Discover Cost-Saving Benefits of Manifold Gasket (2025)
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for manifold gasket
The global market for manifold gaskets presents a unique set of challenges for international B2B buyers, particularly when it comes to sourcing high-quality components that meet specific industry standards. Whether you are in Africa, South America, the Middle East, or Europe, understanding the nuances of manifold gasket types, applications, and supplier reliability is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your operations. This guide is designed to address these complexities, equipping buyers with the knowledge necessary to navigate the manifold gasket landscape confidently.
In the following sections, we will delve into various aspects of manifold gaskets, including the different types available on the market, their applications across industries, and best practices for supplier vetting. Additionally, we will discuss cost considerations and strategies for negotiating favorable terms, ensuring that you make informed purchasing decisions.
By empowering international buyers with actionable insights and practical strategies, this guide aims to streamline your sourcing process and enhance your supply chain efficiency. Whether you are looking for durable gaskets for automotive applications or specialized solutions for industrial machinery, our comprehensive overview will provide the necessary tools to make informed choices that align with your operational needs. Prepare to navigate the manifold gasket market with confidence and precision, tailored specifically for your regional context and business requirements.
Understanding manifold gasket Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Layer Steel | Composed of multiple layers for enhanced sealing | Automotive engines, heavy machinery | Pros: High durability; Cons: More expensive than single-layer gaskets. |
| Composite | Made from various materials (rubber, silicone, etc.) | HVAC systems, industrial machinery | Pros: Versatile; Cons: Less heat resistance. |
| Solid Copper | Single-piece design for high-temperature applications | Aerospace, high-performance engines | Pros: Excellent thermal conductivity; Cons: Prone to corrosion. |
| Graphite | Flexible and compressible material for high-performance use | Marine engines, power generation | Pros: High resistance to thermal expansion; Cons: Can degrade under certain conditions. |
| Fiber-Reinforced | Reinforced with fibers for added strength | Construction machinery, automotive | Pros: Strong and lightweight; Cons: Limited lifespan under extreme conditions. |
What Are the Key Characteristics of Multi-Layer Steel Manifold Gaskets?
Multi-layer steel (MLS) gaskets are engineered with several layers of steel, typically coated with a sealing material. This design provides superior sealing capabilities, making them ideal for high-performance automotive engines and heavy machinery. B2B buyers should consider their durability and ability to withstand extreme pressure and temperature fluctuations. However, the higher cost compared to single-layer gaskets may be a deterrent for some buyers, especially in cost-sensitive markets.
How Do Composite Manifold Gaskets Compare to Other Types?
Composite manifold gaskets are made from a blend of materials, including rubber and silicone, allowing for flexibility and adaptability in various applications. They are commonly used in HVAC systems and industrial machinery due to their versatility. Buyers should note that while composite gaskets are cost-effective and provide good sealing performance, they may lack the heat resistance required for high-temperature applications, which could lead to premature failure.
What Are the Advantages of Using Solid Copper Manifold Gaskets?
Solid copper gaskets are favored in applications requiring high thermal conductivity, such as aerospace and high-performance engines. Their single-piece design ensures a tight seal, particularly in environments with extreme temperatures. However, B2B buyers must consider the potential for corrosion, which can compromise the gasket’s integrity over time. Therefore, maintenance and material compatibility should be key considerations when selecting this type.
Why Choose Graphite Manifold Gaskets for High-Performance Applications?
Graphite gaskets are known for their flexibility and compressibility, making them suitable for high-performance applications such as marine engines and power generation. Their ability to withstand thermal expansion and high pressures makes them a popular choice among B2B buyers. However, it is essential to be aware that under certain conditions, graphite can degrade, so understanding the operational environment is crucial for ensuring long-term performance.
What Makes Fiber-Reinforced Manifold Gaskets a Strong Choice?
Fiber-reinforced gaskets incorporate fibers to enhance strength and durability, making them suitable for construction machinery and automotive applications. They offer a lightweight solution while providing robust sealing capabilities. Buyers should weigh the benefits of their strength against the potential for a limited lifespan in extreme conditions. Understanding the operational demands and maintenance requirements will help in making informed purchasing decisions.
Related Video: Intake manifold gasket comparison
Key Industrial Applications of manifold gasket
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of manifold gasket | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Engine assembly in vehicles | Ensures optimal sealing, reducing the risk of leaks and improving engine efficiency. | Material compatibility, temperature resistance, and OEM specifications are crucial. |
| Oil & Gas | Pipeline flanges and connections | Prevents leakage of hazardous materials, enhancing safety and regulatory compliance. | Consider local regulations, pressure ratings, and chemical resistance of gasket materials. |
| Manufacturing & Machinery | Industrial equipment assembly | Enhances durability and operational efficiency by preventing fluid leaks. | Assess compatibility with operating conditions and maintenance requirements. |
| Aerospace | Aircraft engine and component assembly | Critical for safety and performance, ensuring reliable operation under extreme conditions. | Certification standards and weight considerations are vital for sourcing. |
| Renewable Energy | Wind turbine and solar panel installations | Improves system reliability, contributing to overall energy efficiency and lower maintenance costs. | Evaluate environmental impact, material sustainability, and performance in varying climates. |
How is Manifold Gasket Used in the Automotive Industry?
In the automotive sector, manifold gaskets are essential for engine assembly, where they provide a seal between the engine block and the intake or exhaust manifold. This application is critical as it prevents the leakage of gases and fluids, which can lead to reduced engine performance and increased emissions. International buyers should focus on sourcing gaskets that meet OEM specifications and offer compatibility with various engine types, especially considering the diverse automotive standards across regions such as Africa, South America, and Europe.
What Role Does Manifold Gasket Play in the Oil & Gas Sector?
Within the oil and gas industry, manifold gaskets are employed in pipeline flanges and connections to maintain the integrity of systems transporting hazardous materials. The primary benefit is the prevention of leaks, which is vital for safety and compliance with stringent environmental regulations. Buyers must consider local regulations and the specific chemical resistance of gasket materials, as well as pressure ratings, to ensure reliable and safe operation in diverse geographical conditions.
How Does Manifold Gasket Enhance Manufacturing & Machinery Operations?
In manufacturing and machinery, manifold gaskets are used in the assembly of various industrial equipment. They play a crucial role in preventing fluid leaks, which can lead to equipment failures and operational downtime. For international B2B buyers, it is essential to assess the compatibility of gaskets with the specific operating conditions of their machinery, as well as the maintenance requirements to ensure long-term reliability and efficiency.
Why is Manifold Gasket Critical in Aerospace Applications?
In the aerospace industry, manifold gaskets are critical components in the assembly of aircraft engines and other systems. They ensure a reliable seal that withstands extreme temperatures and pressures, which is paramount for safety and performance. Buyers in this sector must prioritize sourcing gaskets that meet stringent certification standards and consider weight constraints, as these factors significantly impact aircraft design and operation.
How Does Manifold Gasket Contribute to Renewable Energy Systems?
In renewable energy applications, such as wind turbines and solar panels, manifold gaskets are used to ensure proper sealing in fluid and gas systems. This contributes to the overall reliability and efficiency of energy systems, reducing maintenance costs and enhancing performance. When sourcing gaskets for these applications, buyers should evaluate the environmental impact of materials and the performance of gaskets in varying climatic conditions, ensuring sustainability aligns with their operational goals.
Related Video: Permatex Pro Tips – Selecting the Right Gasket for an Exhaust Manifold Replacement
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘manifold gasket’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inconsistent Quality of Manifold Gaskets
The Problem:
B2B buyers frequently encounter inconsistent quality in manifold gaskets, which can lead to severe operational issues. For example, a manufacturer in South America may source gaskets from multiple suppliers but finds significant variances in material quality and performance. This inconsistency can result in premature gasket failure, leading to costly downtime, increased labor costs for replacements, and potential damage to engine components.
The Solution:
To mitigate quality inconsistency, buyers should establish long-term relationships with trusted suppliers who provide rigorous quality assurance processes. It is essential to request detailed specifications and certifications for the materials used in the gaskets. Implementing a standardized testing protocol upon receipt can further ensure that the gaskets meet the required specifications. Additionally, consider investing in high-quality gaskets designed for specific applications, as these often have better performance and reliability. Collaborating with suppliers on joint quality initiatives can also enhance product consistency over time.
Scenario 2: Difficulty in Sourcing the Right Manifold Gasket Size
The Problem:
Buyers often struggle to find manifold gaskets that fit specific engine models, especially when dealing with older or less common engines. This issue is particularly prevalent in regions like Africa and the Middle East, where certain engines may not have widespread aftermarket support. The frustration of receiving gaskets that do not match specifications can lead to delays in production and increased costs.
The Solution:
To overcome sourcing difficulties, it is crucial for buyers to maintain a comprehensive database of their engine models and the corresponding gasket specifications. Engaging with manufacturers that offer custom gasket solutions can also be beneficial. Buyers should leverage online platforms and databases that specialize in automotive parts to cross-reference gasket sizes and compatibility. Additionally, forming alliances with local distributors can help streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that the right gaskets are readily available when needed.
Scenario 3: Lack of Technical Support for Installation and Maintenance
The Problem:
Many B2B buyers face challenges related to the installation and maintenance of manifold gaskets, particularly when technical expertise is limited. In Europe, for instance, a small automotive repair shop may not have access to the latest installation techniques or tools, which can lead to improper gasket installation, resulting in leaks and further mechanical issues.
The Solution:
To address this pain point, buyers should prioritize suppliers who offer comprehensive technical support and installation training. This could include access to detailed installation manuals, video tutorials, or even on-site training sessions. Collaborating with suppliers to create a support network can help technicians acquire the necessary skills for effective gasket installation. Furthermore, establishing a feedback loop with the supplier regarding installation challenges can lead to improved product designs and better support resources in the future. Investing in proper tools and equipment tailored for gasket installation is also a vital step towards ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for manifold gasket
When selecting materials for manifold gaskets, international B2B buyers must consider various factors that influence performance, durability, and compliance with industry standards. Below is an analysis of four common materials used in manifold gaskets, focusing on their key properties, advantages and disadvantages, and specific considerations for buyers from diverse regions, including Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Compressed Fiber Gaskets?
Compressed fiber gaskets are widely used due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. These gaskets typically consist of a blend of aramid fibers and other fillers, providing excellent compressibility and sealing capabilities.
- Key Properties: They can withstand temperatures up to 300°C and pressures around 20 MPa, making them suitable for various applications. Their resistance to oil and water enhances their utility in automotive and industrial settings.
- Pros & Cons: While they offer good durability and are relatively inexpensive, compressed fiber gaskets may not perform well in highly corrosive environments. Their manufacturing process is straightforward, which helps keep costs low.
- Impact on Application: These gaskets are compatible with a range of media, including oils and coolants, but may degrade when exposed to certain chemicals.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local standards such as ASTM or DIN, particularly in Europe, where regulatory compliance is stringent. In regions like Africa and South America, sourcing from reliable manufacturers is crucial to ensure quality.
How Do Metal Gaskets Perform in High-Pressure Applications?
Metal gaskets, often made from materials like stainless steel or copper, are designed for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Their robust nature makes them ideal for demanding environments.
- Key Properties: Metal gaskets can withstand temperatures exceeding 600°C and pressures above 100 MPa. Their corrosion resistance, especially in stainless steel variants, is a significant advantage.
- Pros & Cons: The durability and longevity of metal gaskets are unmatched, but they come at a higher cost and require precise manufacturing techniques. Their rigidity can also be a disadvantage in applications where flexibility is needed.
- Impact on Application: These gaskets are suitable for applications involving aggressive media, such as steam and chemicals, making them a preferred choice in industries like oil and gas.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers in Europe, particularly in Italy and France, must consider compliance with EN standards. In the Middle East, where high temperatures are common, selecting the right metal type is essential for performance.
What Are the Benefits of Using Rubber Gaskets?
Rubber gaskets, made from materials like nitrile or silicone, are known for their flexibility and excellent sealing properties. They are commonly used in automotive and HVAC applications.
- Key Properties: Rubber gaskets can handle temperatures ranging from -40°C to 120°C and are resistant to a variety of chemicals, including oils and fuels.
- Pros & Cons: The main advantage of rubber gaskets is their excellent sealing capability and ease of installation. However, they may not be suitable for high-pressure applications and can degrade over time, especially when exposed to extreme temperatures.
- Impact on Application: These gaskets are ideal for applications involving liquids and gases but may not perform well in high-stress environments.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should check for compliance with ISO standards, especially in regions like Europe and South America, where quality assurance is critical.
Why Choose PTFE Gaskets for Chemical Resistance?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) gaskets are renowned for their chemical resistance and are often used in applications involving aggressive substances.
- Key Properties: PTFE gaskets can withstand temperatures up to 260°C and are inert to most chemicals, making them ideal for corrosive environments.
- Pros & Cons: Their exceptional chemical resistance is a significant advantage, but they can be more expensive than other materials. Additionally, they require careful handling during installation due to their low friction properties.
- Impact on Application: PTFE gaskets are particularly suitable for chemical processing applications where other materials would fail.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with specific chemical standards is essential, especially in Europe, where regulations are stringent. Buyers in Africa and South America should ensure that suppliers provide certifications for chemical compatibility.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Manifold Gaskets
| Material | Typical Use Case for manifold gasket | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compressed Fiber | Automotive and industrial applications | Cost-effective and versatile | Limited chemical resistance | Low |
| Metal | High-pressure and high-temperature | Exceptional durability | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Rubber | Automotive and HVAC systems | Excellent sealing capability | Not suitable for high pressures | Medium |
| PTFE | Chemical processing | Outstanding chemical resistance | Higher cost and handling care | High |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for manifold gaskets, assisting international B2B buyers in making informed decisions tailored to their specific needs and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for manifold gasket
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Manifold Gaskets?
The manufacturing process of manifold gaskets involves several critical stages that ensure the final product meets the stringent requirements of performance and durability. Here’s a detailed look at each stage:
Material Preparation: What Materials Are Used and How Are They Processed?
The first step in manufacturing manifold gaskets is material preparation. Common materials include rubber, silicone, graphite, and composite materials, each selected based on the specific application and environmental conditions.
-
Material Selection: Quality assurance begins with selecting high-grade materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures. For instance, silicone gaskets are suitable for high-temperature applications, while rubber gaskets are often used for lower temperature environments.
-
Pre-Processing: Once selected, materials undergo pre-processing, which may involve cutting, molding, or curing. This stage ensures the materials are ready for forming.
How Are Manifold Gaskets Formed and Assembled?
The forming stage typically employs various techniques tailored to the material and design specifications of the gasket.
-
Molding: Compression or injection molding techniques are commonly used, particularly for rubber and silicone gaskets. This method allows for precise control over the shape and thickness of the gasket.
-
Cutting: For materials like graphite and composite, laser or die cutting is utilized to achieve the desired dimensions. This is crucial for maintaining tight tolerances that ensure proper sealing.
-
Assembly: If the gasket design requires multiple components, assembly takes place after forming. This may involve bonding layers or adding reinforcements to enhance strength and durability.
What Finishing Processes Are Applied to Manifold Gaskets?
Finishing processes are vital for improving the gasket’s performance and longevity.
-
Surface Treatment: Techniques such as coating or surface grinding are used to enhance the gasket’s sealing properties and resistance to wear. Surface treatments can also improve chemical resistance, which is particularly important in automotive applications.
-
Inspection: A thorough inspection occurs at this stage to check for any defects or inconsistencies that could affect performance.
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Manifold Gasket Production?
Quality assurance (QA) is a fundamental aspect of the manufacturing process, ensuring that every gasket produced meets international and industry-specific standards.
Which International Standards Should Buyers Be Aware Of?
For manifold gaskets, adherence to international standards is crucial for ensuring product reliability and safety. The following certifications are particularly relevant:
-
ISO 9001: This standard outlines the requirements for a quality management system, emphasizing continuous improvement and customer satisfaction. Buyers should look for suppliers certified under this standard, as it indicates a commitment to quality.
-
CE Marking: In Europe, CE marking demonstrates that a product meets EU safety and environmental requirements. This is particularly important for buyers in Italy and France, where compliance with EU regulations is mandatory.
-
API Standards: For gaskets used in the oil and gas industry, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards is crucial. These standards ensure that the gaskets can withstand the demanding conditions found in these sectors.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure product integrity. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of raw materials before production begins. It helps identify any defective materials that could compromise the gasket’s performance.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process allows for immediate detection of issues. This includes regular checks of dimensions, material properties, and adherence to specifications.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): The final inspection occurs after production is complete. This step includes comprehensive testing to ensure that gaskets meet all necessary standards and specifications before they are shipped.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Manifold Gaskets?
Testing methods are essential for validating the performance of manifold gaskets. Common methods include:
-
Pressure Testing: This method evaluates the gasket’s ability to maintain a seal under pressure. It is particularly important for automotive applications where leaks can cause significant issues.
-
Thermal Cycling Tests: This test assesses the gasket’s performance under extreme temperature variations, simulating real-world conditions.
-
Chemical Resistance Testing: For gaskets exposed to various chemicals, this testing ensures that materials do not degrade when in contact with specific substances.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
International B2B buyers should take proactive steps to ensure that their suppliers maintain high-quality standards. Here are some actionable insights:
-
Conduct Audits: Regular audits of suppliers can provide deep insights into their QC processes. Buyers should request audit reports and follow up on any discrepancies.
-
Request Documentation: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality management systems, including ISO certifications, test reports, and compliance with industry standards.
-
Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s QC processes and product quality.
What Are the Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
For buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding regional nuances in quality control and certification is vital.
-
Regional Regulations: Different regions may have specific regulations that affect quality standards. For instance, buyers in the Middle East should be aware of local standards that may differ from those in Europe or South America.
-
Cultural Considerations: Building relationships with suppliers in diverse regions can facilitate better communication about quality expectations. Cultural nuances may influence how quality control is perceived and implemented.
-
Supply Chain Transparency: Ensuring transparency in the supply chain can help buyers mitigate risks associated with quality. This includes understanding the sourcing of materials and the manufacturing processes used by suppliers.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place for manifold gaskets, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they partner with suppliers that align with their quality expectations and regulatory requirements.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘manifold gasket’
In the competitive landscape of international manufacturing and automotive industries, sourcing high-quality manifold gaskets is essential for operational efficiency. This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By following these steps, you can ensure that you procure the right products from reliable suppliers, minimizing risk and maximizing value.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Before initiating the sourcing process, it’s critical to have a clear understanding of your technical requirements. This includes dimensions, material types, and performance standards specific to your application.
– Material Considerations: Determine whether you need rubber, metal, or composite gaskets based on the environment and performance needs.
– Compatibility: Ensure that the gasket is compatible with the specific manifold and engine types you work with.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers that specialize in manifold gaskets. Utilize industry directories, trade shows, and online platforms to compile a list.
– Geographical Focus: Pay attention to suppliers in regions with a strong manufacturing presence, such as Europe and South America.
– Local vs. Global: Consider both local suppliers for shorter lead times and global suppliers for potentially better pricing or unique offerings.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Capabilities
Before committing, thoroughly evaluate the capabilities of potential suppliers. Request company profiles, case studies, and references from buyers in similar industries or regions.
– Quality Assurance: Look for suppliers that have established quality control processes and certifications, such as ISO 9001.
– Production Capacity: Assess whether they can meet your volume requirements without compromising quality.
Step 4: Request Samples and Technical Data
Always request samples and detailed technical data sheets before finalizing your order. This allows you to verify that the gaskets meet your specifications.
– Performance Testing: Conduct tests on samples to ensure they can withstand the operational conditions of your application.
– Documentation: Ensure that the technical data includes information on temperature tolerance, pressure ratings, and installation guidelines.
Step 5: Negotiate Pricing and Terms
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, begin the negotiation process. Discuss pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules to ensure that they align with your business needs.
– Bulk Discounts: Inquire about discounts for bulk purchases, which can significantly reduce costs.
– Flexible Payment Terms: Explore options for payment terms that suit your cash flow, especially if you are ordering large quantities.
Step 6: Verify Supplier Certifications and Compliance
Before making a final decision, verify that your chosen supplier holds the necessary certifications and complies with international standards.
– Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with local and international regulations, particularly if you are importing gaskets into your country.
– Sustainability Practices: Consider suppliers that prioritize sustainability, as this can enhance your company’s reputation and align with modern consumer values.
Step 7: Establish a Clear Communication Channel
Effective communication is vital throughout the sourcing process. Establish a clear channel with your supplier to facilitate updates, queries, and feedback.
– Regular Updates: Schedule regular check-ins to track the progress of your orders and address any potential issues.
– Crisis Management: Ensure that your supplier has a protocol in place for handling emergencies or delays, which can help mitigate risks in your supply chain.
By adhering to this comprehensive sourcing checklist, B2B buyers can streamline their procurement processes for manifold gaskets, ensuring quality, compliance, and efficiency in their operations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for manifold gasket Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components in Manifold Gasket Sourcing?
When sourcing manifold gaskets, understanding the cost structure is essential for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The choice of raw materials significantly influences pricing. Common materials such as rubber, silicone, or composite materials vary in cost based on quality and availability. For instance, high-grade materials may incur a higher initial price but can lead to long-term savings due to durability.
-
Labor: Labor costs can fluctuate based on the manufacturing location. Regions with lower labor costs, such as parts of Africa and South America, may offer competitive pricing. However, it is essential to consider the skill level of the workforce, which can affect the quality of the finished product.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes utilities, facility costs, and indirect labor. Buyers should evaluate how these overheads impact the overall price. Manufacturers with efficient operations may offer better pricing due to lower overhead costs.
-
Tooling: Custom tooling for specific gasket shapes can be a significant upfront expense. Buyers should assess the necessity of custom tooling versus off-the-shelf solutions to optimize their costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are vital for ensuring product reliability. While QC may increase costs, it can prevent expensive failures and warranty claims later. Investing in a supplier with strong QC can lead to better long-term outcomes.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely depending on the origin and destination. Buyers should factor in logistics when comparing prices from different suppliers, as these costs can add up significantly, particularly for international shipments.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding typical margins in the industry can help buyers gauge whether a quote is competitive.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Manifold Gasket Costs?
Several factors can influence the final price of manifold gaskets:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders often lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should negotiate for better pricing based on their purchasing volume.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized gaskets tailored to specific applications typically incur higher costs. Buyers should balance their need for customization against potential cost savings from standard options.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Premium materials and certifications (e.g., ISO, TS) can drive up costs but may be necessary for specific applications. Buyers should evaluate the necessity of these factors based on their operational requirements.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more for their expertise and reliability, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms (International Commercial Terms) is crucial for international buyers. Different terms can affect shipping costs and responsibilities, impacting the overall cost structure.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs in Manifold Gasket Sourcing?
To navigate the complexities of manifold gasket sourcing effectively, buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing and terms. Highlighting potential long-term partnerships can encourage suppliers to provide better pricing.
-
Cost-Efficiency Analysis: Conduct a Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) analysis that goes beyond the purchase price. Consider factors such as maintenance costs, expected lifespan, and warranty claims.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations, import duties, and taxes that can affect overall costs. Establishing relationships with suppliers that offer stable pricing or favorable payment terms can mitigate these risks.
-
Research and Compare Suppliers: Take time to evaluate multiple suppliers. Look beyond the initial price and consider factors such as delivery times, customer service, and after-sales support.
Disclaimer on Indicative Prices
Prices for manifold gaskets can vary widely based on the aforementioned factors. It is advisable for buyers to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough due diligence before making purchasing decisions.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing manifold gasket With Other Solutions
Understanding Alternatives to Manifold Gaskets
When selecting sealing solutions for manifold applications, it is crucial to evaluate alternatives that may offer better performance, cost-effectiveness, or ease of use. This analysis compares manifold gaskets against two viable alternatives: metal O-rings and liquid gasket sealants. Each of these options has unique characteristics that may better suit specific operational needs for international B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
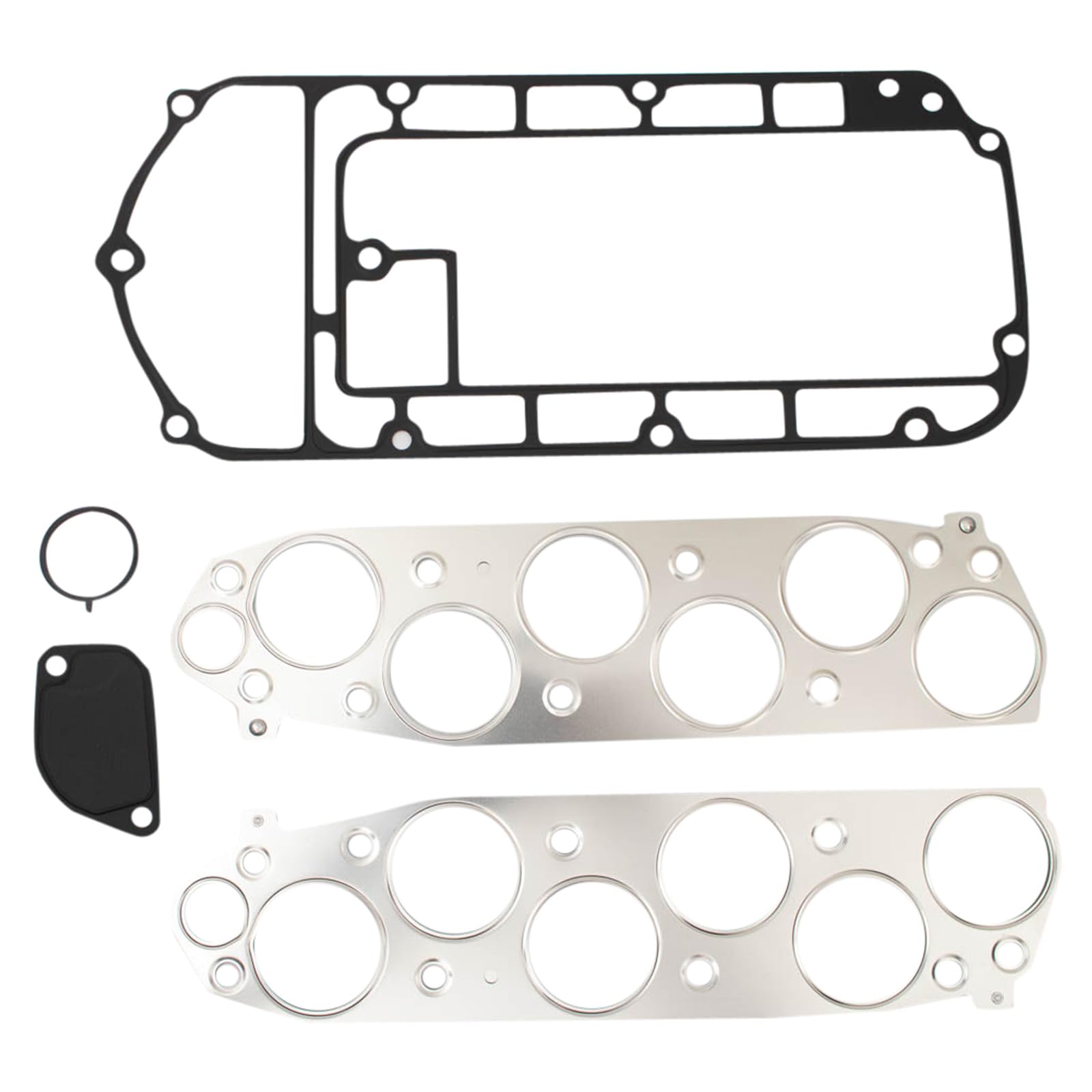
A stock image related to manifold gasket.
Comparison Table of Manifold Gasket and Alternatives
| Comparison Aspect | Manifold Gasket | Metal O-Rings | Liquid Gasket Sealants |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High sealing integrity | Excellent for high temperatures | Flexible, good for irregular surfaces |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires precision fitting | Easy to install | Requires curing time |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance | Durable but can corrode | May require reapplication |
| Best Use Case | Standard manifold applications | High-performance engines | Custom applications with irregular shapes |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using Metal O-Rings?
Metal O-rings are highly regarded for their durability and ability to withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. They offer excellent sealing performance, especially in high-performance applications, such as racing engines or industrial machinery. However, their higher initial cost can be a barrier for some businesses, particularly smaller operations. Additionally, the installation requires precision to avoid leaks, and they can be susceptible to corrosion in certain environments, necessitating regular checks.
How do Liquid Gasket Sealants compare to Manifold Gaskets?
Liquid gasket sealants provide a flexible sealing solution that can conform to irregular surfaces, making them ideal for custom applications. They are generally less expensive than manifold gaskets, which can be attractive for budget-conscious buyers. However, one downside is the curing time required for liquid sealants, which can delay production schedules. Moreover, they may require reapplication over time, adding to long-term maintenance costs. Their adaptability makes them suitable for various applications but may not provide the same level of sealing integrity as a well-fitted manifold gasket.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Sealing Solution for Your Needs
When selecting a sealing solution, B2B buyers should consider the specific requirements of their applications, including performance expectations, budget constraints, and installation capabilities. Manifold gaskets offer reliable sealing for standard applications, while metal O-rings excel in high-performance scenarios. Liquid gasket sealants may be the best choice for irregularly shaped components or when cost is a primary concern. By carefully evaluating these alternatives, businesses can make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and ultimately enhance their product reliability.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for manifold gasket
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Manifold Gaskets?
When sourcing manifold gaskets, understanding their technical properties is essential for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Manifold gaskets are typically made from materials such as rubber, metal, or composite materials. The material grade indicates the quality and suitability for specific applications. For example, higher-grade materials like graphite or multi-layer steel offer superior heat resistance and durability, making them ideal for high-performance vehicles. Buyers should evaluate the material grade based on the operational environment and the specific requirements of their machinery.
2. Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable variation in the dimensions of the gasket. Precise tolerances are crucial for ensuring a proper seal between the manifold and engine components. A gasket with tight tolerances minimizes the risk of leaks, which can lead to engine inefficiencies and costly repairs. Buyers should specify the required tolerance levels to ensure compatibility with their systems.
3. Temperature Resistance
The temperature resistance of a gasket indicates its ability to withstand high temperatures without degrading. This property is particularly important for manifold gaskets, which are exposed to extreme heat from the engine. Materials with high-temperature resistance can prolong the lifespan of the gasket and improve overall system reliability. Buyers should assess the maximum operating temperatures of their engines to select appropriately rated gaskets.
4. Compression Set
Compression set is the measure of a material’s ability to return to its original shape after being compressed. A low compression set indicates that the gasket will maintain its sealing capabilities over time, even under pressure. This characteristic is crucial in preventing leaks and maintaining performance. International buyers should inquire about compression set ratings to ensure long-term efficacy in their applications.
5. Fluid Resistance
Fluid resistance pertains to a gasket’s ability to withstand exposure to various automotive fluids, including oil, coolant, and fuel. A gasket that is resistant to these substances will prevent degradation and extend its service life. Buyers should consider the types of fluids their systems use when selecting a gasket to ensure compatibility and reliability.
What Are Common Trade Terms Related to Manifold Gaskets?
Familiarity with industry terminology can streamline the purchasing process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are key terms every B2B buyer should know:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to manufacturers that produce parts used in the assembly of new vehicles. When sourcing manifold gaskets, buyers may opt for OEM parts to ensure compatibility and quality. Understanding whether a gasket is OEM or aftermarket can influence purchasing decisions, especially for high-performance applications.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest number of units a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for budget-conscious buyers as it can affect overall project costs. Buyers should negotiate MOQs based on their needs, especially when exploring new suppliers or entering markets with high demand.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document used to solicit price quotes from suppliers. It typically includes specifications for the manifold gaskets needed. Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from different suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms
Incoterms are a set of international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping agreements. Understanding Incoterms is vital for international transactions, as they dictate who bears the risk and cost during transport. Buyers should familiarize themselves with terms like FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) to ensure clear agreements with suppliers.
5. Lead Time
Lead time is the time required for a supplier to fulfill an order after it has been placed. This metric is essential for planning production schedules and inventory management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to align their supply chain needs with production timelines.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing manifold gaskets, ensuring compatibility, quality, and efficiency in their operations.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the manifold gasket Sector
What are the Key Market Dynamics and Trends in the Manifold Gasket Sector?
The manifold gasket market is currently experiencing significant growth driven by various global factors. Increased automotive production and a rise in demand for efficient engine performance are critical drivers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, and Europe. Technological advancements in materials science, including the development of high-performance gaskets that withstand extreme temperatures and pressures, are reshaping sourcing strategies for international B2B buyers.
Emerging trends such as digital procurement platforms and supply chain transparency are transforming how businesses in the manifold gasket sector source their products. These platforms allow buyers to access a wider range of suppliers, compare prices in real-time, and make informed purchasing decisions quickly. Additionally, the push towards Industry 4.0 is prompting manufacturers to adopt smart technologies, enhancing production efficiency and product quality. B2B buyers must stay updated with these technological innovations to remain competitive and ensure they are sourcing the best products available.
How Can Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impact Your Manifold Gasket Procurement?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial consideration in the manifold gasket sector. As global awareness of environmental issues increases, buyers are seeking suppliers who prioritize eco-friendly practices. The production of gaskets often involves materials that can have significant environmental impacts, such as asbestos or certain synthetic compounds. Buyers should prioritize suppliers that offer ‘green’ certifications and utilize sustainable materials, such as bio-based polymers or recycled metals.
An ethical supply chain is also essential for fostering long-term business relationships. Ensuring that suppliers comply with fair labor practices and environmental regulations not only protects your brand reputation but also aligns with the values of a growing number of consumers and businesses. Buyers from regions such as Europe, where regulatory frameworks are stringent, should emphasize sourcing from suppliers who transparently share their sustainability practices and certifications.
What is the Historical Context of the Manifold Gasket Market?
The manifold gasket has evolved significantly over the past century, adapting to the changing demands of the automotive and industrial sectors. Initially made from simple materials like cork and paper, the evolution of engine technology necessitated the development of more durable materials capable of withstanding higher temperatures and pressures. This led to the introduction of composite materials and advanced elastomers in the 20th century, enhancing performance and longevity.
The shift towards performance-driven engines and a greater emphasis on environmental sustainability has further influenced the design and manufacturing processes of manifold gaskets. As engines become more efficient and emissions regulations tighten, the demand for innovative gasket solutions continues to grow. This historical context not only informs current procurement strategies but also highlights the importance of aligning sourcing decisions with long-term market trends.
Conclusion
For international B2B buyers in the manifold gasket sector, understanding these market dynamics, sustainability practices, and historical developments is crucial. By leveraging insights into sourcing trends and ethical considerations, businesses can make informed decisions that enhance their competitive edge while contributing to a more sustainable future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of manifold gasket
-
How do I choose the right manifold gasket for my application?
Selecting the appropriate manifold gasket involves assessing the specific requirements of your engine or machinery. Consider factors such as operating temperature, pressure ratings, and the materials used in both the gasket and the manifold. Additionally, reviewing the manufacturer’s recommendations can provide insights into compatibility. Engaging with suppliers for technical specifications and product samples can also facilitate informed decisions. -
What is the best material for manifold gaskets in different environments?
The ideal material for manifold gaskets varies depending on the operating conditions. For high-temperature applications, materials like graphite or metal-reinforced composites are recommended. In contrast, rubber or silicone gaskets may suffice for lower temperature environments. Understanding your specific operational context—such as exposure to chemicals or extreme temperatures—will guide you in selecting the most durable and effective option. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) for manifold gaskets?
Minimum order quantities can significantly vary by supplier and the type of gasket required. Generally, MOQs may range from 50 to 100 units for standard products, while custom gaskets could have higher MOQs due to manufacturing setup costs. It’s essential to communicate your needs clearly with potential suppliers and inquire about bulk purchase options that may offer cost savings. -
How can I vet suppliers for manifold gaskets effectively?
To vet suppliers, begin by researching their industry reputation through reviews and testimonials. Verify their certifications and compliance with international standards, such as ISO. Request samples to assess quality and performance, and consider visiting their manufacturing facilities if feasible. Building relationships with suppliers who have a track record of reliability can lead to better long-term partnerships. -
What payment terms should I negotiate with suppliers?
When negotiating payment terms, consider options like letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms based on order size and supplier trustworthiness. Establishing clear payment schedules can help manage cash flow, especially for large orders. Be sure to clarify any penalties for late payments and explore potential discounts for early payment to optimize your procurement strategy.

A stock image related to manifold gasket.
-
How do I ensure quality assurance in manifold gasket procurement?
Implementing a quality assurance strategy involves setting clear specifications and performance criteria before procurement. Ask suppliers about their quality control processes, including testing and certifications. Consider conducting periodic audits or third-party inspections to ensure compliance with your standards. Establishing a feedback loop can also help maintain quality over time, fostering continuous improvement. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing manifold gaskets?
Logistics for importing manifold gaskets include understanding shipping methods, lead times, and customs regulations specific to your region. Collaborate with freight forwarders familiar with your target market to streamline the shipping process. Additionally, factor in import duties and taxes, and consider using Incoterms to clarify responsibilities in the shipping process, which can mitigate unexpected costs and delays. -
How can I customize manifold gaskets to meet specific requirements?
Customization of manifold gaskets typically involves working closely with your supplier to define your specific needs, such as dimensions, material, and performance characteristics. Suppliers often offer design services or modifications to existing products based on your specifications. Be prepared to discuss your application in detail, including environmental conditions and operational pressures, to ensure the final product meets your expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.

A stock image related to manifold gasket.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for manifold gasket
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of manifold gaskets represents a pivotal opportunity for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. By prioritizing quality, supplier reliability, and cost-efficiency, businesses can enhance their operational performance and competitive edge. Understanding regional market dynamics and leveraging local suppliers can further facilitate effective sourcing strategies, ensuring that the gaskets meet both technical specifications and regulatory standards.
How can buyers leverage technology for better sourcing of manifold gaskets? Embracing digital platforms and data analytics can streamline the sourcing process, allowing for better supplier selection and risk management. Additionally, fostering strong relationships with manufacturers can lead to improved innovation and customization, essential for meeting unique market demands.
Looking ahead, international B2B buyers should remain proactive in identifying emerging trends and technological advancements within the manifold gasket industry. By doing so, they can not only secure the best products but also position themselves as leaders in their respective markets. Now is the time to evaluate your sourcing strategies and explore partnerships that will drive growth and sustainability in your operations.