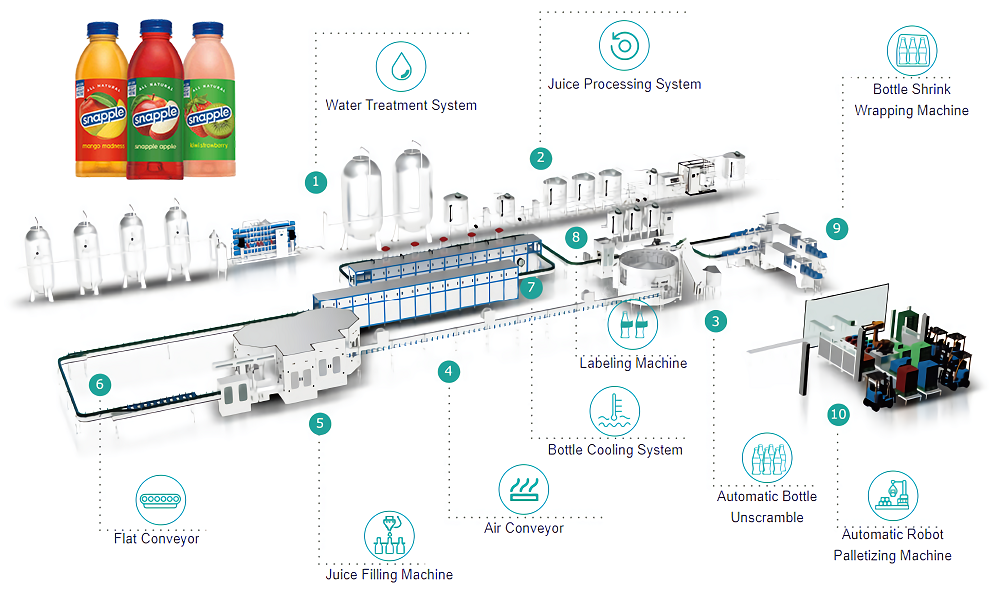
Juice Filling Equipment: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Juice Filling Equipment
In the competitive beverage industry, efficient juice filling equipment is the backbone of production success, enabling manufacturers to meet rising consumer demand for fresh, high-quality juices. As global markets expand, companies in the USA and Europe face increasing pressure to optimize operations, comply with stringent regulations, and adopt cutting-edge technologies.
The challenge lies in navigating a complex landscape: varying standards across regions, such as FDA guidelines in the US and EU food safety directives, alongside rapid technological shifts like automation and sustainability demands. Inadequate equipment can lead to inefficiencies, product recalls, and lost market share, while over-investment risks financial strain.
This guide empowers B2B decision-makers to make informed choices. Drawing from industry leaders like Filling Equipment Company, Inc.—a pioneer since 1959 in designing reliable filling machines for food and beverages—we provide practical insights. The guide covers:
- Market Overview: Key trends, regulations, and player analysis in USA and Europe.
- Equipment Types: From semi-automatic to rotary piston fillers, tailored for juice production.
- Selection Criteria: Evaluating features like accuracy, speed, and compliance.
- Implementation Strategies: Best practices for integration, maintenance, and ROI.
- Case Studies: Real-world examples of successful deployments.
Equip your business to thrive in the global juice market with this essential resource. (248 words)
Top 10 Juice Filling Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Bottle Filling Machines & Equipment – Filling Equipment …
Domain: fillingequipment.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: We specialize in the design, sale, and repair of filling machines, as well as cappers, used in bottling food, drinks, spreads, chemicals, and cosmetics….
2. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
3. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer – ACASI Machinery – Acasi
Domain: acasi.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: ACASI offers bottle unscramblers, fillers, cappers, labelers, neck banders, conveyors, accumulation tables, liquid filling, and bottle handling equipment….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Top 10 Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers in Pharma
Domain: pharmanow.live
Registered: N/A
Introduction: Injectables At Scale: The 10 Best Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturers You Should Know · 1. Syntegon (Germany) · 2. IMA Life (Italy) · 3. Groninger (Germany).Missing: juice suppliers…
5. Ideal Pase: Filling Machines
Domain: idealpase.com
Registered: 2022 (3 years)
Introduction: We build Volumetric Fillers, Net Weight Liquid Fillers, Drum Fillers, Lid Placers and Closers, Conveyors and more….
6. Automatic Liquid Filling Machine Manufacturer, Supplier in USA …
Domain: chitramechtech.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: America’s leading manufacturer : Get high-quality Automatic Volumetric Liquid Bottle Filling Machine offered by Shree Bhagwati – a leading manufacturer of ……
7. Table Top Filling Machinery Manufacturers and Suppliers in the …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer of standard and custom table and bench top filling machinery. Precision and micro liter liquid fillers and semi and fully automatic filling and ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. Top 20 Juice Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: finbolink.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: BW Filling Machinery is one of the top global juice filling equipment manufacturers, known for delivering advanced bottling and processing systems. Their ……
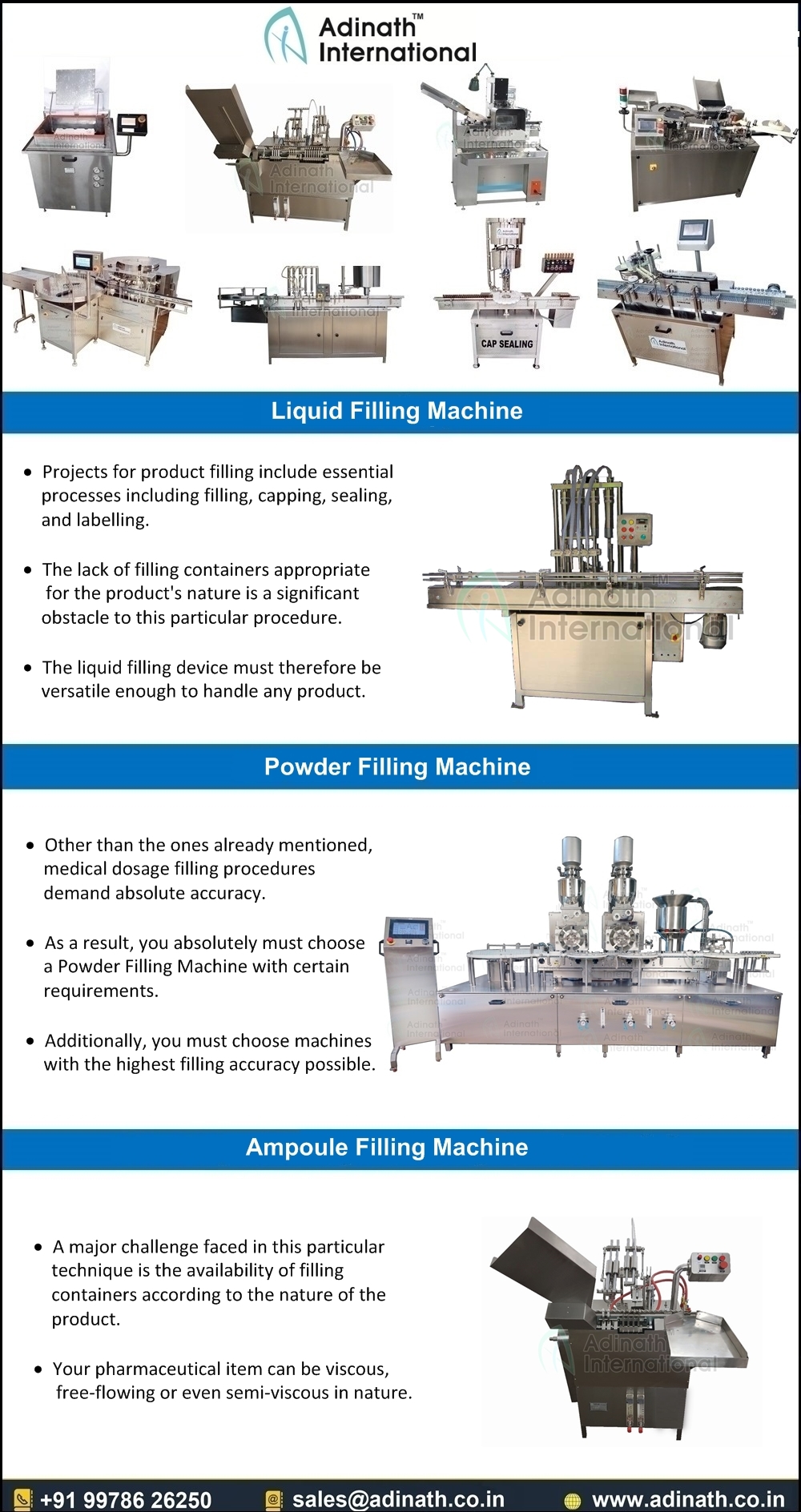
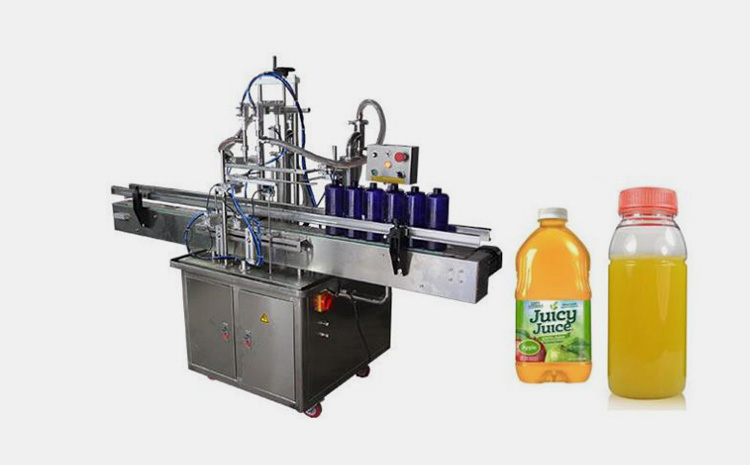
Understanding juice filling equipment Types and Variations
Understanding Juice Filling Equipment Types and Variations
Based on industry standards and equipment from leading manufacturers, juice filling equipment can be categorized into several types, each suited to different production scales and requirements. Below, we identify four common types relevant to juice bottling operations in the USA and Europe. These are informed by established filling machine designs that handle liquids like juices, ensuring accuracy, hygiene, and efficiency.
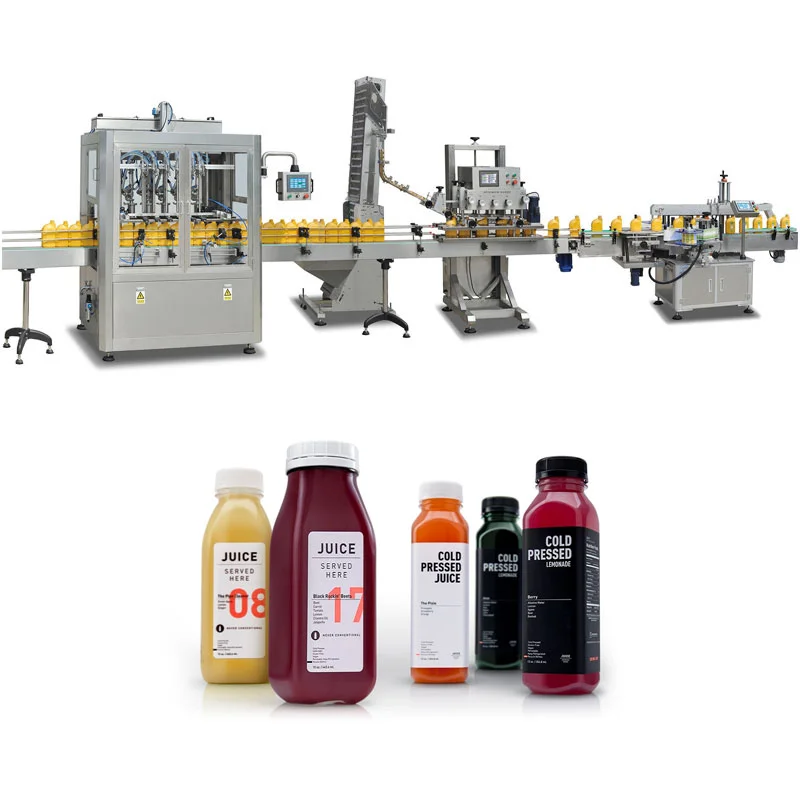

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Types of Juice Filling Equipment
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-Automatic Liquid Filling Machines | Operator-initiated filling with manual bottle placement; uses pumps or gravity for dispensing; adjustable for volume and speed; integrates with capping and labeling. | Small to medium juice production lines (e.g., artisanal or startup operations) requiring flexibility for various bottle sizes. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy maintenance, adaptable to custom needs. Cons: Labor-intensive, slower output (up to 1,000 bottles/hour), prone to human error. |
| Rotary Liquid Filling Machines | Rotates bottles on a carousel; multiple nozzles for simultaneous filling; automated bottle handling via conveyors; supports high-speed operations. | High-volume juice plants (e.g., commercial fruit juice producers) needing continuous production. | Pros: High throughput (up to 10,000+ bottles/hour), efficient for large-scale runs, minimizes downtime. Cons: High initial cost, complex maintenance, requires skilled operators. |
| Piston Fillers | Uses positive displacement pistons for precise volume control; handles viscous or thin juices; available in single to multi-station setups; includes sanitizable components for hygiene. | Medium to high-volume operations (e.g., organic juice lines) where accuracy is critical for consistent fill levels. | Pros: Excellent precision (±1% tolerance), versatile for different juice consistencies, durable. Cons: Higher maintenance for pistons, potential for clogging with particulates, energy-intensive. |
| Automatic Straight Line Liquid Fillers | Linear conveyor system with automated bottle indexing; nozzles dispense sequentially; integrates sensors for fill level detection; customizable for bottle types. | Mid-sized juice manufacturers (e.g., beverage co-packers) seeking automated, space-efficient solutions. | Pros: Reliable automation, scalable speed (1,000-5,000 bottles/hour), easy integration with other lines. Cons: Less flexible for varying bottle shapes, requires precise alignment, moderate setup complexity. |
Detailed Overview of Each Type
Semi-Automatic Liquid Filling Machines
These machines require manual intervention for bottle loading and triggering the fill cycle, making them ideal for low to medium production volumes. Key features include adjustable fill volumes, often via pump systems, and compatibility with various nozzle types for different juice viscosities. In juice applications, they are commonly used for craft or seasonal productions where customization is key. They ensure hygienic operations through easy-to-clean designs but may not scale well for large facilities due to reliance on operator speed and accuracy.
Rotary Liquid Filling Machines
Designed for high-throughput environments, rotary fillers feature a rotating platform that moves bottles under fixed nozzles, allowing for simultaneous filling of multiple units. Features include automatic bottle orientation, drip-free nozzles, and integration with upstream and downstream processes like pasteurization. For juice manufacturers, this type excels in large-scale operations producing carbonated or non-carbonated varieties, ensuring minimal product waste. However, the complexity can lead to higher operational costs and requires robust preventive maintenance programs.
Piston Fillers
Piston-based systems employ mechanical pistons to draw and dispense precise volumes of juice, offering superior control over fill accuracy. Configurations range from single-station units for small batches to 12-station models for increased efficiency. They are particularly effective for juices with varying densities, such as those containing pulp or fibers, due to their ability to handle thicker liquids without foaming. In B2B contexts, they support compliance with food safety standards like FDA or EU regulations through CIP (clean-in-place) capabilities, though they demand regular inspection to prevent wear on pistons.
Automatic Straight Line Liquid Fillers
These linear systems automate the filling process along a conveyor belt, with sensors ensuring even distribution and reducing overfills. Features often include programmable logic controllers (PLCs) for customization and compatibility with diverse bottle formats. They are well-suited for juice operations needing consistent output without the footprint of rotary systems, such as in regional bottling plants. While highly efficient for steady-state production, they may require adjustments for highly irregular bottle shapes, and downtime can occur if sensors malfunction during changeovers.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of juice filling equipment
Key Industrial Applications of Juice Filling Equipment
The following table outlines key industrial applications for juice filling equipment, drawing from established practices in beverage manufacturing. Each entry includes the primary application, targeted industries, and detailed benefits derived from high-precision liquid filling technologies, such as those offered by leading manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company.
| Application | Targeted Industries | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Fruit Juice and Beverage Bottling | Beverage manufacturing, food processing (USA and Europe) | Enhances production efficiency by automating filling processes, reducing manual labor and minimizing contamination risks. Improves accuracy in volume control (e.g., piston fillers for viscous juices), ensuring consistent product quality and compliance with FDA/EU regulations. Supports scalability for high-volume operations, with rotary machines handling up to 12 stations, boosting throughput and reducing downtime in facilities producing juices like orange, apple, or mixed blends. |
| Soft Drink and Carbonated Juice Production | Beverage and bottling sectors (global, with emphasis on USA/EU markets) | Delivers precise carbonation integration during filling, maintaining fizz and flavor integrity. Weight fillers ensure exact dosing for variable viscosities, cutting waste by up to 5-10% and optimizing resource use. Semi-automatic and automatic straight-line fillers facilitate quick changeovers for different juice variants, enhancing operational flexibility and meeting seasonal demands in plants producing sparkling juices or flavored drinks. |
| Plant-Based and Dairy-Alternative Juices | Food and beverage innovation, health and wellness (USA and Europe) | Accommodates diverse consistencies (e.g., nut milks, oat juices) with specialized nozzles, preventing product separation and ensuring uniform fills. High-quality materials in filling machines resist corrosion from acidic or organic contents, extending equipment lifespan. Improves hygiene with easy-to-clean designs, supporting clean-label certifications and reducing recall risks in facilities focused on vegan or functional juices. |
| Concentrate and Syrup Filling for Juice Blends | Ingredient manufacturing, beverage supply chain (USA and Europe) | Enables high-accuracy dosing for thick concentrates using piston or syphon fillers, minimizing spillage and ensuring precise mixing ratios. Integrates seamlessly with capping and conveying systems for end-to-end automation, streamlining supply chain logistics. Enhances cost-effectiveness by handling small-batch productions or large-scale contracts, with benefits like reduced energy consumption and faster ROI in juice concentrate plants. |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care Products with Juice Extracts | Cosmetics, personal care (USA and Europe, crossover with food-grade liquids) | Applies gentle filling techniques for sensitive, juice-based extracts (e.g., aloe vera juices in lotions), preserving active ingredients. Customizable nozzles support various bottle sizes and shapes, aiding product differentiation in competitive markets. Boosts production reliability with durable, repairable machines, ensuring consistent fills for items like fruit-infused serums, while complying with strict cosmetic regulations. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘juice filling equipment’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Juice Filling Equipment & Their Solutions
Based on industry insights from manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company, juice producers in the USA and Europe often face challenges related to production efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. Below, we outline three common pain points, structured by scenario, problem, and solution.
Pain Point 1: Bottlenecks in Production Scaling
- Scenario: A mid-sized juice manufacturer in Europe experiences seasonal spikes in demand for bottled fruit juices, requiring rapid increases in output from 1,000 to 10,000 units per hour.
- Problem: Manual or outdated filling equipment leads to slowdowns, delays, and inability to meet production targets, resulting in lost revenue and customer dissatisfaction.
- Solution: Invest in rotary liquid filling machines or automatic straight-line fillers that support high-speed operations (e.g., up to 12 stations). These systems, as offered by established providers, integrate seamlessly with conveyors for continuous flow, reducing bottlenecks and enabling scalable growth.
Pain Point 2: Inaccurate Filling and Product Waste
- Scenario: A USA-based beverage company bottling viscous juices like smoothies or purees struggles with inconsistent fill volumes across batches.
- Problem: Poor accuracy results in overfills (wasting product and increasing costs) or underfills (leading to regulatory non-compliance and recalls), especially with varying juice consistencies.
- Solution: Adopt piston fillers or high-quality nozzles designed for precise liquid handling. These ensure volumetric accuracy within 0.5-1% tolerance, minimizing waste and aligning with FDA/EU standards for food safety.
Pain Point 3: Equipment Downtime and Maintenance Issues
- Scenario: An international juice producer operating in both USA and European facilities faces frequent breakdowns in filling machines during 24/7 operations.
- Problem: Unplanned downtime disrupts supply chains, increases repair costs, and affects overall equipment lifecycle, particularly in harsh production environments.
- Solution: Opt for durable, manufacturer-supported machines like semi-automatic liquid fillers with modular designs for easy maintenance. Partner with suppliers offering repair services since 1959, such as Filling Equipment Company, to implement preventive maintenance schedules and reliable cappers, ensuring uptime above 95%.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for juice filling equipment
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Juice Filling Equipment
In the juice processing industry, selecting the right materials for filling equipment is critical to ensure product safety, operational efficiency, and compliance with regulatory standards such as FDA (U.S.) and EU Food Contact Materials regulations. Material choices directly impact hygiene, durability, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. This guide analyzes key materials commonly used in juice filling machines, drawing from industry best practices and equipment design principles.
Key Factors in Material Selection
When evaluating materials for juice filling equipment, consider the following:
– Hygiene and Sanitation: Materials must resist contamination, be easy to clean, and comply with food-grade standards to prevent microbial growth.
– Corrosion Resistance: Juices vary in acidity (e.g., citrus vs. neutral), so materials must withstand chemical exposure.
– Durability and Wear: Equipment handles high-volume production, requiring resistance to abrasion and mechanical stress.
– Cost and Maintenance: Initial investment, longevity, and repair frequency influence total cost of ownership.
– Regulatory Compliance: Materials must meet certifications like 3-A Sanitary Standards or EHEDG (Europe) for food processing.
– Application-Specific Needs: For example, hot-fill processes may require heat-resistant materials, while cold-fill uses standard options.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Analysis of Commonly Used Materials
Based on equipment from manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company, Inc., which specializes in liquid fillers for food and beverages, the following materials are analyzed for their suitability in juice filling machines:
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304, 316 Grades):
- Ideal for contact surfaces like nozzles, pistons, and tanks due to excellent corrosion resistance, especially against acidic juices.
- Offers superior hygiene with smooth finishes that minimize bacterial adhesion.
- Durable under high-pressure operations, with 316 grade preferred for salty or highly acidic products.
-
Cost-effective for long-term use, though initial machining can be higher; complies with FDA and EU standards.
-
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE):
- Used for non-contact components like conveyor belts or housing due to its lightweight and chemical resistance.
- Suitable for low-acidity juices, but may degrade with prolonged exposure to citrus.
-
Low cost and easy to mold, making it viable for budget-conscious operations; however, it lacks the robustness of metals for high-wear areas.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE/Teflon):
- Applied in seals, gaskets, and valves for its inertness and low friction, reducing contamination risks.
- Excellent for acidic juices as it resists chemical attack; however, it’s prone to wear in abrasive environments.
-
Higher cost but justified for precision filling; FDA-approved for food contact.
-
Aluminum Alloys:
- Employed in lightweight frames or structural parts to reduce overall machine weight and energy consumption.
- Cost-effective and recyclable, but less ideal for direct juice contact due to potential corrosion in acidic conditions—often anodized for protection.
-
Best for non-critical components in automated lines.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Elastomers (e.g., Silicone, EPDM Rubber):
- Essential for seals and O-rings to ensure leak-proof operations.
- Silicone offers heat resistance for hot-fill processes, while EPDM provides flexibility and chemical stability.
-
Must be food-grade to avoid leaching; regular inspection is needed due to wear.
-
Ceramics:
- Used in specialized nozzles for precision filling, offering hardness and inertness.
- Resistant to abrasion and corrosion, suitable for high-viscosity juices; however, it’s brittle and expensive, limiting widespread use.
Strategic selection involves balancing these factors with juice type: For instance, stainless steel 316 is recommended for orange juice due to its superior acid resistance, while HDPE suffices for milder apple juice. Always consult equipment manufacturers for custom recommendations to align with specific production needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Comparison Table
The table below compares key materials based on critical criteria for juice filling equipment. Scores are relative (1-5, with 5 being highest) and informed by industry standards from sources like Filling Equipment Company.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance (to Acids) | Hygiene & Cleanability | Durability/Wear | Cost (Initial & Maintenance) | Regulatory Compliance | Best for Juice Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (304) | 4 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | Neutral/Moderate Acidity |
| Stainless Steel (316) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 5 | High Acidity (e.g., Citrus) |
| HDPE | 3 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | Low Acidity (e.g., Apple) |
| PTFE | 5 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | All Types (Seals) |
| Aluminum Alloys | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 3 | Non-Contact Parts |
| Elastomers (Silicone) | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Hot-Fill Processes |
| Ceramics | 5 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | High-Precision Filling |
This comparison highlights stainless steel as the gold standard for contact parts in juice filling, while cost-driven alternatives like HDPE are viable for non-essential components. For optimal results, integrate material selection with equipment design from reputable manufacturers to enhance productivity and compliance.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for juice filling equipment
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Juice Filling Equipment
Juice filling equipment must adhere to rigorous manufacturing processes to ensure durability, precision, and compliance with industry standards. Drawing from established practices in the filling equipment sector, such as those employed by manufacturers since 1959, the following outlines key manufacturing steps and quality assurance measures tailored for B2B applications in the USA and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of juice filling equipment involves a structured sequence to achieve high performance in bottling operations. Below are the core steps:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Preparation: Raw materials, including stainless steel components, nozzles, and electronic parts, are sourced and inspected for quality. This phase includes material selection based on corrosion resistance for juice products, followed by cutting and machining to specifications.
- Forming: Components are shaped through processes like CNC machining or molding. For example, liquid nozzles and pistons are formed to precise tolerances to handle varying juice viscosities, ensuring efficient filling without contamination.
- Assembly: Parts are integrated into the final machine, including the attachment of filling heads, conveyors, and control systems. Automation features, such as rotary or straight-line fillers, are calibrated to meet production demands, with a focus on modularity for customization.
- Quality Control (QC): Each unit undergoes testing for functionality, including fill accuracy, leak detection, and operational speed. Post-assembly inspections verify compliance with client specifications, such as handling high-volume juice production lines.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance in juice filling equipment prioritizes reliability and safety to support food and beverage manufacturing. Key standards include:
| Standard | Description | Relevance to Juice Filling Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems standard ensuring consistent production and continuous improvement. | Ensures traceability in manufacturing, reducing defects in filling processes for juice products. |
| ISO 22000 | Food safety management for the food industry. | Critical for equipment handling edible liquids, preventing contamination and ensuring hygienic design. |
| ISO 45001 | Occupational health and safety management. | Addresses safe operation of equipment in production facilities, minimizing risks in high-speed bottling lines. |
These standards are integrated into the design and testing phases, with manufacturers like those with over 60 years of experience conducting audits and certifications to meet USA and European regulations. This results in equipment that supports scalable, efficient juice production while maintaining product integrity.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘juice filling equipment’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Juice Filling Equipment
Sourcing juice filling equipment requires a structured approach to ensure compatibility with production needs, regulatory standards, and operational efficiency. This checklist draws from industry expertise, such as that of established manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company, Inc., which has provided reliable filling machines since 1959. Follow these steps to streamline your procurement process for markets in the USA and Europe.
1. Assess Your Production Requirements
- Define juice type (e.g., viscous, thin, carbonated) and required fill volume per cycle to match equipment capabilities.
- Evaluate production scale: low-volume (e.g., semi-automatic fillers) vs. high-volume (e.g., rotary liquid filling machines for larger operations).
- Consider bottle sizes, materials (glass, plastic), and integration with existing lines (e.g., conveyors or capping systems).
- Factor in speed and accuracy needs, such as piston fillers for precise dosing in food-grade applications.
2. Research and Identify Suppliers
- Seek manufacturers with proven track records in food and beverage filling, prioritizing those with FDA or CE compliance for USA and EU markets.
- Review supplier portfolios: Look for specialists like Filling Equipment Company, offering semi-automatic, rotary, and piston fillers tailored to juice bottling.
- Check for industry certifications (e.g., GMP, HACCP) and experience in handling sensitive products like juices to ensure equipment meets hygiene standards.
- Use B2B directories, trade shows, or online platforms to shortlist 3-5 reputable vendors.
3. Evaluate Equipment Types and Specifications
- Compare options based on your needs:
- Semi-automatic liquid filling machines for flexible, lower-volume production.
- Rotary liquid filling machines for high-speed, automated bottling lines.
- Piston fillers (single to 12-station) for accurate fills in varying consistencies.
- Assess additional features like nozzles, cappers, and conveyors for seamless juice processing.
- Verify material compatibility (e.g., stainless steel for corrosion resistance in juice environments).
4. Verify Compliance and Safety Standards
- Ensure equipment adheres to USA regulations (e.g., FDA food safety guidelines) and EU standards (e.g., CE marking, REACH for materials).
- Request documentation on hygiene, sanitation, and safety features to prevent contamination in juice production.
- Confirm environmental compliance, such as energy-efficient designs to align with sustainability goals in both regions.
5. Compare Pricing, Warranties, and Total Cost of Ownership
- Obtain detailed quotes, including base price, installation, and ongoing maintenance.
- Evaluate warranties, repair services (e.g., as offered by Filling Equipment Company), and availability of spare parts.
- Calculate total cost: Factor in energy consumption, downtime reduction, and scalability for long-term ROI.
6. Request Demonstrations and References
- Schedule product demos to test performance on sample juices.
- Ask for client references in similar industries (e.g., beverage manufacturers) to validate reliability and support.
- Inquire about customization options for unique juice formulations.
7. Negotiate Terms and Finalize Purchase
- Negotiate delivery timelines, payment terms, and training for operators.
- Secure contracts that include after-sales support, such as technical assistance and equipment upgrades.
- Plan for installation, testing, and integration into your facility to minimize production disruptions.
8. Implement and Monitor Post-Purchase
- Oversee installation by qualified technicians and conduct initial runs to ensure functionality.
- Train staff on operation and maintenance to optimize uptime.
- Track performance metrics (e.g., fill accuracy, speed) and maintain relationships with suppliers for future needs or repairs.
This checklist helps mitigate risks and ensures you select equipment that enhances efficiency in juice production. Consult experts like Filling Equipment Company for tailored advice.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for juice filling equipment Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Juice Filling Equipment Sourcing
Sourcing juice filling equipment involves evaluating total costs across materials, labor, and logistics to ensure alignment with production needs and budget constraints. Drawing from industry leaders like Filling Equipment Company, Inc., which has provided reliable, affordable solutions since 1959, this analysis highlights typical breakdowns and factors influencing pricing for businesses in the USA and Europe.
Cost Breakdown
The following table outlines average cost components for sourcing juice filling equipment, such as semi-automatic, rotary, or piston fillers. Costs can vary based on equipment type, supplier (e.g., Filling Equipment Company), customization, and regional factors like currency fluctuations or tariffs. Figures are approximate in USD/EUR for mid-range models (e.g., 1-10 stations, 500-5,000 bottles/hour capacity) and exclude taxes or duties.
| Category | Typical Cost Range | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Materials | $5,000–$50,000 (or €4,500–€45,000) per unit | Includes base equipment price, nozzles, and parts (e.g., high-quality nozzles from suppliers like Filling Equipment). Influenced by automation level (semi-automatic vs. fully rotary) and material durability for juice (corrosion-resistant stainless steel). |
| Labor | $2,000–$10,000 (or €1,800–€9,000) per project | Covers installation, training, and initial setup by skilled technicians. Higher for custom integrations; lower with in-house teams or supplier support. |
| Logistics | $1,000–$5,000 (or €900–€4,500) per shipment | Encompasses shipping, insurance, and customs duties. Costs rise for international sourcing (e.g., USA to Europe), with potential tariffs on industrial machinery under agreements like the USMCA or EU regulations. |
These estimates are based on industry standards for juice bottling lines, where equipment must handle viscous liquids like fruit juices. For larger-scale operations, economies of scale can reduce per-unit costs.
Pricing Factors
Pricing for juice filling equipment is determined by several variables, ensuring equipment matches production demands without overspending:
– Capacity and Automation: Semi-automatic models (e.g., from Filling Equipment Company) start at lower prices but limit throughput; fully automatic rotary fillers increase costs for higher efficiency.
– Customization: Additions like specialized nozzles or cappers for juice-specific needs (e.g., anti-drip features) add 10-30% to base prices.
– Supplier Reputation and Support: Established providers like Filling Equipment Company offer competitive pricing with warranties and repair services, reducing long-term expenses.
– Market and Regional Variations: In the USA, domestic sourcing minimizes logistics; in Europe, EU-compliant machines may include eco-features, impacting costs due to regulations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Tips to Save Costs
To optimize sourcing, consider these strategies tailored for B2B operations:
– Bulk or Multi-Unit Purchases: Negotiate discounts for multiple units or integrated lines (e.g., combining fillers with cappers from the same supplier like Filling Equipment Company).
– Prioritize Standardized Equipment: Opt for off-the-shelf models over heavy customization to leverage lower material costs and faster delivery.
– Leverage Supplier Programs: Partner with manufacturers offering maintenance contracts or financing options to spread labor and logistics expenses.
– Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in energy efficiency and repair costs—reliable brands reduce downtime and long-term labor needs.
– Explore Local Sourcing: Source from regional suppliers (e.g., USA-based for American buyers) to cut logistics fees and avoid international duties.
– Conduct Comparative Analysis: Request quotes from 3-5 providers, including after-sales support, to identify the best value without compromising quality for juice production.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing juice filling equipment With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Juice Filling Equipment With Other Solutions
In the juice production industry, selecting the right filling solution impacts efficiency, cost, and product quality. Juice filling equipment typically refers to automated systems like piston or rotary fillers, which are optimized for high-volume, precise liquid handling. Below, we compare this with two alternatives: manual filling (labor-intensive methods) and gravity filling machines (such as syphon fillers). This analysis draws from industry standards for food and beverage production, considering factors like speed, accuracy, and scalability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Juice Filling Equipment (Automated Piston/Rotary Fillers) | Manual Filling (Hand-Poured or Basic Labor Methods) | Gravity Filling Machines (Syphon Fillers) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | High (up to 100+ bottles/min, depending on model) | Low (10-20 bottles/min per worker) | Medium (50-80 bottles/min) |
| Accuracy | High (precision to within 0.5-1% fill volume) | Low (variable, prone to over/under-filling) | Medium (depends on liquid viscosity; less precise for thick juices) |
| Labor Requirements | Low (1-2 operators for monitoring) | High (multiple workers needed for sustained output) | Low-Medium (1-2 operators) |
| Initial Cost | High ($10,000-$100,000+ for industrial models) | Low (minimal equipment; labor costs dominate) | Medium ($5,000-$30,000) |
| Operating Costs | Medium (energy, maintenance, and consumables) | High (wages, training, and potential waste) | Low-Medium (low energy, but cleaning intensive) |
| Scalability | High (easily expandable for large production) | Low (limited by workforce availability) | Medium (suitable for small-to-medium runs) |
| Hygiene & Safety | High (automated, reduces contamination risks) | Medium (human error can introduce contaminants) | Medium (open systems may allow air exposure) |
| Best For | Large-scale juice manufacturers in USA/Europe seeking efficiency | Small-scale or startup operations with low budgets | Medium-volume producers handling simple liquids |
Analysis
-
Juice Filling Equipment (Automated Systems): Ideal for B2B juice producers prioritizing precision, speed, and compliance with FDA/EU regulations for food safety. These systems minimize waste and labor costs over time, making them scalable for global supply chains. However, the higher upfront investment requires justification through volume—suitable for operations exceeding 5,000 units/day. In regions like the USA and Europe, where automation is standard in beverage plants, this option supports growth without compromising quality.
-
Manual Filling: Cost-effective for small operations or testing new juice formulations, as it eliminates machinery expenses. However, it struggles with consistency and speed, leading to higher long-term costs from rework and labor turnover. Not recommended for regulated markets like Europe, where traceability and hygiene standards (e.g., HACCP) demand automation to prevent contamination risks.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Gravity Filling Machines: A balanced alternative for mid-tier producers, offering simplicity and lower energy use compared to automated fillers. They perform well with low-viscosity juices but may underperform with pulpy varieties due to overflow risks. This option is viable for USA-based facilities scaling up from manual methods, though it lacks the precision of piston/rotary systems, potentially increasing waste in high-stakes export scenarios.
For optimal decision-making, evaluate based on production volume, budget, and regulatory requirements. Automated juice filling equipment generally outperforms alternatives in efficiency and quality for established B2B operations.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for juice filling equipment
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Juice Filling Equipment
This section outlines key technical specifications and industry terminology essential for selecting, purchasing, and operating juice filling equipment in B2B contexts across the USA and Europe. Focus is on properties that ensure efficiency, compliance, and scalability for beverage production.
Key Technical Properties
Juice filling equipment must meet rigorous standards for hygiene, precision, and throughput, especially for perishable liquids like fruit juices. Below is a table summarizing essential properties, informed by industry practices for liquid fillers handling food-grade products.
| Property | Description | Relevance to Juice Filling |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Accuracy | Precision in volume delivery, typically ±0.5% to 1% tolerance. | Critical for consistent juice portions, minimizing waste and ensuring label claims. |
| Filling Speed | Measured in bottles per minute (BPM), ranging from 20-200+ BPM for automatic models. | Supports high-volume production; rotary fillers excel for juices in glass or PET bottles. |
| Equipment Types | Includes piston fillers (for viscous juices), rotary fillers (for high-speed lines), and semi-automatic models. | Piston fillers suit pulpy juices; rotary for clear juices with aseptic options. |
| Hygiene Standards | Compliance with GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices) and EHEDG guidelines for cleanability. | Essential for juice safety; features like CIP (Clean-in-Place) prevent contamination. |
| Material Compatibility | Handles liquids, semi-viscous products; stainless steel construction for corrosion resistance. | Juices may contain acids; equipment must resist pitting and ensure product integrity. |
| Automation Level | From semi-automatic to fully automated with PLC controls and sensors. | Improves efficiency in large-scale juice plants; integrates with conveyors for seamless lines. |
| Power and Footprint | Typically 1-10 kW; compact designs for space-constrained facilities. | Energy-efficient for cost savings; modular setups allow expansion in USA/Europe factories. |
These properties align with standards from organizations like the FDA (USA) and EFSA (Europe), ensuring equipment suitability for juice bottling.
Trade Terminology
Understanding B2B terminology is crucial for procurement, customization, and international trade in juice filling equipment. Below is a list of common terms, including those referenced in industry sources.
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of equipment or parts a supplier requires for an order. For juice fillers, MOQ might be 1-5 units, depending on customization.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to branded or custom-built equipment from manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company. In juice filling, OEM options allow for tailored nozzles and cappers.
- CIP (Clean-in-Place): A system for cleaning equipment without disassembly, essential for juice production to maintain hygiene and reduce downtime.
- GMP (Good Manufacturing Practices): Regulatory standards for food equipment, ensuring safety and quality in juice filling operations.
- PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): Electronic controls for automating filling processes, common in rotary and piston fillers for precision.
- SKU (Stock Keeping Unit): A unique code for inventory tracking, used for parts like nozzles or cappers in B2B supply chains.
- FOB (Free on Board): Incoterms term indicating when the seller transfers responsibility to the buyer; often used in USA/Europe shipments of filling machines.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight): Another Incoterms term covering costs up to the destination port, relevant for importing juice equipment from Europe to the USA.
- Nozzles and Cappers: Specialized components; nozzles ensure accurate dispensing, while cappers seal bottles—key for juice packaging integrity.
- Rotary vs. Linear Fillers: Rotary for high-speed circular lines (up to 200 BPM); linear for straight-line setups in smaller juice facilities.
For B2B transactions, always verify supplier certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and consult local regulations in the USA or Europe to align with juice industry needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the juice filling equipment Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Juice Filling Equipment Sector
The juice filling equipment sector has evolved significantly, driven by technological advancements, shifting consumer demands, and regulatory pressures. Understanding these dynamics is essential for businesses aiming to optimize production, ensure compliance, and maintain competitiveness in the USA and European markets. Below, we explore key market trends, sustainability considerations, and historical context, informed by industry insights from established manufacturers like Filling Equipment Company, which has served the sector since 1959.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Historical Evolution of the Sector
- Post-War Industrialization (1950s-1970s): The sector’s roots trace back to the mid-20th century, with the rise of mass production in food and beverage industries. Companies like Filling Equipment Company pioneered liquid filling machines in 1959, focusing on reliability for bottling food, drinks, and spreads to meet growing factory demands.
- Automation Boom (1980s-2000s): Technological integration accelerated, introducing rotary and piston fillers for higher throughput. This era emphasized precision to reduce waste and improve efficiency, laying the foundation for modern, customizable equipment.
- Digital Transformation (2010s-Present): The adoption of smart sensors, IoT, and automated systems has redefined operations, enabling real-time monitoring and scalability for juice producers facing global supply chain complexities.
Current Market Dynamics
Market dynamics in the juice filling equipment sector are shaped by increasing consumer preferences for premium, organic, and functional beverages, alongside regulatory standards in the USA (e.g., FDA guidelines) and Europe (e.g., EU hygiene directives). Key trends include:
– Rising Demand for Automation: With juice production scaling to meet e-commerce and health-focused trends, automated straight-line and rotary fillers are essential for handling diverse viscosities (e.g., from thin juices to thicker concentrates) and achieving fill accuracies of ±0.5-1%.
– Customization and Flexibility: No two operations are identical, driving demand for modular equipment that adapts to small-batch artisanal juices or high-volume commercial lines. For instance, piston fillers can be configured from single-station to 12-station setups.
– Global Supply Chain Pressures: Disruptions have heightened the need for reliable, in-house capabilities, with a shift toward local sourcing to minimize delays and costs.
– Economic Factors: Post-pandemic recovery has boosted investments in equipment upgrades, with a projected 5-7% annual growth in the liquid filling machinery market through 2028, per industry reports.
Sustainability in Juice Filling Equipment
Sustainability is a core driver, as juice producers face pressure to minimize environmental impact through reduced water usage, energy-efficient machinery, and recyclable packaging integration. Key considerations include:
– Energy-Efficient Designs: Modern fillers incorporate variable-speed drives and low-power nozzles, reducing energy consumption by up to 30% compared to legacy models.
– Waste Reduction: Advanced capping and filling systems minimize spillage and product loss, aligning with EU sustainability targets (e.g., Circular Economy Action Plan) and US initiatives like the EPA’s waste reduction guidelines.
– Eco-Friendly Materials: Equipment compatible with biodegradable or recyclable bottles supports juice brands targeting eco-conscious consumers, with trends favoring automated systems that integrate seamlessly with green supply chains.
– Adoption Rates: Businesses are increasingly prioritizing suppliers like Filling Equipment Company, which offer repair services to extend equipment lifecycles, reducing the carbon footprint of frequent replacements.
Sourcing Trends and Best Practices
Effective sourcing of juice filling equipment involves evaluating reliability, scalability, and after-sales support, especially in fragmented markets like the USA and Europe. Trends highlight a move toward strategic partnerships over one-off purchases:
– Preferred Supplier Criteria: Seek manufacturers with over 60 years of experience (e.g., since 1959) for proven quality in food-grade applications, including NSF-certified components for juice processing.
– Customization and Integration: Trends favor suppliers offering turnkey solutions, from semi-automatic fillers for startups to fully automated rotary systems for large-scale operations, ensuring compatibility with existing bottling lines.
– Digital Procurement: Online platforms and direct manufacturer networks are rising, enabling faster access to inventory, with a focus on modular upgrades to avoid full system overhauls.
– Cost-Effectiveness and ROI: Businesses prioritize equipment with quick ROI through faster production cycles (e.g., rotary fillers handling 100-500 bottles/minute) and comprehensive warranties. Key metrics for evaluation include downtime rates (<1%) and maintenance costs.
– Regional Considerations: In the USA, emphasize FDA-compliant designs; in Europe, prioritize CE-marked equipment for seamless cross-border operations.
| Aspect | USA Focus | Europe Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA standards for hygiene and safety | EU directives on food contact materials and emissions |
| Sourcing Strategy | Local manufacturers for quick delivery | Pan-European suppliers for harmonized standards |
| Sustainability Emphasis | Energy rebates and waste audits | Carbon neutrality goals and circular economy incentives |
| Market Trends | Automation for craft juices | Premium organic lines with eco-labels |
By navigating these dynamics, juice producers can source equipment that enhances efficiency, sustainability, and market responsiveness. For tailored recommendations, consult established experts to align with specific operational needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of juice filling equipment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Juice Filling Equipment
What types of juice filling machines are commonly available?
Common types include semi-automatic liquid filling machines for small-scale operations, rotary liquid filling machines for high-volume production, and piston fillers for precise, viscous juices. Equipment like syphon fillers and weight fillers are also used for specific juice consistencies, ensuring compatibility with various bottle sizes and production demands.
How do I select the right juice filling machine for my business?
Evaluate based on production volume, juice type (e.g., viscous or thin), bottle size, and automation level. For instance, rotary machines suit high-demand scenarios, while piston fillers handle accurate fills. Consult suppliers for custom options to match your operational needs, considering factors like speed (e.g., 50-500 bottles per minute) and integration with existing lines.
What maintenance is required for juice filling equipment?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning nozzles and pistons after each run to prevent contamination, lubricating moving parts, and inspecting for wear. Schedule professional servicing quarterly or as per manufacturer guidelines (e.g., from suppliers like Filling Equipment Company). Proper upkeep extends equipment lifespan and ensures compliance with food safety standards like FDA or EU regulations.
Are juice filling machines customizable for specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization, such as adjustable nozzles for different viscosities, conveyor integrations, and capping attachments. For juice-specific applications, options include stainless steel construction for hygiene and modifications for non-carbonated or organic products. Discuss requirements upfront to align with production goals.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
What is the typical cost range for juice filling machines?
Costs vary by type and capacity: semi-automatic models range from $5,000-$20,000, rotary machines from $50,000-$200,000, and fully automated lines can exceed $500,000. Factors like customization, brand (e.g., established since 1959 like Filling Equipment Company), and features (e.g., precision filling) influence pricing. Request quotes for accurate estimates.
Do juice filling machines comply with industry regulations?
Leading machines meet standards such as FDA requirements in the USA for food contact materials and EU directives for hygienic design. Ensure equipment includes features like easy-clean surfaces and traceability. Suppliers provide documentation for audits, emphasizing safety and quality in juice bottling.
What after-sales support is available for buyers?
Support typically includes installation assistance, operator training, and technical troubleshooting. Many suppliers offer on-site repairs and spare parts availability. For example, companies like Filling Equipment Company provide ongoing service to maintain uptime, with warranties often covering 1-5 years depending on the model.
How does energy efficiency factor into juice filling machine selection?
Look for machines with variable speed drives and low-energy components to reduce operational costs. Efficient models can lower electricity use by 20-30% compared to older systems. In USA and Europe, prioritize ENERGY STAR-rated or equivalent equipment for sustainability, especially in high-volume juice production.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for juice filling equipment
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Juice Filling Equipment
Strategic sourcing of juice filling equipment is essential for manufacturers seeking reliable, high-performance solutions to optimize production efficiency. Partnering with established providers like Filling Equipment Company, Inc., founded in 1959, ensures access to premium liquid filling machines, cappers, and ancillary equipment tailored for beverages, including juices. These systems deliver fast, accurate filling to meet escalating demands, minimizing downtime and enhancing scalability.
Key Value Propositions
- Quality and Reliability: Precision-engineered machines support consistent output for food-grade applications, with options from semi-automatic to rotary fillers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable designs reduce operational costs while handling various consistencies, from thin liquids to viscous juices.
- Customization and Support: Comprehensive services, including repair and customization, ensure seamless integration into existing lines.
Looking ahead, the outlook for juice filling equipment emphasizes innovation in automation, sustainability, and Industry 4.0 integration. In the USA and Europe, expect advancements in energy-efficient systems and smart technologies for real-time monitoring, driving higher yields and compliance with evolving regulations. Strategic sourcing from trusted manufacturers positions businesses for growth, with projected market expansion in organic and functional juices.
| Aspect | Current Benefits | Future Outlook |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High-speed filling reduces labor costs | AI-driven automation for predictive maintenance |
| Sustainability | Low-waste designs | Eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient models |
| Compliance | Meets FDA/EU standards | Enhanced traceability for global supply chains |
By prioritizing proven suppliers, manufacturers can achieve competitive advantages in a dynamic market. (198 words)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.