and product quality. For international B2B buyers, especially from diverse regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, evaluating alternatives to the bm06 3D sensor can lead to more informed purchasing decisions. This section provides a comparative analysis of the bm06 3D sensor against two viable alternatives, focusing on performance, cost, ease of implementation, maintenance, and best use cases.
Comparison Table of 3D Sensor Solutions
| Comparison Aspect | Bm06 3D Sensor | Alternative 1: Lidar Technology | Alternative 2: Structured Light Scanning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High precision and depth perception | Excellent range and speed | Good accuracy for small objects |
| Cost | Mid-range pricing | Higher initial investment | Cost-effective for specific applications |
| Ease of Implementation | User-friendly with standard interfaces | Requires skilled setup | Generally easy to implement |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Moderate due to complexity | Low, minimal calibration needed |
| Best Use Case | Robotics, automation | Autonomous vehicles, mapping | Quality control, reverse engineering |
What Are the Pros and Cons of Lidar Technology Compared to the Bm06 3D Sensor?
Lidar technology offers excellent range and speed, making it suitable for applications like autonomous vehicles and large-scale mapping. However, the initial investment is significantly higher than that of the bm06 3D sensor, which may deter some businesses, especially in developing regions. Additionally, Lidar systems often require skilled technicians for setup and maintenance, which could increase operational costs in terms of training and support.
How Does Structured Light Scanning Compare to the Bm06 3D Sensor?
Structured light scanning is known for its cost-effectiveness, particularly in applications focused on quality control and reverse engineering. It provides good accuracy, especially for small objects, making it a popular choice in manufacturing settings. However, it may not perform as well in environments requiring high precision or depth perception compared to the bm06 3D sensor. The ease of implementation for structured light systems is generally high, but businesses should consider the specific application requirements to determine its effectiveness.
How Can B2B Buyers Choose the Right 3D Sensor Solution?
When evaluating the right 3D sensor solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including the operational environment, budget constraints, and application objectives. While the bm06 3D sensor is a solid choice for robotics and automation due to its balance of performance and cost, alternatives like Lidar and structured light scanning may offer distinct advantages depending on the use case. Conducting a thorough analysis of the pros and cons of each solution, along with a consideration of long-term operational needs, will empower buyers to make the most informed decision for their business.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for bm06 3d sensor
What Are the Key Technical Properties of the bm06 3D Sensor?
When considering the bm06 3D sensor for your business, understanding its technical specifications is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are some essential properties to consider:
-
Measurement Range
– The bm06 3D sensor typically has a specified measurement range that defines the minimum and maximum distances it can accurately detect. This property is vital for applications where precise measurement is critical, such as in robotics or industrial automation. -
Resolution
– Resolution refers to the smallest detail the sensor can detect. A higher resolution allows for more accurate data collection, which is essential in applications requiring fine detail, such as quality control in manufacturing. For B2B buyers, understanding resolution helps in aligning the sensor’s capabilities with specific project needs. -
Data Output Format
– The bm06 sensor may support various data output formats, such as USB, Ethernet, or serial communication. This flexibility is important for integration into existing systems. Buyers should ensure compatibility with their operational infrastructure to avoid additional costs or complications during implementation. -
Operating Temperature Range
– This specification indicates the temperature limits within which the sensor can function effectively. B2B buyers operating in extreme environments, such as outdoor construction sites or manufacturing facilities, must consider this property to ensure the sensor’s reliability and longevity. -
Power Consumption
– The power consumption of the bm06 sensor can impact operational costs, especially in large-scale implementations. A sensor with lower power requirements can lead to significant savings over time, making it a crucial consideration for budget-conscious businesses.
Which Trade Terms Should International Buyers Understand for the bm06 3D Sensor?
Navigating the trade landscape can be complex, especially when sourcing technical equipment like the bm06 3D sensor. Here are some common terms that every B2B buyer should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify trusted suppliers and ensure they are sourcing high-quality products. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– MOQ indicates the smallest number of units that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for budget planning and inventory management, especially for businesses in Africa or South America that may have limited initial demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific products. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to gather competitive pricing and negotiate better terms, which can significantly impact their purchasing strategy. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– These are internationally recognized rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding the delivery of goods. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for international transactions, particularly for buyers in the Middle East and Europe, as they clarify shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities. -
Lead Time
– This term describes the time taken from placing an order to receiving it. Understanding lead times is vital for project planning and inventory management. Buyers should account for lead times when sourcing from international suppliers to avoid delays in production or operations. -
Warranty and Support Terms
– These refer to the guarantees provided by the manufacturer regarding the product’s performance and the level of support available post-purchase. Knowing these terms helps buyers ensure they are protected against defects and have access to assistance when needed.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing the bm06 3D sensor, ensuring it meets their specific needs and operational requirements.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the bm06 3d sensor Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends in the bm06 3D Sensor Sector?
The bm06 3D sensor market is experiencing robust growth, driven by advancements in automation, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT). International B2B buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, are increasingly prioritizing these technologies due to their potential to enhance operational efficiency and accuracy in various applications, including manufacturing, healthcare, and robotics. The demand for high-resolution 3D sensing solutions is being fueled by sectors such as automotive and consumer electronics, where precision is paramount.
Emerging trends in sourcing practices include the adoption of cloud-based solutions for data management, which allow for real-time analysis and processing. Buyers are also looking for suppliers that offer integrated systems combining 3D sensors with machine learning capabilities, enabling predictive maintenance and improved quality control. Additionally, as the market becomes more competitive, international buyers are focusing on establishing long-term partnerships with suppliers who can provide innovative technologies and responsive customer service.
The geopolitical landscape and trade regulations also play a significant role in market dynamics. For instance, buyers in Europe may face different tariffs and import regulations compared to those in Africa or South America. Understanding these nuances is crucial for optimizing sourcing strategies and ensuring compliance while maximizing value.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact the bm06 3D Sensor Supply Chain?
Sustainability has become a critical consideration for B2B buyers in the bm06 3D sensor sector. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, particularly in terms of waste management and energy consumption, is under scrutiny. Buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to sustainable practices, including the use of recyclable materials and energy-efficient manufacturing methods.
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as businesses aim to build transparent supply chains that respect labor rights and promote fair trade. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and Fair Trade certification can serve as benchmarks for evaluating potential suppliers. By prioritizing these aspects, buyers not only enhance their corporate responsibility profiles but also mitigate risks associated with supply chain disruptions and reputational damage.
Furthermore, many companies are now exploring partnerships with suppliers who invest in sustainable technologies. For instance, some manufacturers are developing eco-friendly 3D sensors that utilize biodegradable materials or minimize toxic components. By aligning purchasing decisions with sustainability goals, B2B buyers can foster innovation and create a competitive advantage in their respective markets.
What Is the Historical Context Behind the bm06 3D Sensor Development?
The development of 3D sensor technology has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, 3D sensors were primarily used in specialized applications, such as industrial automation and quality control. However, advancements in sensor technology, coupled with the increasing demand for precision in various sectors, have led to a broader adoption of 3D sensors.
The introduction of the bm06 model represents a significant milestone in this evolution, as it integrates cutting-edge technologies that enhance measurement accuracy and processing speed. This evolution not only reflects the technological advancements but also the changing needs of industries that require more sophisticated and reliable sensing solutions. For B2B buyers, understanding this historical context can provide insights into the technology’s reliability and the ongoing innovations that can influence future procurement decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of bm06 3d sensor
-
How do I choose the right bm06 3D sensor for my business needs?
Selecting the right bm06 3D sensor involves assessing your specific application requirements, such as measurement range, accuracy, and environmental conditions. Consider factors like the type of objects you will be scanning, the necessary resolution, and integration capabilities with existing systems. It may also be beneficial to consult with suppliers who can provide insights based on industry standards and best practices. -
What are the typical applications for the bm06 3D sensor in various industries?
The bm06 3D sensor is widely used across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare. Common applications include quality control in production lines, object detection in automated systems, and spatial mapping in robotics. Understanding how similar businesses leverage the sensor can guide you in determining its relevance to your operations. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) for bm06 3D sensors when sourcing from suppliers?
MOQs for bm06 3D sensors vary by supplier and may depend on factors such as the level of customization required and production capabilities. Generally, established manufacturers may offer lower MOQs for standard models, while customized sensors may come with higher MOQs. Always inquire directly with suppliers to negotiate terms that align with your purchasing strategy. -
How can I ensure quality assurance when sourcing bm06 3D sensors internationally?
To ensure quality assurance when sourcing bm06 3D sensors, conduct thorough research on potential suppliers, checking certifications and industry standards. Request samples for testing, and consider third-party inspections or audits to assess quality control processes. Building a strong communication channel with suppliers can also facilitate transparency regarding production practices. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing bm06 3D sensors from international suppliers?
Payment terms can vary significantly based on supplier policies and your business relationship. Common arrangements include upfront payments, net 30/60 terms, or payment upon delivery. For new suppliers, it may be prudent to negotiate favorable terms that mitigate risk while ensuring timely delivery. Establishing trust through clear contracts can enhance your negotiation position.

A stock image related to bm06 3d sensor.
- How do I assess the reliability of a supplier for bm06 3D sensors?
Assessing supplier reliability involves reviewing their track record, customer testimonials, and industry reputation. Request references from past clients and investigate their ability to meet deadlines and quality standards. Additionally, consider their after-sales support and responsiveness to inquiries, which can indicate their commitment to customer service.
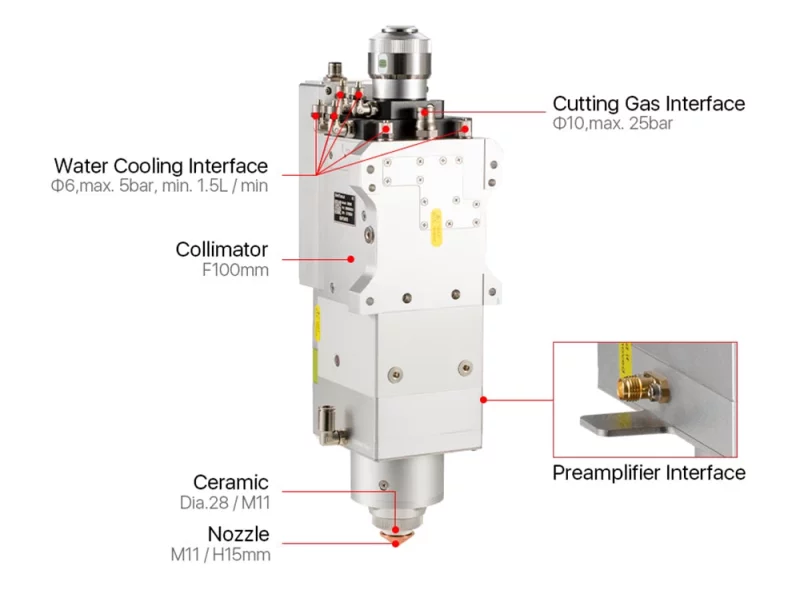
A stock image related to bm06 3d sensor.
-
What are the logistics considerations when importing bm06 3D sensors?
When importing bm06 3D sensors, key logistics considerations include shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations. Evaluate the total cost of ownership, factoring in shipping fees, taxes, and duties. Collaborating with a logistics partner familiar with international trade can simplify the process and ensure compliance with local regulations. -
Can bm06 3D sensors be customized to meet specific industry requirements?
Yes, bm06 3D sensors can often be customized to align with specific industry requirements, such as unique measurement parameters or integration features. When discussing customization options with suppliers, provide detailed specifications and use cases to facilitate the development of a tailored solution. Keep in mind that customization may impact lead times and pricing, so plan accordingly.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for bm06 3d sensor
The strategic sourcing of the bm06 3D sensor presents a transformative opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By leveraging the unique capabilities of the bm06 3D sensor, businesses can enhance their operational efficiency, improve product quality, and ultimately drive innovation. The insights gained from strategic sourcing decisions not only foster strong supplier relationships but also ensure a competitive edge in fast-evolving markets.
How can B2B buyers maximize value from their sourcing strategies? It’s essential to conduct thorough market research, understand regional regulatory requirements, and align sourcing strategies with long-term business objectives. Emphasizing partnerships with suppliers that prioritize quality and sustainability can lead to more resilient supply chains and better product outcomes.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced sensing technologies like the bm06 is expected to grow, driven by advancements in automation and artificial intelligence. B2B buyers should seize this moment to invest in these technologies, ensuring they are well-positioned to meet future challenges and capitalize on emerging opportunities. Take action today by exploring strategic partnerships and innovative sourcing solutions that can propel your business forward in this dynamic landscape.