Tube Sealing Machines: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Tube Sealing Machines
In the competitive landscape of packaging solutions, tube sealing machines stand as essential tools for businesses aiming to preserve product integrity, extend shelf life, and ensure compliance across diverse industries—from food processing and pharmaceuticals to electronics and chemicals. These machines, which heat-seal or vacuum-seal tubes and pouches, enable efficient, high-volume packaging that meets stringent quality standards.
However, navigating the global market presents significant challenges: fluctuating regulations in the USA and Europe, such as FDA and EU standards for food safety; supply chain disruptions affecting component availability; rapid technological advancements in automation and IoT integration; and intensifying competition from emerging markets. Without a strategic approach, companies risk operational inefficiencies, compliance violations, and lost market share.
This guide equips B2B decision-makers with actionable insights to overcome these hurdles. It explores:
- Market Overview: Key players, trends, and regional dynamics in the USA and Europe.
- Machine Types and Features: From band sealers and chamber vacuum models to custom heat sealers, including options for gas flush and explosion-proof variants.
- Selection Criteria: Factors like capacity, material compatibility (e.g., mylar bags, foil pouches), and integration with existing workflows.
- Best Practices: Cost analysis, maintenance tips, and compliance strategies to optimize ROI.
- Case Studies: Real-world applications in packaging for long-term storage and tamper-evident solutions.
By leveraging this guide, you’ll streamline procurement and enhance your packaging operations in a global context.
Top 10 Tube Sealing Machines Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Tube Filling & Sealing Machinery and Change Parts
Domain: thewholepkg.com
Registered: 2004 (21 years)
Introduction: Fully Automatic rotary machinery used for filling of plastic, laminate and aluminum tubes at up to 80 tubes per minute. Used and Rebuilt Tube Filling Machines….
2. 8 Best Tube Filling Machine Brands in the USA 2025 – LIENM
Domain: lienm.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: 1. ProSys Filling Systems (California, USA) … Overview: ProSys has a strong reputation for precision tube filling & sealing machine brands, ……
3. Squeezable Tube Filling Sealing Machine
Domain: zonesuntech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: Tube filling machine is designed to fill liquid & paste products like facial cleanser, hand cream, mustard sauce into squeezable tubes and seal them….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
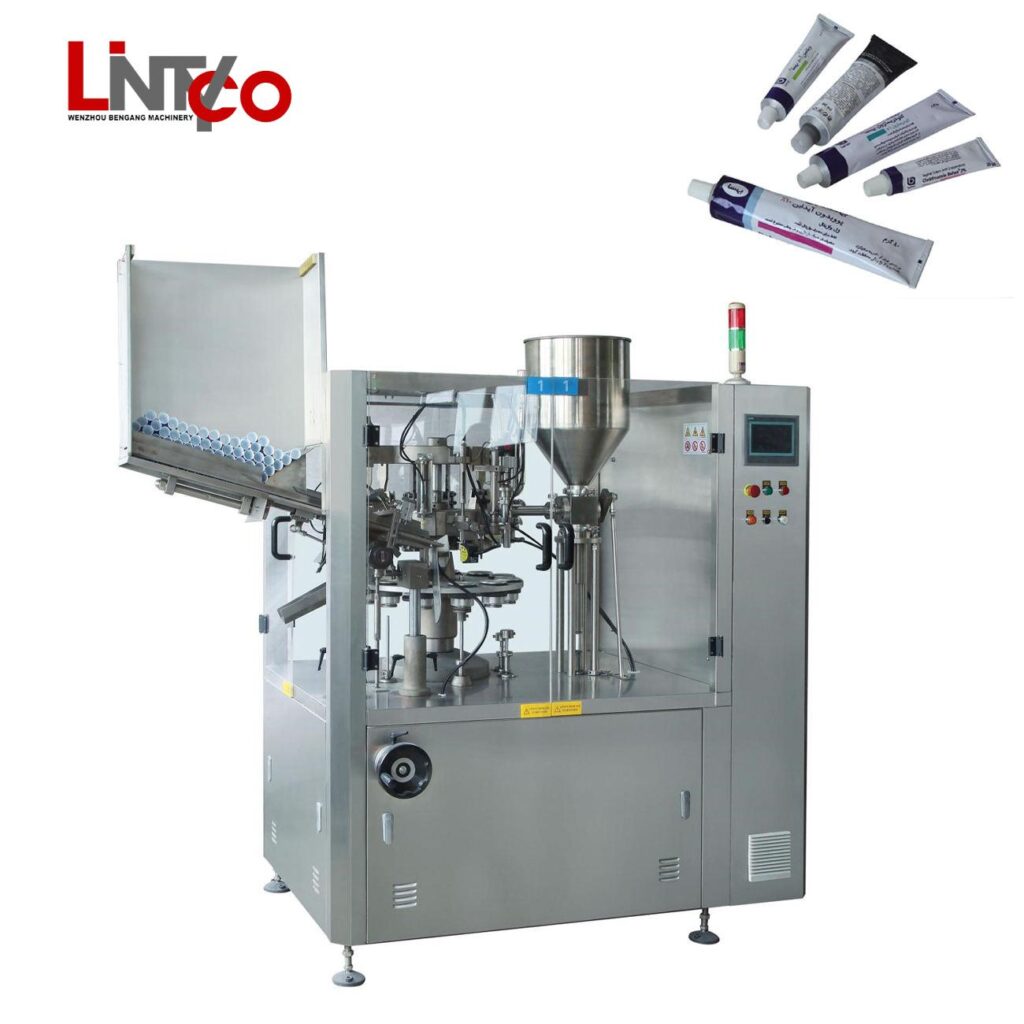
4. Tube Filling And Sealing Machine – Micmachinery
Domain: micmachinery.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: As a trusted supplier, we take pride in offering a wide selection of tube filling and sealing machines to cater to diverse industry needs….
5. Tube Filling Sealing Machine in USA- Gel, Ointment, Cream, Tooth …
Domain: chitramechtech.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Tube Filling Machine is an advance type of equipment widely used for filling cream, gel, toothpaste and other semi solid products in plastic or aluminium tubes….
6. Automatic Tube Filling & Sealing Machine – Patron Business Solutions
Domain: patronbusinesssolutions.com
Registered: 2025 (0 years)
Introduction: Top-Tier Manufacturing – We specialize in advanced tube filling and sealing solutions designed for high performance and reliability. ✔️ Tailored Solutions ……
Understanding tube sealing machines Types and Variations
Understanding Tube Sealing Machines: Types and Variations
Tube sealing machines are essential for packaging operations in industries such as food, pharmaceuticals, and consumer goods, ensuring product integrity and shelf life. Based on industry standards and equipment categories, we identify the following key types. These variations cater to different sealing needs, from simple heat sealing to advanced vacuum and gas flush options.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Band Sealers | Continuous sealing with band elements; options for vacuum, gas flush, or both; adjustable speed and temperature. | Food packaging, retail bags, industrial tubes. | Pros: High throughput, consistent seals. Cons: Limited to straight seals, higher energy use. |
| Chamber Vacuum Sealers | Vacuum chamber for air removal; single or double chamber models; includes tabletop and industrial variants. | Perishable goods, medical supplies, tube packaging. | Pros: Superior vacuum for freshness. Cons: Slower for high-volume, requires maintenance. |
| Impulse Sealers | Impulse heating for quick seals; horizontal/vertical orientations; heavy-duty options. | Flexible pouches, tubes, small batches. | Pros: Energy-efficient, portable. Cons: Not for continuous sealing, lower durability on thick materials. |
| Custom Heat Sealers | Tailored designs for specific materials; explosion-proof options; integrated with filling equipment. | Specialized tubes, hazardous materials. | Pros: Versatile, safe for volatile products. Cons: Higher cost, custom fabrication time. |
Band Sealers
Band sealers utilize heated bands to create continuous seals on tubes or pouches, ideal for high-volume production. Features include adjustable sealing speeds (up to 20-30 feet per minute) and options for vacuum to remove air or gas flush for modified atmosphere packaging (MAP). They are commonly used in food processing for sealing vacuum bags or tubes containing liquids and solids. Pros include reliability in continuous operations and compatibility with various materials like polyethylene. Cons involve higher power consumption and the need for straight-line sealing, making them less suitable for curved or complex shapes.
Chamber Vacuum Sealers
These machines feature a vacuum chamber that draws out air before sealing, ensuring airtight closures. Single-chamber models are compact for small operations, while double-chamber ones allow loading one side while the other seals, improving efficiency. Applications span pharmaceutical tubes, food storage pouches, and industrial packaging requiring extended shelf life. Pros are excellent oxygen barrier for product preservation and built-in safety features like code printers for traceability. Cons include longer cycle times (10-30 seconds per seal) and the need for regular maintenance of vacuum pumps.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Impulse Sealers
Impulse sealers deliver quick, energy-efficient seals using short bursts of heat, minimizing material distortion. They come in horizontal or vertical configurations, with heavy-duty models for thicker materials up to 10-20 mils. Suitable for sealing tubes in cosmetics, adhesives, or small-scale food packaging. Pros are portability and low energy costs, making them ideal for lab or field use. Cons involve limitations on continuous production and potential for weaker seals on very thick or multi-layered tubes compared to band sealers.
Custom Heat Sealers
Designed for specialized needs, these sealers integrate custom heating elements, often with explosion-proof ratings for hazardous environments. They can include features like automated controls and compatibility with filling machines. Used in industries like pharmaceuticals for sealing tubes with desiccants or oxygen absorbers. Pros are adaptability to unique requirements and enhanced safety for volatile contents. Cons are the premium cost and lead time for customization, typically requiring consultation with manufacturers.
Key Industrial Applications of tube sealing machines
Key Industrial Applications of Tube Sealing Machines
Tube sealing machines are essential for automating the sealing of flexible tubes used in packaging, ensuring product integrity, efficiency, and compliance in various industries. The following table outlines key industrial applications, drawing from common uses in food storage, pharmaceutical, and industrial packaging solutions. Each entry includes specific applications and detailed benefits tailored to B2B operations in the USA and Europe.
| Industry | Key Applications | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Sealing tubes for condiments (e.g., ketchup, mustard), sauces, and dairy products; vacuum-sealing for long-term food storage and retort pouches. | Enhances shelf life by creating airtight seals that prevent oxidation and contamination, reducing waste by up to 30% through precise sealing; improves supply chain efficiency with high-speed operations (up to 100 tubes/min), complying with FDA and EU food safety standards like HACCP; lowers operational costs via automated processes that minimize manual labor and material waste. |
| Pharmaceuticals and Healthcare | Sealing tubes for ointments, creams, gels, and injectable solutions; tamper-evident sealing for vials and desiccants. | Ensures product sterility and tamper resistance, critical for compliance with ISO 13485 and EMA regulations; reduces contamination risks by 40% through vacuum and heat sealing, extending drug efficacy; boosts production scalability with customizable sealing options, enabling faster time-to-market for generics and specialty medications while cutting packaging defects. |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care | Sealing tubes for lotions, shampoos, toothpaste, and beauty creams; child-resistant and frangible seal options. | Provides aesthetic and functional integrity, enhancing brand appeal with consistent, leak-proof seals; minimizes product loss from evaporation or spillage, improving ROI by 25% in high-volume lines; supports sustainability goals through reduced plastic waste via efficient sealing techniques, aligning with EU Green Deal initiatives and US eco-labeling standards. |
| Chemicals and Adhesives | Sealing tubes for lubricants, adhesives, paints, and industrial fluids; high-temperature and Mil-Spec pouches for hazardous materials. | Delivers robust barriers against chemical leaks and environmental factors, ensuring safety in transportation and storage; increases operational uptime by 35% with durable seals that withstand harsh conditions, reducing recalls; facilitates compliance with OSHA and REACH regulations through explosion-proof and gas-flush options, optimizing inventory management in bulk packaging. |
| Electronics and Semiconductors | Sealing tubes for conductive pastes, thermal compounds, and moisture-sensitive components; anti-static and shield bags. | Protects sensitive materials from electrostatic discharge and humidity, preserving component functionality; enhances yield rates by 20% via precise sealing that prevents contamination in cleanroom environments; streamlines logistics with compact, sealed tubes that comply with IPC standards, lowering shipping costs and supporting just-in-time manufacturing in US and European fabs. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘tube sealing machines’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Tube Sealing Machines & Their Solutions
Below, we outline three prevalent pain points faced by B2B users in manufacturing, packaging, and distribution sectors across the USA and Europe when implementing tube sealing machines. Each is presented in a scenario/problem/solution format, drawing from industry best practices and product features like those offered by specialized sealers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Sealing Quality Leading to Product Losses
Scenario: In a pharmaceutical packaging facility in Europe, operators are sealing tubes for sensitive ointments and creams using standard heat sealers. The process results in variable seal integrity, causing leaks during transport and leading to regulatory non-compliance under EU standards like ISO 11607.
Problem: Inconsistent seals compromise product sterility and safety, resulting in wasted materials, recalls, and reputational damage, with costs estimated at 5-10% of production value in affected batches.
Solution: Invest in advanced tube sealers with precision temperature control and vacuum options, such as those from Impak’s Vacuum & Heat Sealers category (e.g., band sealers with gas flush). These ensure uniform heat application and minimize air pockets, reducing defects by up to 50% and ensuring compliance with stringent EU and FDA regulations.
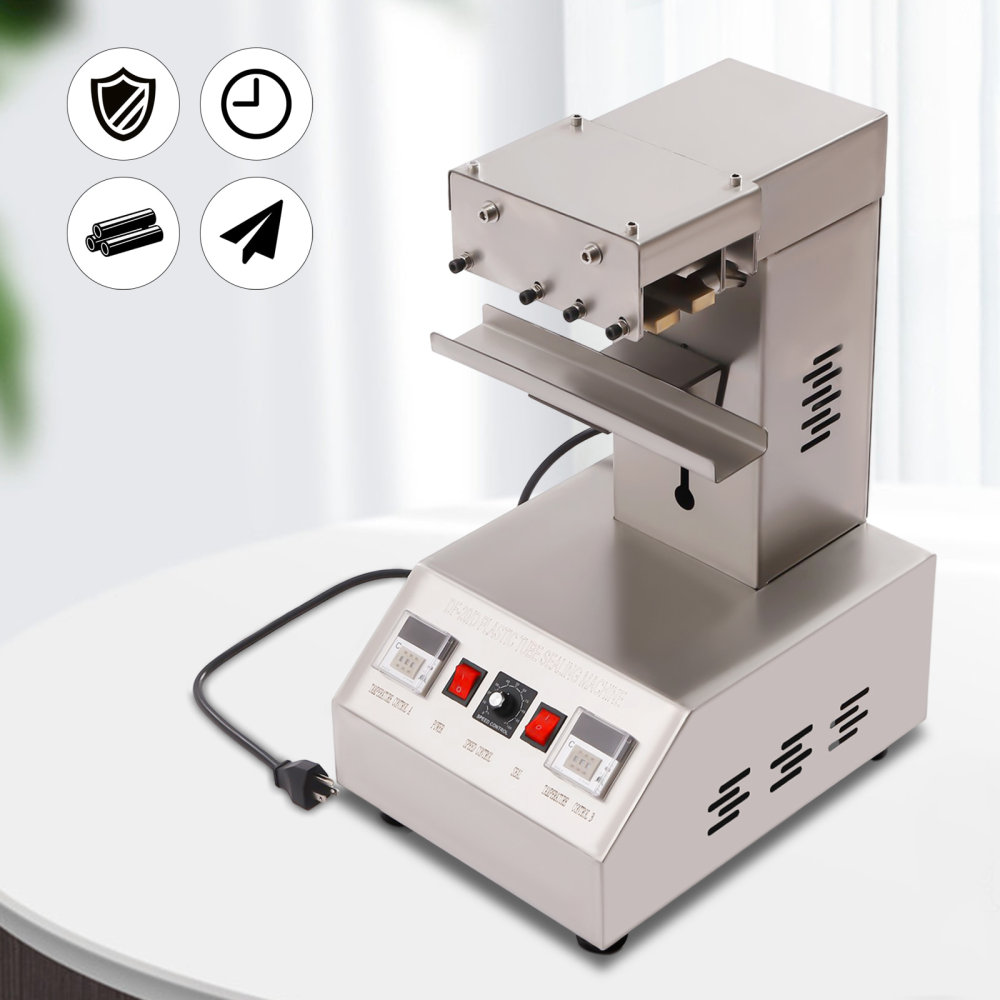
Pain Point 2: Frequent Downtime Due to Maintenance and Repairs
Scenario: A food processing plant in the USA relies on tube sealing machines for packaging sauces and condiments in high-volume runs. Machines break down weekly due to wear on heating elements, halting production lines and disrupting supply chains to retailers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Problem: Unplanned downtime increases operational costs by 15-20% annually, delays shipments, and strains workforce productivity, particularly in lean manufacturing environments.
Solution: Opt for durable, heavy-duty tube sealers designed for continuous operation, like Impak’s Heavy Duty Rapid Sealers or remanufactured options. These incorporate robust components and easy-access parts (e.g., spare parts for 1525/1575 series), enabling predictive maintenance scheduling and reducing breakdowns by 40%, while offering rental alternatives for backup during peaks.
Pain Point 3: Scalability Challenges with Varying Production Volumes
Scenario: A cosmetics manufacturer in the USA scales from small-batch R&D to full-scale production, but their existing tube sealing setup struggles with diverse tube sizes and materials, causing bottlenecks during seasonal demand spikes.
Problem: Inflexible machines lead to inefficient workflows, higher labor costs, and missed market opportunities, with scalability issues costing businesses 10-15% in lost revenue from delayed launches.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Solution: Deploy versatile tube sealers with adjustable features, such as Impak’s Tabletop Models or Custom Heat Sealers, which accommodate various tube diameters and materials (e.g., from tubing rolls to stand-up pouches). Integrating automation options like code printers enhances throughput, allowing seamless scaling while maintaining quality and reducing per-unit costs by 25%.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for tube sealing machines
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Tube Sealing Machines
This guide provides a strategic overview of material selection for tube sealing machines, focusing on packaging tubes and related components. Tube sealing machines are designed to create airtight, tamper-evident seals on tubular structures, commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food packaging, and electronics. The choice of material impacts seal integrity, product protection, and operational efficiency. Below, we analyze key materials based on properties like barrier performance, compatibility with sealing technologies, and cost-effectiveness, drawing from industry standards in the USA and Europe.
Analysis of Materials Used
Tube sealing machines work with a variety of materials, primarily thermoplastic films and laminates that can be heat-sealed, vacuum-sealed, or impulse-sealed. The reference information from Impak Corporation highlights categories such as Mylar bags, foil-based pouches, Tyvek alternatives, and various plastic films (e.g., polyethylene, polypropylene). Key considerations include:
-
Polyethylene (PE): A flexible, low-cost thermoplastic used for general-purpose tubes. It offers good moisture resistance but limited oxygen and light barriers. Ideal for non-sensitive products like food storage or basic packaging. Compatible with impulse and band sealers, with sealing temperatures typically 100-150°C. Common in USA and European food packaging standards.
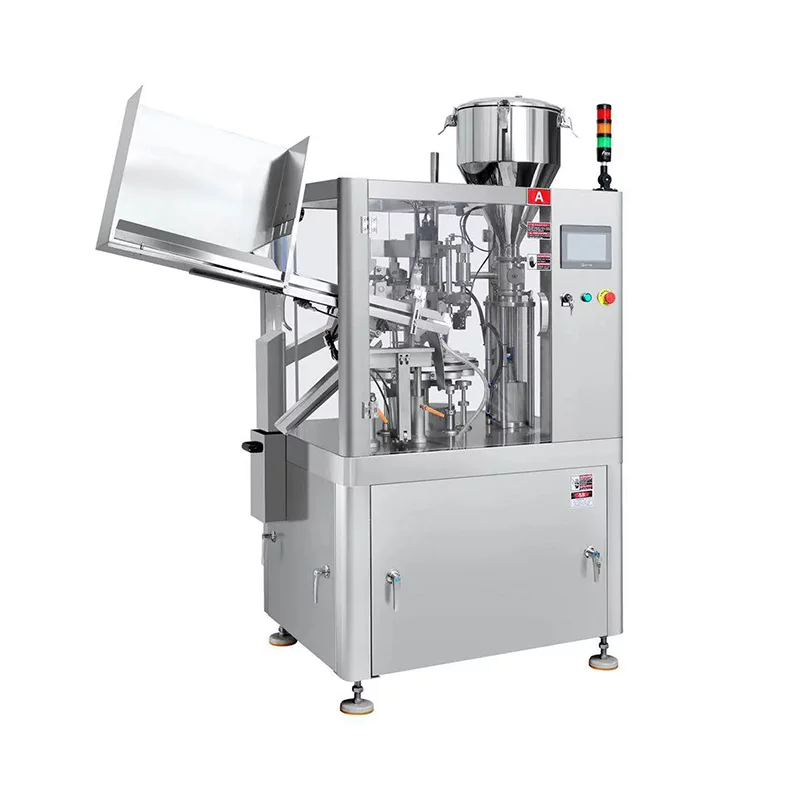

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Polypropylene (PP): Similar to PE but with higher heat resistance and better clarity. Provides moderate barrier properties and is recyclable. Suitable for tubes requiring sterilization or high-temperature processing. Works well with vacuum and gas-flush sealers, sealing at 140-180°C. Often used in pharmaceutical and industrial applications per EU regulations.
-
Aluminum Foil Laminates (e.g., Mylar or Foil Bags): Multi-layer materials combining foil with PE or PP for superior barrier against moisture, oxygen, and light. Essential for long-term food storage or sensitive electronics. Requires precise heat sealing to avoid delamination, compatible with band sealers and vacuum systems at 150-200°C. Compliant with Mil-Spec and FDA standards in the USA.
-
Tyvek or Tyvek Alternatives (e.g., Teknapore): Non-woven, breathable materials for sterile or medical tubes. Offers excellent puncture resistance and porosity for gas exchange. Not ideal for high-barrier needs but excellent for tamper-evident seals. Compatible with impulse sealers, with sealing at lower temperatures (80-120°C). Widely used in European medical packaging directives.
-
Laminates with Specialty Additives (e.g., Frangible Seals or Desiccant-Integrated): Advanced composites including silica gel or oxygen absorbers for controlled environments. These enhance shelf life but increase complexity. Suitable for high-value products, sealed via chamber vacuum sealers at 160-220°C. Aligns with global standards like ISO 11607 for sterile packaging.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
When selecting materials, consider machine compatibility (e.g., band sealers for continuous rolls, chamber vacuum for pouches), regulatory compliance (FDA in USA, EFSA in Europe), and end-use requirements like shelf life and environmental impact. Testing for seal strength (e.g., ASTM F88) is recommended to ensure reliability.
Comparison Table
The following table compares key materials based on barrier properties, sealability, cost, and common applications. Ratings are qualitative: High (H), Medium (M), Low (L).
| Material | Barrier Properties (Moisture/Oxygen/Light) | Sealability with Tube Sealers | Cost per Unit | Common Applications | Compatibility Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyethylene (PE) | M / L / L | H | L | General food, retail packaging | Impulse/band sealers; basic setups |
| Polypropylene (PP) | M / M / M | H | M | Pharmaceuticals, industrial tubes | Vacuum/gas-flush; heat-resistant |
| Aluminum Foil Laminates | H / H / H | M | H | Long-term storage, electronics | Band/vacuum; precision control needed |
| Tyvek/Tyvek Alternatives | L / L / M | H | M | Medical, sterile packaging | Impulse sealers; breathable design |
| Specialty Laminates | H / H / H (with additives) | M | H | High-value, controlled-environment | Chamber vacuum; advanced features |
This comparison aids in aligning material choice with machine capabilities and business objectives. For custom recommendations, consult machine specifications and material suppliers.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for tube sealing machines
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Tube Sealing Machines
Tube sealing machines are precision-engineered devices used in packaging industries for hermetic sealing of tubes containing products like pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. Their manufacturing demands rigorous processes to ensure durability, accuracy, and compliance with international standards. Below, we outline the key manufacturing steps and quality assurance protocols, informed by industry practices in vacuum and heat sealing equipment.
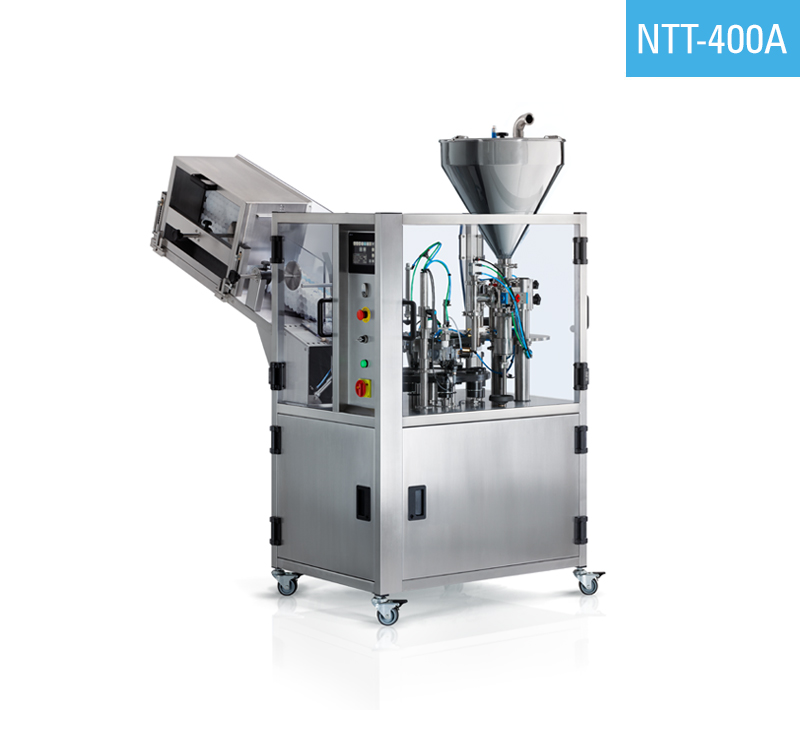

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Manufacturing Processes
The production of tube sealing machines typically follows a structured workflow, emphasizing material selection, precision machining, and integration of components. This process ensures machines can handle high-volume operations while maintaining seal integrity under varying conditions.
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation | Sourcing and preparing raw materials, including metals (e.g., stainless steel for frames), electronics (e.g., sensors and controllers), and components like heating elements. | Focus on supplier vetting for quality alloys resistant to corrosion. Includes design validation using CAD software to optimize machine dimensions for tube sizes (e.g., 10-50mm diameters). |
| Forming | Machining and shaping core components, such as the sealing head, conveyor systems, and pneumatic actuators. This involves CNC machining for precise tolerances. | Ensures components meet specifications for temperature control (up to 300°C) and pressure (e.g., 1-5 bar). Prototyping tests simulate tube sealing cycles to refine designs. |
| Assembly | Integrating components into the full machine, including wiring electrical systems, installing software for automation, and calibrating sensors for real-time monitoring. | Modular assembly allows for customization, such as adding gas flush capabilities. Final integration includes testing subsystems like vacuum pumps and heat applicators. |
| Quality Control (QC) | Post-assembly inspections, including dimensional checks, functional testing (e.g., sealing 100 tubes per cycle), and endurance runs under simulated production conditions. | Defects are traced using statistical process control (SPC) tools. Machines are calibrated to prevent over-sealing or leaks, with pass/fail criteria based on ISO benchmarks. |
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance for tube sealing machines adheres to international standards, primarily ISO 9001 for quality management systems, ensuring consistent performance and reliability. Key aspects include:
- ISO 9001 Compliance: Manufacturers implement risk-based thinking to identify potential failures in sealing accuracy or material fatigue. This standard mandates documented processes for design, production, and post-market surveillance, with annual audits to verify compliance.
- Additional Standards: Integration of ISO 14001 for environmental management reduces waste in metalworking, and ISO 45001 for occupational health and safety minimizes risks during assembly. For electronics, adherence to IEC standards ensures electromagnetic compatibility.
- Testing Protocols: Machines undergo validation testing, including burst tests for seals (e.g., maintaining integrity at 0.5-2 MPa) and cycle testing for durability (up to 10,000 operations). In the USA and Europe, compliance with FDA guidelines (for food/pharma applications) and CE marking is mandatory, requiring traceability of components and end-of-life disposal plans.
- Continuous Improvement: Data from QC informs iterative design enhancements, such as upgrading to servo-driven motors for better precision, reducing defect rates below 1%.
This structured approach minimizes downtime in B2B operations, ensuring tube sealing machines deliver efficient, compliant packaging solutions. For specific machine models or customizations, consult manufacturers aligned with these standards.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘tube sealing machines’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Tube Sealing Machines
This checklist provides a structured approach to sourcing tube sealing machines, drawing from established categories such as band sealers, chamber vacuum sealers, and custom heat sealers. Tailor it to your operational needs in the USA or Europe, ensuring compliance with local regulations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Step 1: Define Requirements
- Assess Application Needs: Determine the type of tubes (e.g., vacuum-sealed, heat-sealed, or gas-flushed) and materials (e.g., mylar bags, foil pouches). Consider production volume, tube size (e.g., A to G sizes), and features like tamper-evident seals or explosion-proof options.
- Set Budget and Timeline: Establish a cost range, including initial purchase, maintenance, and delivery. Factor in lead times for international shipping if sourcing from Europe to the USA.
- Identify Key Specifications: List must-haves, such as sealing speed, power requirements, and certifications (e.g., FDA for food packaging or Mil-Spec for military use).
Step 2: Research Suppliers and Options
- Compile a Supplier List: Use industry directories, B2B platforms, and references like Impak Corporation’s catalog to identify providers offering tube sealers, band sealers (e.g., with vacuum or gas flush), and chamber vacuum sealers.
- Evaluate Supplier Credentials: Check for ISO certifications, years in business, and customer reviews. Prioritize suppliers with expertise in flexible packaging and vacuum/heat sealing technologies.
- Explore Product Categories: Review options such as tabletop single/double chamber vacuum sealers, heavy-duty impulse sealers, or custom heat sealers for specialized needs like retort-autoclavable pouches.
Step 3: Gather and Compare Quotes
- Request Detailed Proposals: Contact suppliers with your requirements. Ask for quotes including pricing, warranties, spare parts availability (e.g., for 1525/1575 series band sealers), and training.
- Incorporate Logistics: Inquire about shipping costs, customs duties (especially for USA-Europe trade), and after-sales support like rentals or remanufactured units.
- Document Responses: Create a comparison table to track key metrics.
| Supplier | Product Type | Price Range | Delivery Time | Key Features | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Example Supplier A | Band Sealer with Vacuum | $5,000–$10,000 | 4–6 weeks | Gas flush capability, 220V | 2 years |
| Example Supplier B | Chamber Vacuum Sealer | $8,000–$15,000 | 6–8 weeks | Tabletop model, FDA compliant | 3 years |
Step 4: Evaluate and Select
- Technical Fit: Test compatibility with existing workflows (e.g., integration with filling equipment or code printers).
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Calculate total cost of ownership, including energy efficiency and potential ROI from features like high-speed sealing for large barrier bags.
- Compliance Check: Ensure machines meet USA/Europe standards for safety, emissions, and industry-specific regs (e.g., child-resistant pouches or food storage).
Step 5: Negotiate and Purchase
- Discuss Terms: Negotiate pricing, payment terms, and customization (e.g., adding spouts to tube sealers).
- Finalize Contract: Secure agreements covering delivery, installation, and training. Include clauses for support and parts sourcing.
- Arrange Delivery: Coordinate logistics, accounting for any import duties or local regulations.
Step 6: Post-Purchase Setup and Support
- Installation and Training: Schedule on-site setup and operator training provided by the supplier.
- Monitor Performance: Track initial usage and address any issues via warranty or service agreements.
- Plan Maintenance: Source spare parts (e.g., from suppliers like Impak) and establish a service schedule to ensure longevity.
By following this checklist, you can efficiently source reliable tube sealing machines, minimizing risks and optimizing for your B2B operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for tube sealing machines Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Tube Sealing Machines Sourcing
When sourcing tube sealing machines for B2B applications in the USA and Europe, a detailed cost breakdown is essential for budgeting and profitability. Below, we outline the primary cost components—materials, labor, and logistics—based on industry standards from suppliers like Impak Corporation. Prices can vary by machine type (e.g., band sealers, chamber vacuum sealers, or custom heat sealers), volume, and regional factors. Average costs are estimated in USD/EUR for a mid-range tube sealer (e.g., $5,000–$20,000 base price).
Cost Breakdown
| Component | Description | Average Cost (USD) | Average Cost (EUR) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Components such as heating elements, seals, casings, and electronics. Sourced from manufacturers like those listed in Impak’s catalog (e.g., vacuum sealers, band sealers). | $2,000–$10,000 (40–60% of total cost) | €1,800–€9,000 | Includes raw materials like stainless steel and plastics; higher for custom or specialized machines. |
| Labor | Assembly, testing, and customization by the supplier or third-party manufacturers. Factors in skilled technicians for precision sealing tech. | $1,000–$5,000 (20–30% of total cost) | €900–€4,500 | Labor rates in Europe may be 10–20% higher due to regulations; USA costs lower for domestic production. |
| Logistics | Shipping, import duties, insurance, and warehousing. Includes freight from suppliers (e.g., Impak’s remanufactured or rental options). | $500–$2,000 (10–20% of total cost) | €450–€1,800 | EU faces higher tariffs (5–10%) vs. USA; air freight for urgent needs doubles costs. |
| Total Estimated Sourcing Cost | Sum of above, excluding overheads. | $3,500–$17,000 per unit | €3,150–€15,300 per unit | Scales with order volume; bulk buys reduce per-unit costs by 15–25%. |
These figures are approximate and based on 2023 market data from B2B suppliers in packaging equipment. Actual costs depend on specifications (e.g., vacuum vs. heat sealing) and negotiation.
Tips to Save Costs
- Bulk Purchasing: Order 10+ units to negotiate discounts of 10–20% from suppliers like Impak, reducing per-unit material and logistics costs.
- Supplier Negotiation: Compare quotes from multiple vendors (e.g., via Impak’s categories like band sealers or chamber vacuum sealers) and request volume rebates or bundled services.
- Opt for Remanufactured or Rental Options: Choose Impak’s remanufactured sealers to cut initial costs by 30–50%, ideal for testing or low-volume needs in the USA/Europe.
- Minimize Customization: Stick to standard models to avoid labor surcharges; use modular designs for future upgrades.
- Efficient Logistics Planning: Source domestically where possible (e.g., USA-based for US markets) to eliminate import duties; consolidate shipments for lower freight rates.
- Leverage Trade Agreements: Utilize EU-US trade pacts to reduce tariffs on components, potentially saving 5–10% on logistics.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing tube sealing machines With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Tube Sealing Machines With Other Solutions
In the realm of packaging solutions, tube sealing machines are specialized for sealing tubular products, such as flexible tubes used in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food. However, businesses may consider alternatives like band sealers and chamber vacuum sealers for different applications. Below, we compare tube sealing machines with these two alternatives across key criteria: speed, versatility, cost, and maintenance. This analysis draws from industry-standard sealing technologies to inform procurement decisions for USA and European markets.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparison Table
| Criterion | Tube Sealing Machines | Band Sealers | Chamber Vacuum Sealers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | High-speed operation for continuous production lines, ideal for large volumes of tubes. | Moderate to high speed for sealing bags, pouches, and rolls; suitable for batch processing. | Moderate speed due to vacuum cycles; best for smaller batches requiring air removal. |
| Versatility | Specialized for tubular formats (e.g., plastic or foil tubes); limited to cylindrical shapes. | Highly versatile for flat seals on pouches, bags, and rollstock; adaptable to various sizes. | Versatile for vacuum-sealing a range of items, including irregular shapes, but requires compatible pouches. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment due to specialized components; long-term savings in high-volume tube production. | Lower upfront cost; cost-effective for general sealing needs without vacuum requirements. | Moderate cost; higher than band sealers due to vacuum features, but efficient for preservation-focused applications. |
| Maintenance | Requires regular calibration and cleaning of sealing heads; downtime for specialized parts. | Low maintenance with simple impulse sealing; easy-to-replace bands or wires. | Higher maintenance for vacuum pumps and chambers; needs periodic checks to ensure airtight seals. |
Analysis
Tube sealing machines excel in high-volume, specialized environments where precise sealing of tubes is critical, such as in pharmaceutical packaging to ensure product integrity and compliance with regulations like those from the FDA in the USA or EMA in Europe. Their speed and efficiency make them preferable for manufacturers prioritizing throughput over flexibility, though the higher cost and maintenance may not suit smaller operations.
Band sealers offer a cost-effective alternative for businesses needing quick, reliable seals on flat products like pouches or bags. They are ideal for general packaging without vacuum needs, providing simplicity and lower operational expenses, making them suitable for startups or companies with diverse product lines in both USA and European markets.
Chamber vacuum sealers stand out for applications requiring airtight preservation, such as food storage or moisture-sensitive goods, by removing air to extend shelf life. While less specialized than tube sealers, they provide better versatility for non-tubular items and are favored in industries like retail and logistics where vacuum sealing enhances product quality without the premium price of tube-specific equipment.
When selecting, evaluate based on production scale, product type, and budget. Tube sealing machines are optimal for dedicated tube workflows, while band sealers suit broad, low-cost needs and chamber vacuum sealers address preservation demands. Consult equipment suppliers for tailored assessments.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for tube sealing machines
Essential Technical Properties of Tube Sealing Machines
Tube sealing machines are critical equipment for packaging industries, enabling secure, airtight seals on tubes made from materials like plastic, foil, or laminate. Below are key technical properties based on standard industry specifications for models such as band sealers, chamber vacuum sealers, and impulse sealers. These properties ensure compatibility with B2B applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and industrial packaging.
Core Technical Specifications
| Property | Description | Typical Range/Options |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Method | Process used to create the seal (e.g., heat, vacuum, impulse). | Heat sealing, vacuum sealing, gas flush, or combination (e.g., vacuum + heat). |
| Sealing Width | Maximum width of the seal per cycle. | 1-50 mm (e.g., 5-15 mm for small tubes; up to 50 mm for industrial models). |
| Sealing Length | Length of the tube that can be sealed. | 50-2000 mm, depending on machine type (e.g., tabletop models up to 500 mm). |
| Sealing Speed | Number of seals per minute. | 1-50 seals/min (e.g., 10-20 for semi-automatic; higher for automated lines). |
| Temperature Control | Adjustable heat settings for different materials. | 50-300°C (digital controls for precision; auto-adjust for material thickness). |
| Power Supply | Electrical requirements. | 110-230V AC, 50/60 Hz, 500-2000W (USA/Europe compatible with adapters). |
| Dimensions and Weight | Machine footprint for installation. | Tabletop: 200x300x400 mm, 5-15 kg; Floor-standing: 500x800x1200 mm, 50-200 kg. |
| Material Compatibility | Types of tubes and films supported. | Polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), PVC, foil laminates; thickness 0.1-0.5 mm. |
| Vacuum Level | For vacuum-sealing models. | Up to -1 bar (adjustable for food preservation or gas flushing). |
| Safety Features | Built-in protections. | Overheat protection, emergency stop, CE/UL certified for USA/Europe compliance. |
| Automation Level | Manual, semi-automatic, or fully automated. | Semi-automatic (foot pedal); fully automated with conveyor integration. |
These properties vary by manufacturer and model (e.g., Impak Corporation’s band sealers or chamber vacuum sealers). Always verify specifications against your application to ensure optimal performance.
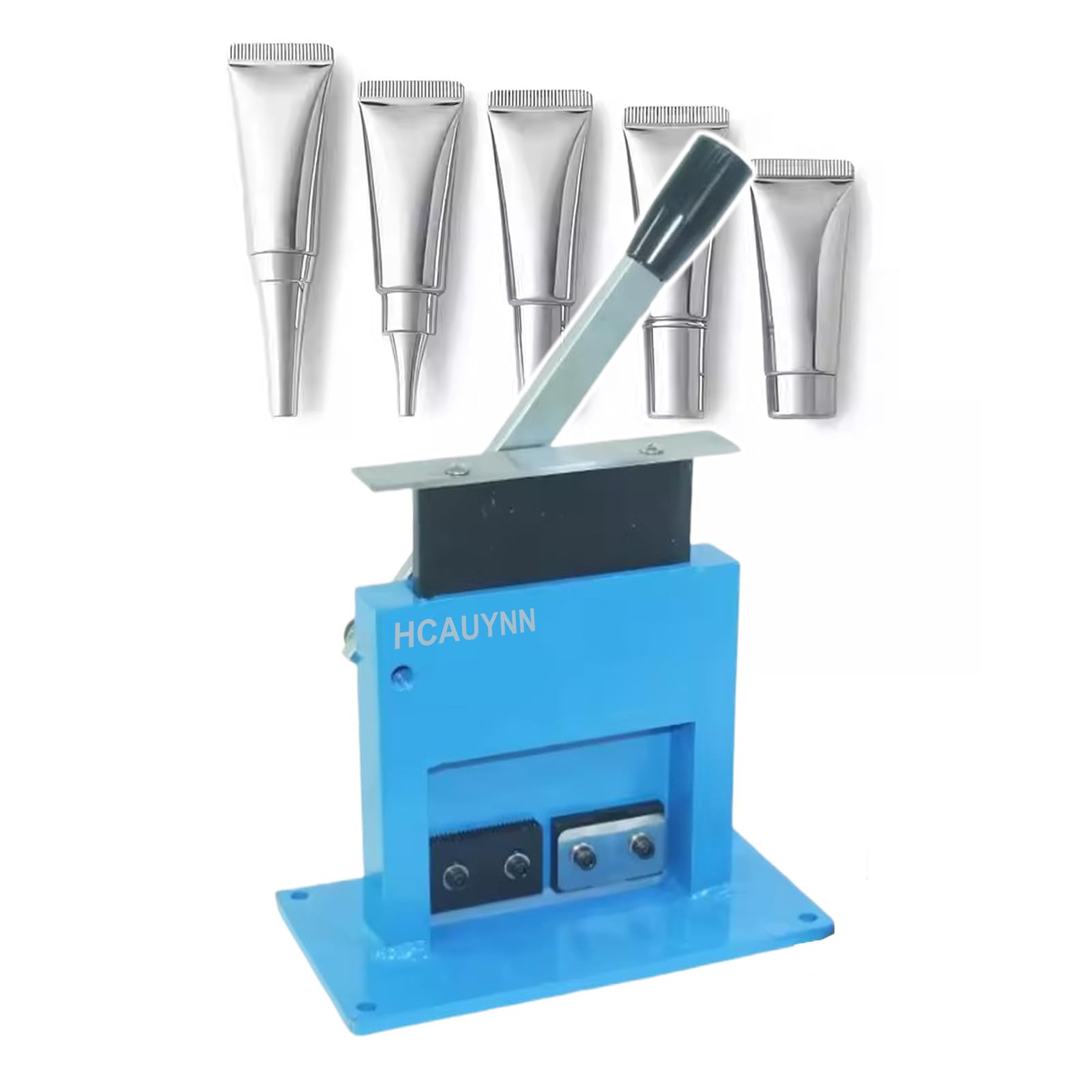
Trade Terminology for Tube Sealing Machines
In B2B transactions for tube sealing machines, understanding key trade terms is essential for negotiations, procurement, and compliance. Below is a list of common terminology, with definitions tailored to USA and Europe markets.
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest number of units a supplier will sell. Typically 1-10 units for standard models; higher for custom configurations.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to producing machines under a buyer’s brand. Common for private labeling in Europe/USA markets.
- Lead Time: Time from order to delivery. Ranges from 2-12 weeks for standard models; longer for customized machines.
- FOB (Free on Board): Shipping term where the seller pays costs until goods are loaded. Popular in USA/Europe for international shipments.
- Customization: Modifications like adding sensors or adjusting dimensions. Often requires engineering quotes.
- Warranty: Manufacturer guarantee (e.g., 1-3 years). Includes parts and labor for defects.
- CE Marking: European conformity certification for safety and quality. Required for sales in Europe.
- UL Certification: Underwriters Laboratories approval for safety. Mandatory for USA markets.
- Incoterms: International trade rules (e.g., CIF, DDP) defining responsibilities for shipping and duties.
- HS Code: Harmonized System code for customs classification (e.g., 8422.30 for sealing machines). Essential for tariffs in USA/Europe.
- Payment Terms: Conditions like Net 30 (pay within 30 days) or LC (Letter of Credit) for large orders.
For procurement, consult suppliers like Impak Corporation for specific terms. Always include these in contracts to avoid disputes.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the tube sealing machines Sector
History of Tube Sealing Machines
Tube sealing machines have evolved significantly since their inception in the mid-20th century, driven by advancements in packaging technology and industrial needs. Originating from basic heat-sealing devices in the 1950s, these machines were initially used for simple plastic and foil packaging in food and pharmaceutical sectors. The 1980s saw the integration of vacuum and gas-flush capabilities, enhancing preservation and extending shelf life, as seen in early models from manufacturers like those in the USA and Europe.
By the 2000s, automation and precision engineering transformed tube sealers into high-efficiency equipment, incorporating features like tamper-evident seals and compatibility with materials such as Mylar® bags and retort pouches. Today, the sector reflects a shift toward digital controls and IoT-enabled monitoring, with companies like Impak Corporation leading in customizable solutions for diverse applications, from single-dose bags to large barrier bags.
Market Dynamics in the Tube Sealing Machines Sector
The global tube sealing machines market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5-7% through 2030, fueled by rising demand in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics in the USA and Europe. Key dynamics include:
- Demand Drivers: Increasing emphasis on product safety and shelf-life extension, particularly in the USA’s stringent FDA-regulated environments and Europe’s EU standards for packaging. E-commerce growth has boosted the need for resealable pouches and vacuum-sealed tubes.
- Regional Variations: In the USA, adoption is high in consumer goods due to automation in manufacturing. Europe focuses on sustainable packaging, with regulations like the EU Packaging Directive influencing machine design.
- Challenges: Supply chain disruptions and raw material costs, exacerbated by global events, have led to price volatility. Competition from emerging markets like Asia is intensifying, pushing innovation in energy-efficient models.
- Opportunities: Customization for niche sectors, such as child-resistant pouches and scent-shield bags, offers growth potential. Digital integration via software for predictive maintenance is emerging as a competitive edge.
| Market Segment | Key Growth Factors | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Food Processing | Extended shelf life for perishables | Compliance with hygiene standards |
| Pharmaceuticals | Tamper-evident sealing | High-precision requirements |
| Cosmetics | Aesthetic and resealable designs | Material compatibility |
Sustainability in Tube Sealing Machines
Sustainability is a core trend, with manufacturers prioritizing eco-friendly operations to meet USA and EU regulations. Key aspects include:
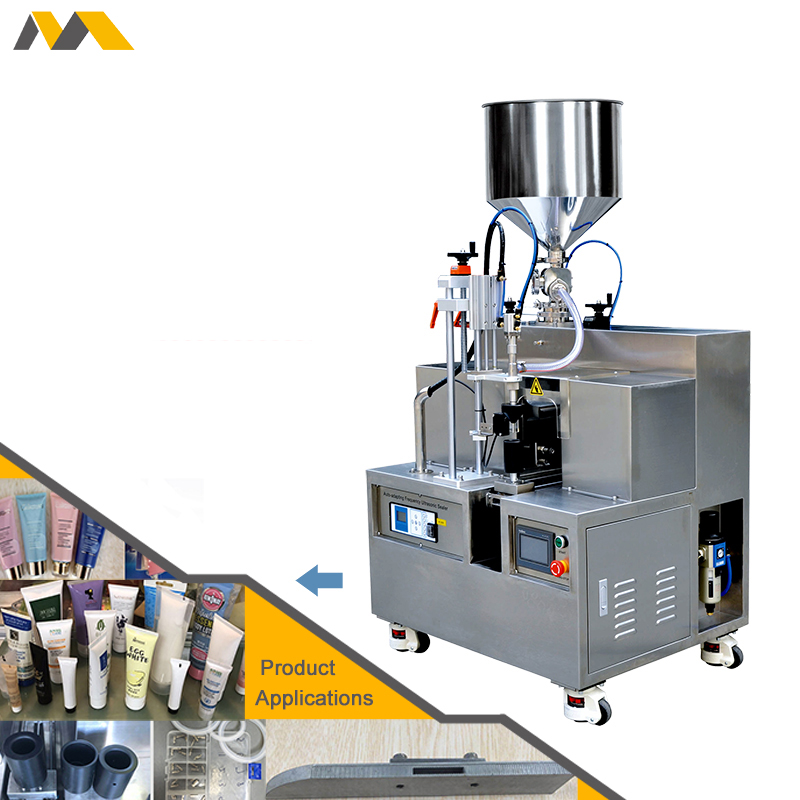

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Material Innovations: Shift toward recyclable materials like bioplastics and reduced-plastic pouches, such as those in Impak’s lineup (e.g., Teknapore as a Tyvek® alternative). Machines now support processing of high-temperature and frangible seal pouches to minimize waste.
- Energy Efficiency: Modern tube sealers incorporate low-energy impulse sealing and vacuum systems, reducing carbon footprints. For instance, heavy-duty rapid sealers optimize power usage, aligning with Europe’s Green Deal targets.
- Waste Reduction: Integration of features like desiccant packets and oxygen absorbers in sealed tubes extends product life without excess packaging. In the USA, certifications like USDA Organic drive demand for sustainable sourcing.
- Industry Initiatives: Suppliers are adopting circular economy practices, such as remanufactured sealers and reusable components, to lower environmental impact.
Sourcing Trends in Tube Sealing Machines
Sourcing strategies are adapting to global dynamics, emphasizing reliability and compliance. Key trends:
- Supplier Landscape: Leading providers like Impak Corporation offer a range of tube sealers, from basic band sealers to advanced chamber vacuum models, catering to USA and European buyers. Diversification beyond domestic suppliers is common to mitigate risks.
- Global Sourcing: Increased procurement from Asia for cost-effective components, balanced with EU and USA-based manufacturing for quality assurance. This hybrid approach addresses tariffs and lead times.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Emphasis on digital platforms for real-time inventory and predictive analytics. Buyers prioritize vendors with certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and support for custom configurations.
-
Emerging Trends: Rise of e-procurement and direct B2B marketplaces for sourcing, with a focus on after-sales support and training.
-
Top Sourcing Tips:
- Evaluate suppliers on scalability for small to large-scale operations.
- Prioritize eco-certified machines to align with sustainability goals.
- Negotiate long-term contracts for stable pricing amid market fluctuations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of tube sealing machines
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is a tube sealer and how does it differ from other sealing machines?
A tube sealer is a specialized heat sealing machine designed to seal flexible tubes or pouches, creating airtight, tamper-evident closures for products like food, pharmaceuticals, or industrial goods. Unlike band sealers or impulse sealers, tube sealers are optimized for cylindrical or tubular packaging, often incorporating vacuum or gas flush features to extend shelf life and prevent contamination. In B2B applications, they enhance efficiency in high-volume production lines.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
2. What types of tube sealers are available for B2B buyers?
Common types include band sealers (for continuous sealing), chamber vacuum sealers (for degassing and sealing under vacuum), and impulse sealers (for quick, on-demand operations). Options may feature gas flush for modified atmosphere packaging or custom configurations for specific tube sizes. B2B buyers in the USA and Europe can select models like tabletop or heavy-duty versions based on production scale, with remanufactured options available for cost savings.
3. What industries benefit most from tube sealing machines?
Tube sealers are ideal for food packaging (e.g., extending shelf life of snacks or liquids), pharmaceuticals (for sterile, tamper-evident seals), chemicals (for hazardous material containment), and electronics (for moisture-proofing components). In B2B contexts, they support compliance with regulations like FDA standards in the USA or EU food safety directives, ensuring product integrity across supply chains.
4. How do I choose the right tube sealer for my business?
Evaluate based on tube diameter, material compatibility (e.g., Mylar, foil, or plastic), sealing speed, and features like vacuum or gas flush. Consider production volume—tabletop models for small operations vs. heavy-duty ones for high throughput. Assess energy efficiency and spare parts availability for long-term ROI. Reference specs from providers like Impak Corporation to match with your packaging needs.
5. What maintenance is required for tube sealing machines?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning sealing bars, inspecting heating elements, and calibrating temperature controls to prevent uneven seals. Lubricate moving parts and replace worn components like belts or clips as needed. Schedule quarterly professional servicing to ensure compliance with safety standards. Proper upkeep minimizes downtime and extends equipment lifespan in B2B environments.
6. Are tube sealers compatible with various tube materials?
Yes, most tube sealers handle materials like foil, Mylar, polyethylene, or laminated films, provided the machine’s temperature and pressure settings are adjusted. For specialized needs, such as high-temperature pouches or frangible seals, select models with customizable heating profiles. Compatibility ensures reliable sealing without material degradation, critical for diverse B2B applications.
7. What are the cost considerations and ROI for investing in a tube sealer?
Initial costs range from $500 for basic models to $10,000+ for advanced vacuum units, depending on features and capacity. Factor in operational savings from reduced waste, improved product shelf life, and labor efficiency. ROI is typically realized within 6-12 months for high-volume users, with benefits amplified in regulated industries like pharmaceuticals where sealing quality directly impacts compliance and market share.
8. How do tube sealers address safety and regulatory compliance?
Tube sealers incorporate safety features like automatic shut-off and tamper-evident seals to meet standards such as USDA, FDA, or EU hygiene regulations. They prevent contamination by creating hermetic seals, ideal for food or medical products. In B2B settings, choose explosion-proof models for hazardous environments and ensure machines are CE or UL certified for safe operation across USA and European markets.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for tube sealing machines
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Tube Sealing Machines
Strategic sourcing of tube sealing machines delivers substantial value through optimized procurement, cost efficiencies, and enhanced operational performance. By leveraging suppliers like Impak Corporation, which offers a range of options including band sealers, chamber vacuum sealers, and custom heat sealers, B2B buyers in the USA and Europe can align machine selection with specific packaging needs—such as vacuum sealing for food storage or gas-flush systems for pharmaceuticals—ensuring compliance with industry standards like Mil-Spec or retort processes.
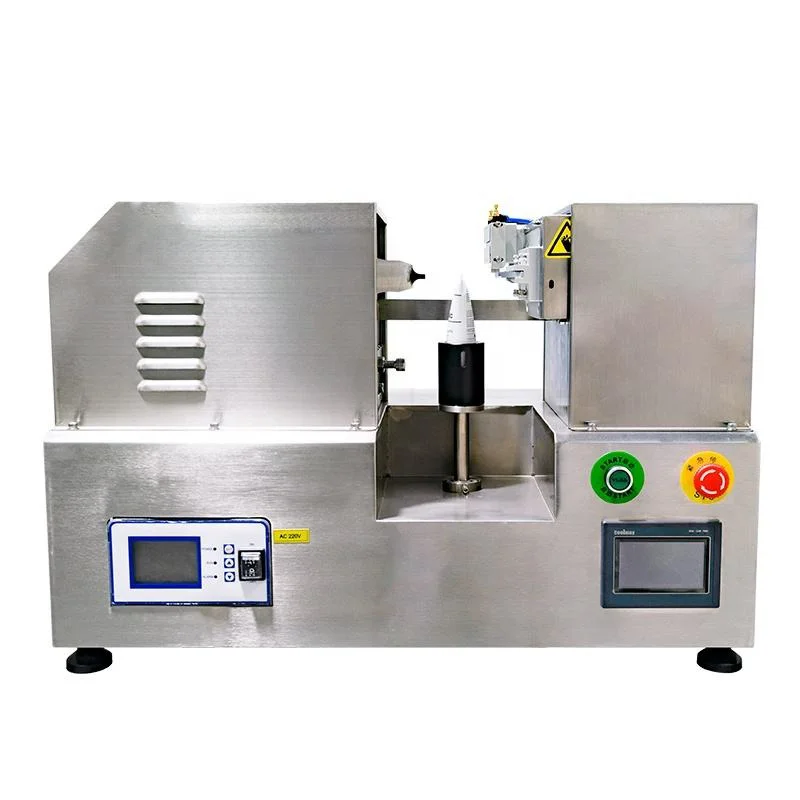

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key values include:
– Cost Reduction: Bulk purchasing and long-term contracts minimize expenses, with potential savings up to 20% on high-volume orders.
– Quality Assurance: Access to advanced features like tamper-evident seals and explosion-proof models enhances product integrity and reduces waste.
– Innovation Integration: Sourcing enables adoption of emerging technologies, such as automated sealers with code printers, driving efficiency in high-demand sectors like flexible packaging.
Looking ahead, the outlook favors digital integration and sustainability, with a projected 15% annual growth in eco-friendly sealing solutions. Strategic partnerships will be crucial for navigating supply chain disruptions and regulatory changes in the EU and US markets, positioning tube sealing machines as essential for scalable B2B packaging operations.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)