Food Machinery Manufacturers: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Food Machinery Manufacturers
The Imperative for Precision in Food Production
In an era where consumer demand for high-quality, sustainable food products drives innovation, food machinery manufacturers face unprecedented opportunities and challenges. From bakery giants like Peerless Food Equipment, renowned for their durable, versatile, and sanitary mixers that ensure “unstoppable production,” to global players adapting to evolving standards, the industry is a linchpin in crafting beloved foods worldwide. Yet, navigating this landscape requires strategic acumen to thrive amid global supply chains, regulatory variances, and technological advancements.
Key Challenges in the Global Arena
Manufacturers in the USA and Europe grapple with intensifying competition, fluctuating raw material costs, and stringent compliance—such as sanitation and safety protocols that Peerless exemplifies through their maintenance-free designs. Supply chain disruptions and the push for eco-friendly machinery further complicate market entry, especially for B2B buyers seeking reliable partners like those offering global support and local expertise.
What This Guide Covers
This comprehensive B2B guide equips decision-makers with actionable insights to navigate the global food machinery market. It includes:
- Market Overview: Analysis of key trends, regional demands (USA vs. Europe), and growth drivers.
- Supplier Selection: Evaluating manufacturers like Peerless for quality, innovation, and service.
- Regulatory Landscape: Navigating FDA, EU standards, and compliance strategies.
- Innovation and Sustainability: Exploring advanced equipment for efficiency and environmental impact.
- Case Studies and Best Practices: Real-world examples from industry leaders.
By leveraging this guide, you’ll identify partners that deliver unparalleled performance, ensuring your operations remain efficient and competitive in a dynamic global environment.
Top 10 Food Machinery Manufacturers Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Top Food Processing Equipment Manufacturers: Leading Compani
Domain: verifiedmarketresearch.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Top names include John Bean Technologies Corporation and Mettler Toledo, known for commercial food processing equipment and precision ……
2. Food Processing Equipment Manufacturers and Suppliers in the …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Food Processing Equipment Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada · Spiral Water Technologies, Inc · Spiral Water Technologies, Inc · Lee Industries, Inc ……
3. Top 10 Food Processing Machinery Manufacturers & Suppliers in …
Domain: sftmachinery.com
Registered: 2017 (8 years)
Introduction: The top 10 food processing machinery manufacturers in China are: SFT Machinery, Heng Lian, Hualing Xichu, Wanjie Intelligent, CPFMC, Haikejia, ……
4. Lyco MFG: Commercial Food Processing Equipment Manufacturer
Domain: lycomfg.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: Manufacturer of industrial equipment used in food processing and production. Our machines are used for rice, dry beans, pasta, vegetables, poultry and beef….
5. The Top 25 Restaurant and Food Equipment Manufacturers
Domain: mpofcinci.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Dragon Food Equipment Inc. … 17. MTC Food Equipment, Inc. … 22. Somerset Industries, Inc. … 24. VR Food Equipment, Inc. 25. Vulcan Manufacturing ……
6. Top 10 Food Packaging Machinery Manufacturers – Yundu
Domain: yundufillingmachine.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Top manufacturers include Yundu, Tetra Pak, Krones, Syntegon, IMA, Ishida, Accutek, KHS, Coesia, and GEA. Bosch, GEA, and IMA hold over half ……
7. The Top 10 Food Processing and Handling Equipment … – Extrapolate
Domain: extrapolate.com
Registered: 2000 (25 years)
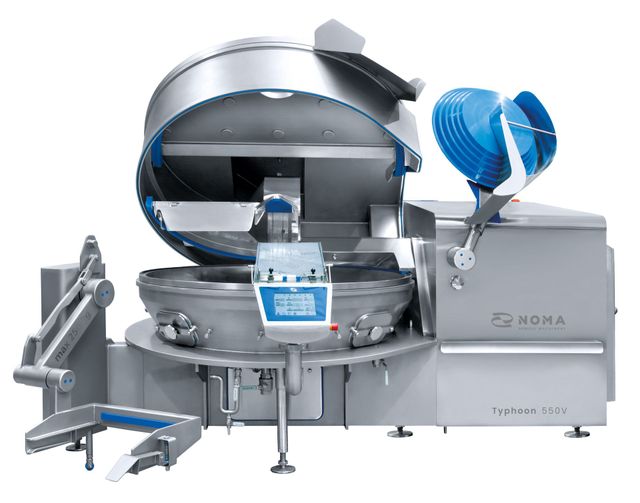
Introduction: Exploring the Top 10 Food Processing and Handling Equipment Manufacturers in 2024 · 1. Bühler Group · 2. Tetra Pak · 3. Alfa Laval AB · 4. Marel HF….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. Top 5 Food Processing Equipment Manufacturers – TechSci Research
Domain: techsciresearch.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: Leading manufacturers like JBT Corporation, GEA Group AG, Tetra Pak, SPX FLOW, Inc., and Alfa Laval AB offer advanced technologies and equipment tailored to ……
Understanding food machinery manufacturers Types and Variations
Understanding Food Machinery Manufacturers Types and Variations
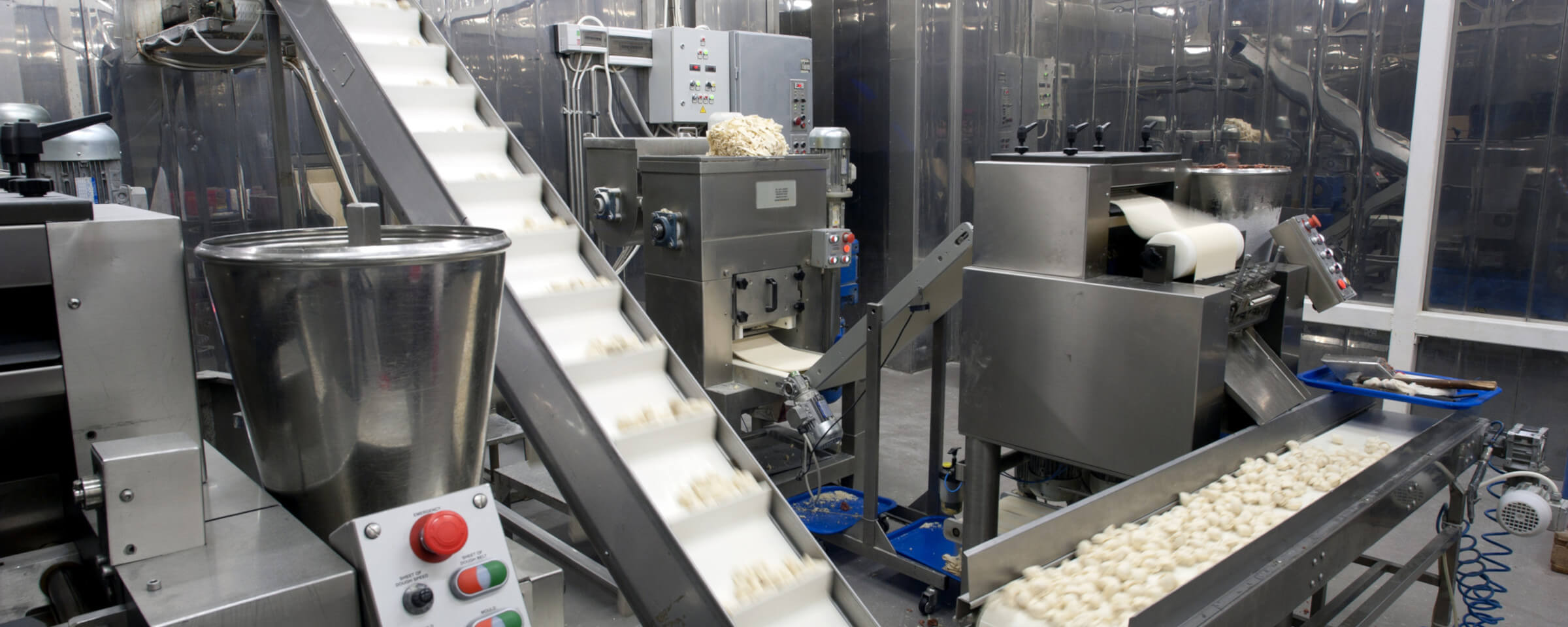
Food machinery manufacturers specialize in producing equipment tailored to specific stages of food production, from mixing and depositing to handling and processing. Based on industry leaders like Peerless Food Equipment and Lyco MFG, manufacturers can be categorized by their core product focus. Below, we identify four key types, highlighting their features, applications, and pros/cons to assist B2B buyers in selecting partners for their operations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing Equipment Manufacturers | Produce dough mixers, cream mixers, and continuous/slurry mixers with open or enclosed frames, sanitary designs, and high durability for consistent batch mixing. | Used in bakeries for bread, biscuits, cakes, and snacks; also in food processing for batters and creams. | Pros: High performance, low maintenance, sanitary construction. Cons: Initial cost may be high for custom designs; requires skilled operation for optimal efficiency. |
| Depositing and Enrobing Equipment Manufacturers | Specialize in depositors, enrobers, and slurry mixers for precise portioning and coating of creams, batters, and toppings. | Ideal for confectionery, bakery, and snack production lines, such as depositing fillings in biscuits or enrobing chocolates. | Pros: Enhances product consistency and reduces waste; versatile for various viscosities. Cons: Complex setup; potential for downtime if not integrated properly with existing lines. |
| Sandwiching Equipment Manufacturers | Offer sandwiching machines, cream delivery systems, and biscuit/cracker delivery units for automated assembly. | Applied in high-volume bakery operations for assembling sandwiches, cookies, and layered products like Oreo-style lines. | Pros: Boosts production speed and scalability; minimizes manual labor. Cons: High upfront investment; may require specialized training for maintenance. |
| Material Handling and Processing Equipment Manufacturers | Provide feeders, conveyors, and handling systems for dough, masa, and other ingredients, often integrated with processing lines. | Suitable for tortilla, bread, and snack manufacturing, including material transfer and sanitation-focused designs. | Pros: Improves workflow efficiency and hygiene; supports large-scale operations. Cons: Integration challenges with legacy systems; ongoing service needs for durability. |
Mixing Equipment Manufacturers
These manufacturers, exemplified by Peerless Food Equipment, focus on mixers designed for uniform blending of ingredients. Key models include open-frame, enclosed-frame, and medium-duty options, emphasizing sanitary stainless steel construction and innovative engineering for maintenance-free performance. In B2B applications, they enable precise control in batch production, reducing variability in quality. Businesses in the USA and Europe benefit from these for cost-effective scaling, as they support high-volume runs in bakeries and food plants, with testimonials highlighting reliability in pizza dough and nutritional product lines.
Depositing and Enrobing Equipment Manufacturers
Drawing from Peerless’s offerings, these specialists produce equipment for accurate depositing of creams or batters and enrobing for coatings. Features include continuous operation and adjustable settings for different product viscosities, ensuring minimal waste. Applications span confectionery and bakery sectors, where precise portioning enhances product appeal and consistency. For B2B buyers, the pros include operational efficiency, though cons involve the need for seamless line integration to avoid bottlenecks.
Sandwiching Equipment Manufacturers
As seen in Peerless’s Peters Sandwiching Machine and delivery systems, these manufacturers deliver automated solutions for layering and assembling food products. They feature high-speed capabilities and sanitary designs to meet hygiene standards. Commonly used in biscuit, cracker, and sandwich production, they streamline assembly processes in industrial settings. Advantages for European and US manufacturers include labor savings and production scalability, offset by the requirement for robust maintenance programs.
Material Handling and Processing Equipment Manufacturers
These manufacturers, informed by Peerless’s dough feeders and handling systems, specialize in equipment for transporting and processing raw materials like masa or dough. Key features include durable, versatile designs with a focus on sanitation and safety. They are essential in tortilla, bread, and snack production for efficient material flow. B2B advantages include enhanced operational flow and reduced contamination risks, though challenges may arise in retrofitting with existing infrastructure.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Key Industrial Applications of food machinery manufacturers
Key Industrial Applications of Food Machinery Manufacturers
The following table outlines key industrial applications for food machinery manufacturers, drawing from established equipment solutions like those provided by Peerless Food Equipment. It highlights relevant equipment, tailored benefits for B2B operations in the USA and Europe, and focuses on efficiency, sanitation, and reliability to optimize production processes.
| Industry/Application | Key Equipment | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bread & Roll Manufacturing | Dough & Cream Mixers (e.g., KleanVue Open Frame, Traditional Enclosed Frame, Pioneer Medium Duty), Sandwiching Equipment (e.g., Peters Sandwiching Machine, Cream Delivery) | Ensures consistent dough mixing for high-volume production, reducing downtime through virtually maintenance-free operations. Enhances product quality with sanitary designs that minimize contamination risks, improving compliance with FDA and EU food safety standards. Supports scalable operations with durable components that maintain performance under continuous use, leading to cost savings on repairs and increased output efficiency for bakeries. |
| Biscuit & Cracker Production | Sandwiching Equipment (e.g., Peters Sandwiching Machine, Biscuit & Cracker Delivery), Dough & Cream Mixers (e.g., KleanVue Open Frame) | Delivers precise layering and delivery of ingredients, optimizing uniformity in product formation. Improves production uptime with innovative, versatile equipment that adapts to varying batch sizes, reducing waste and enhancing yield. Maintains hygiene standards through easy-to-clean surfaces, supporting rigorous sanitation protocols essential for export to European markets and meeting B2B client demands for traceable, high-quality goods. |
| Masa & Tortilla Processing | Creams & Batters Equipment (e.g., Continuous Mixer, Slurry Mixer, Depositor) | Facilitates homogeneous mixing of masa dough, ensuring even texture and flavor distribution in high-speed lines. Offers energy-efficient solutions that minimize operational costs, with robust designs for heavy-duty industrial environments. Enhances product consistency and shelf life through sanitary, enclosed systems, aiding compliance with North American and European quality benchmarks for ethnic food products. |
| Cake & Snack Production | Creams & Batters Equipment (e.g., Enrober, Depositor, Continuous Mixer), Dough & Cream Mixers (e.g., Traditional Enclosed Frame) | Enables precise batter deposition and coating for intricate snack designs, supporting customization for diverse B2B contracts. Reduces production interruptions with durable, versatile machinery that handles multiple recipes seamlessly. Promotes food safety and innovation through maintenance-free components, driving efficiency gains and competitive advantages in fast-moving consumer goods sectors. |
| Other Industries (e.g., Confectionery, Frozen Foods, Nutraceuticals) | Full Range (e.g., Slurry Mixer, Enrober, Depositor, Product Handling like Dough Feeder) | Provides adaptable solutions for specialized applications, such as enrobing or depositing in confectionery lines, ensuring flexibility across diverse food segments. Delivers unparalleled service and global support, minimizing installation risks for multinational operations. Focuses on innovative, sanitary designs that support uninterrupted production, aligning with B2B needs for high-performance equipment that scales with evolving market demands in health and nutrition sectors. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘food machinery manufacturers’ & Their Solutions
3 Common B2B Pain Points for Food Machinery Manufacturers & Their Solutions
Below, we outline three prevalent challenges faced by B2B users of food machinery in the USA and Europe, based on industry insights from manufacturers like Peerless Food Equipment. Each pain point is presented in a scenario/problem/solution format, emphasizing practical resolutions through equipment selection and vendor partnerships.
1. Scenario: High Maintenance Downtime in Food Processing Lines
Problem: Food manufacturers often experience unplanned equipment failures due to wear and tear in high-volume operations, leading to production halts, lost revenue, and rushed repairs. For instance, mixers in bakeries may require frequent servicing, disrupting workflows in bread, biscuit, or cake production.
Solution: Select machinery from manufacturers like Peerless Food Equipment, which offers virtually maintenance-free designs such as the KleanVue Open Frame or Traditional Enclosed Frame mixers. These feature durable components and superior service support, including preventative maintenance programs, to minimize downtime. Partner with vendors providing global support for quick parts replacement and on-site expertise.
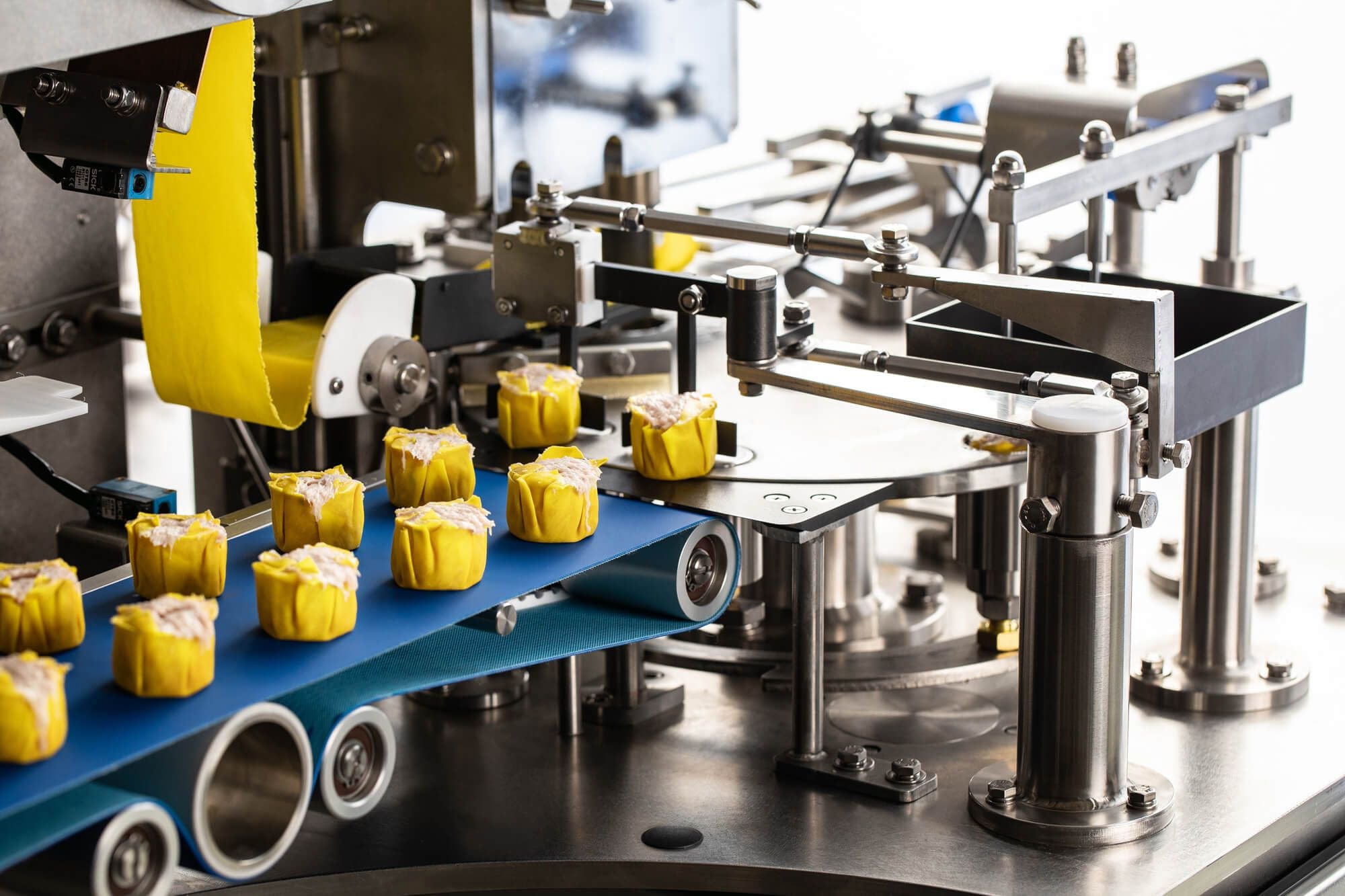
2. Scenario: Sanitation Compliance in Hygienic Environments
Problem: Maintaining strict sanitary standards in food processing facilities is challenging, with risks of contamination from residue buildup on equipment surfaces, especially in applications involving creams, batters, or dough. Non-compliance can result in regulatory fines or product recalls, common in Europe and the USA.
Solution: Invest in sanitary equipment like Peerless’s Enrober or Continuous Mixer, engineered for easy cleaning and hygiene. Manufacturers emphasize innovative, sanitary designs that reduce residue and support compliance with FDA and EU standards. Utilize vendor resources, such as Peerless’s Learning Center on sanitation, for training and best practices to integrate equipment into hygienic workflows.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
3. Scenario: Inefficient Batch Mixing and Production Scaling
Problem: Inconsistent batch quality and low throughput in mixing processes hinder scalability for B2B food producers, particularly in biscuit, cracker, or snack manufacturing, where precise formulations are critical to avoid waste and meet demand.
Solution: Opt for versatile, innovative machinery from providers like Peerless, such as the Pioneer Medium Duty Mixer or Slurry Mixer, designed for efficient, reliable operations. These solutions ensure consistent results and “unstoppable production,” as noted in industry testimonials. Collaborate with manufacturers offering consultation for customized setups, including expert design teams to optimize for specific applications like bread or cake production.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for food machinery manufacturers
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Food Machinery Manufacturers
In the competitive landscape of food machinery manufacturing, selecting the right materials is critical for ensuring equipment durability, compliance with sanitary standards, and operational efficiency. This guide analyzes key materials commonly used in food processing equipment, drawing from industry practices in the USA and Europe. Factors such as corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, USDA in the USA; EU 1935/2004 and HACCP standards in Europe), cost-effectiveness, and longevity are paramount. The goal is to optimize for high-performance, maintenance-free operations while minimizing contamination risks.
Key Considerations for Material Selection
- Sanitary Requirements: Materials must withstand frequent cleaning with harsh chemicals and prevent bacterial growth. Non-porous surfaces are essential to avoid harborage points.
- Durability and Versatility: Equipment faces abrasion, high temperatures, and acidic environments, necessitating materials that resist wear and corrosion.
- Regulatory Compliance: In the USA, materials must meet NSF/ANSI standards for food contact. In Europe, they must comply with EU Food Contact Materials regulations, ensuring no migration of harmful substances.
- Cost and Lifecycle: Initial costs should be balanced against long-term maintenance, repair, and replacement expenses.
- Innovation and Customization: Materials should support modular designs for easy upgrades, as seen in advanced mixers and depositors.
Analysis of Common Materials
Based on equipment like mixers, sandwiching machines, and slurry mixers from manufacturers such as Peerless Food Equipment, the following materials are frequently employed:
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304 or 316 Grades):
- Pros: Excellent corrosion resistance, especially in humid or acidic environments; easy to sanitize and autoclave; high tensile strength for heavy-duty applications. Ideal for enclosed frames in dough mixers and depositors, where durability prevents downtime.
- Cons: Higher initial cost; heavier, which may increase shipping and installation expenses.
- Applications: Primary choice for mixing blades, tanks, and frames in equipment handling creams, batters, and doughs. Compliant with FDA and EU standards for food contact.
-
Strategic Tip: Opt for 316 grade in high-corrosive settings, such as biscuit creamers exposed to salts or acids, to extend equipment lifespan.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Aluminum:
- Pros: Lightweight, cost-effective, and good thermal conductivity, making it suitable for heat transfer in enrobers or continuous mixers.
- Cons: Prone to corrosion if not treated; not ideal for acidic foods, as it can react and leach into products.
- Applications: Used in non-contact components like frames or lightweight conveyor parts, but rarely for direct food exposure due to sanitary risks.
-
Strategic Tip: Reserve for non-critical parts and always apply anodized coatings to enhance durability in European facilities adhering to strict migration limits.
-
Food-Grade Plastics (e.g., PTFE, HDPE, or Nylon):
- Pros: Lightweight, chemical-resistant, and inexpensive; non-reactive with most foods, reducing contamination risks.
- Cons: Lower durability under high temperatures or abrasion; potential for wear in high-throughput lines like slurry mixers.
- Applications: Common in components like conveyor belts, seals, or non-structural parts in depositors and enrobers. Ensures versatility in multi-product lines.
-
Strategic Tip: Verify EU compliance for plastic additives to avoid migration issues; combine with stainless steel for hybrid designs in USA-based operations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Other Alloys (e.g., Titanium or Brass):
- Pros: Superior corrosion resistance in extreme conditions; titanium is biocompatible and used in specialized sanitary applications.
- Cons: Very high cost; limited availability for large-scale manufacturing.
- Applications: Niche use in high-end mixers or parts exposed to aggressive chemicals, such as in health-focused nutrition lines.
- Strategic Tip: Consider only for premium equipment where ROI justifies the expense, aligning with Peerless’s focus on innovative, long-lasting solutions.
Comparison Table of Materials
| Material | Durability (1-5) | Sanitary Compliance | Cost (Low/Med/High) | Corrosion Resistance | Typical Applications in Food Machinery |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (304) | 5 | High (FDA/EU) | Med | Excellent | Mixers, depositors, frames |
| Stainless Steel (316) | 5 | High (FDA/EU) | High | Superior | Acidic environments, creamers |
| Aluminum | 3 | Medium | Low | Fair | Frames, lightweight parts |
| Food-Grade Plastics | 3 | High (with testing) | Low | Good | Seals, belts, non-contact components |
| Titanium | 5 | High (FDA/EU) | High | Exceptional | High-corrosive, specialized equipment |
This table highlights trade-offs: Stainless steel offers the best balance for most food machinery, supporting uninterrupted production as emphasized by manufacturers like Peerless. For custom solutions, consult engineers to integrate materials that align with specific applications, ensuring compliance and efficiency in USA and European markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for food machinery manufacturers
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Food Machinery Manufacturers
Food machinery manufacturers in the USA and Europe prioritize precision, sanitation, and efficiency in their production to deliver equipment that supports high-volume food processing while meeting stringent regulatory standards. Below, we outline key manufacturing steps and quality assurance protocols, informed by industry leaders like Peerless Food Equipment, which emphasizes durable, sanitary designs for applications such as dough mixing and sandwiching.
Manufacturing Processes
Manufacturers follow a structured sequence to produce reliable, high-performance machinery. This process ensures equipment like mixers, depositors, and enrobers meets the demands of bakeries, snack producers, and other food operations. Key steps include:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Preparation (Prep): Raw materials, such as stainless steel alloys and food-grade components, are sourced and inspected for compliance with sanitary standards. Components are cut, machined, or molded to specifications, incorporating features like open frames for easy cleaning (e.g., Peerless’s KleanVue mixers). This phase focuses on material durability and versatility to minimize maintenance.
-
Forming: Core structures are shaped through welding, bending, or casting. Electrical and mechanical elements, such as motors and controls, are integrated to form subassemblies. Innovation in this step includes advanced designs for continuous mixing or depositing, ensuring equipment handles high-viscosity batters or creams efficiently without downtime.
-
Assembly: Subassemblies are combined into final units, including wiring, plumbing, and software integration. Automation tools are often used to align parts precisely, with a emphasis on modular designs for easy upgrades. For instance, sandwiching machines are assembled to deliver consistent cream layers, drawing from proven models like Peerless’s Peters Sandwiching Machine.
-
Quality Control (QC): Post-assembly, equipment undergoes rigorous testing for functionality, safety, and performance. This includes load testing, leak checks, and operational simulations under real-world conditions. Any defects are addressed before packaging, ensuring “unstoppable production” as highlighted by Peerless’s reputation for maintenance-free operations.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Assurance and Standards
To maintain trust in B2B markets, manufacturers adhere to global quality frameworks, ensuring machinery supports food safety and operational reliability.
| Standard | Key Focus | Application in Food Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | Ensures consistent processes from design to delivery, reducing errors in high-volume production lines. |
| ISO 22000 | Food Safety Management | Mandates hazard analysis and critical control points (HACCP) integration, critical for equipment handling dough, creams, or batters to prevent contamination. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Promotes sustainable practices, such as eco-friendly materials in mixers and depositors, aligning with European and US environmental regulations. |
Peerless Food Equipment exemplifies these standards by delivering sanitary, innovative solutions with global support, as evidenced by customer testimonials praising seamless installations and performance. Manufacturers also conduct internal audits and customer validations to exceed expectations, fostering long-term partnerships in the food industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘food machinery manufacturers’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Food Machinery Manufacturers
This checklist provides a structured approach to sourcing food machinery manufacturers, informed by industry standards for durability, versatility, sanitary design, and innovation in equipment like mixers, sandwiching machines, and processing lines. Tailor it to your specific needs in food production applications such as bread, biscuits, or snacks, while ensuring compliance with regulations in the USA and Europe.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Identify key specifications: Equipment type (e.g., dough mixers, depositors, enrobers), capacity, throughput, and application (e.g., bread & roll, biscuit & cracker, masa & tortilla, cake & snack).
- Assess operational needs: Focus on sanitary design, energy efficiency, maintenance-free operations, and integration with existing lines.
- Determine compliance standards: Ensure adherence to FDA (USA) or EU hygiene directives, including material safety (e.g., stainless steel for food contact).
- Set budget and timeline: Include costs for equipment, installation, training, and ongoing support.
Step 2: Research and Identify Potential Manufacturers
- Search industry directories: Use sources like ThomasNet or B2B platforms to find established manufacturers with a history of high-performance equipment (e.g., over 100 years of experience in bakeries).
- Review portfolios: Prioritize manufacturers offering versatile, innovative solutions like continuous mixers, slurry mixers, and sandwiching equipment with global support.
- Check certifications: Verify ISO, GMP, or similar certifications for sanitary and safe production.
- Gather references: Seek testimonials from similar operations (e.g., bakeries or food processors) to confirm reliability and maintenance-free performance.
Step 3: Evaluate and Qualify Suppliers
- Compare product features: Assess durability, versatility, and innovation (e.g., open-frame vs. enclosed mixers) against your defined requirements.
- Analyze service offerings: Look for comprehensive support, including preventative maintenance programs, local service, and parts availability.
- Conduct site visits or virtual demos: Evaluate equipment in action to confirm sanitary design and efficiency.
- Review pricing and terms: Compare total cost of ownership, including warranties, training, and after-sales service.
Step 4: Negotiate and Finalize Agreements
- Request proposals: Obtain detailed quotes covering equipment, customization, delivery, and installation.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss payment schedules, delivery timelines, and service contracts to ensure long-term partnership.
- Verify compliance and testing: Ensure equipment meets regulatory standards with proof of testing (e.g., for sanitary operations).
- Secure contracts: Include clauses for performance guarantees, maintenance, and escalation procedures.
Step 5: Implement and Monitor
- Plan installation and training: Coordinate with the manufacturer for seamless integration and operator training.
- Establish maintenance protocols: Set up preventative maintenance to maintain “unstoppable production” and extend equipment life.
- Monitor performance: Track metrics like uptime, product quality, and efficiency, using feedback loops for continuous improvement.
- Build ongoing relationships: Maintain contact for parts, upgrades, or expansions to leverage superior service.
| Checklist Element | Key Considerations | Reference Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Requirements Definition | Sanitary, durable, versatile equipment for specific applications. | Emphasizes high-performance, maintenance-free operations in food processing. |
| Supplier Research | Established manufacturers with innovation and service focus. | Draws from companies with 100+ years in bakeries, offering global support. |
| Evaluation | Compliance with standards, product versatility. | Highlights sanitary design, energy efficiency, and applications in bread/biscuits. |
| Negotiation | Total cost, including maintenance. | Includes preventative maintenance programs for reliability. |
| Implementation | Training and monitoring for optimal performance. | Focuses on seamless integration and testimonials from successful installations. |
This checklist ensures a methodical sourcing process, minimizing risks and maximizing ROI in food machinery procurement. Adapt based on your location-specific regulations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for food machinery manufacturers Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Food Machinery Manufacturers Sourcing
Sourcing food machinery from manufacturers like Peerless Food Equipment or Lyco Manufacturing requires a thorough understanding of cost drivers to ensure competitive pricing and operational efficiency. This analysis focuses on key components—materials, labor, and logistics—while incorporating insights from industry leaders such as Peerless, known for durable, sanitary equipment with minimal maintenance. Below, we break down costs, outline pricing strategies, and provide actionable tips for cost savings, tailored for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe.
Cost Breakdown
Costs in sourcing food machinery can vary based on equipment type (e.g., mixers, depositors, or enrobers), customization needs, and manufacturer specifics. Peerless Food Equipment exemplifies high-quality, long-lasting solutions, which influence pricing through premium materials and engineering. Use the following table as a benchmark for estimating expenses:
| Component | Description | Estimated Cost Range (USD) | Key Influencers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Raw materials like stainless steel, alloys, and components for sanitary, durable designs (e.g., Peerless’s KleanVue mixers). | $5,000–$50,000 per unit | Quality standards (e.g., FDA-compliant materials for hygiene); bulk sourcing discounts from suppliers like those used by Peerless. |
| Labor | Manufacturing, assembly, and testing by skilled engineers, including custom modifications for applications like bread & roll or biscuit production. | $2,000–$15,000 per unit | Labor rates in manufacturing hubs (e.g., USA Midwest or European facilities); expertise in innovative designs like Peerless’s virtually maintenance-free operations. |
| Logistics | Shipping, import/export duties, insurance, and warehousing for equipment such as sandwiching machines or slurry mixers. | $1,000–$10,000 per unit | Distance (e.g., transatlantic for Europe-USA trade); compliance with regulations like EU CE marking or US FDA standards; carbon-neutral shipping options. |
Total sourcing costs for a mid-range unit (e.g., a Peerless dough mixer) typically range from $10,000–$75,000, excluding customization. Factors like scale (bulk orders) and manufacturer reputation (e.g., Peerless’s 100+ years of service) can drive premiums.
Pricing Considerations
Pricing from manufacturers is influenced by value propositions such as durability and innovation. Peerless positions its equipment as “unstoppable production” with high ROI through reduced downtime and maintenance, justifying higher upfront costs. For B2B buyers:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Base Pricing: Starts at competitive rates for standard models (e.g., $10,000–$30,000), but escalates for sanitary, versatile options.
- Customization Add-Ons: Custom features (e.g., enrobers or depositors tailored to cake & snack applications) add 20–50% to base costs.
- Regional Variations: In the USA, focus on domestic manufacturing for faster delivery; in Europe, emphasize compliance with stringent hygiene regulations, potentially increasing costs by 10–15%.
- Long-Term Value: Factor in TCO (Total Cost of Ownership), where Peerless’s maintenance-free designs yield savings over 5–10 years via lower repair expenses.
Negotiate based on order volume and long-term partnerships, as seen in Peerless’s testimonials from clients like MaMa Rosa’s Pizza.
Tips to Save Costs
Implement these strategies to optimize sourcing from food machinery manufacturers:
- Bulk Sourcing and Negotiation: Order multiple units to leverage volume discounts; negotiate with manufacturers like Peerless for tiered pricing on materials and labor.
- Standardize Specifications: Opt for off-the-shelf models (e.g., Peerless’s Pioneer Medium Duty) over custom builds to reduce labor costs by up to 30%.
- Optimize Logistics: Partner with freight forwarders for consolidated shipping and choose manufacturers with local distribution (e.g., Peerless’s global support network) to cut transportation expenses by 15–25%.
- Leverage Incentives: Seek tax credits for energy-efficient equipment (e.g., EU Green Deal or US incentives) and explore used or refurbished machinery from reputable sources to save 20–40% on new purchases.
- Supplier Partnerships: Build relationships for preventative maintenance programs, as offered by Peerless, which minimize long-term repair costs and downtime.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing food machinery manufacturers With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Food Machinery Manufacturers With Other Solutions
This section evaluates food machinery manufacturers, exemplified by specialized providers like Peerless Food Equipment, against two key alternatives: general industrial equipment suppliers and custom engineering firms. The comparison focuses on critical B2B factors such as customization, cost, expertise, and operational efficiency, drawing from industry standards in the USA and Europe.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Food Machinery Manufacturers (e.g., Peerless Food Equipment) | General Industrial Equipment Suppliers | Custom Engineering Firms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customization | High – Tailored designs for food-specific needs like sanitary mixers and depositors. | Low to Medium – Standardized equipment adaptable with modifications, but not optimized for food hygiene. | High – Fully bespoke solutions engineered from scratch for unique requirements. |
| Cost | Medium to High – Premium pricing for specialized, durable hardware and ongoing support. | Low to Medium – Affordable off-the-shelf options, but may incur retrofit costs. | High – Significant upfront investment in design and prototyping. |
| Expertise | Specialized – Deep knowledge in food processing, compliance (e.g., FDA, EU standards), and maintenance-free operations. | General – Broad industrial knowledge, but limited food-specific insights or certifications. | Technical – Strong engineering focus, but may lack domain expertise in food machinery hygiene and efficiency. |
| Lead Time | Medium – Faster delivery for proven models, with customization options. | Short – Quick access to inventory, but delays for custom fits. | Long – Extended timelines for design, testing, and validation. |
| Support & Maintenance | Comprehensive – Global service, preventive maintenance programs, and local expertise. | Basic – Vendor support varies; often requires third-party maintenance. | Variable – Dependent on firm; may include integrated support but with higher coordination needs. |
| Scalability | High – Designed for high-volume, uninterrupted production in bakeries and processing lines. | Medium – Suitable for smaller operations but may not scale efficiently for food industry demands. | High – Flexible for scaling, but requires ongoing engineering oversight. |
| Compliance & Safety | Strong – Built-in sanitary features, safety protocols, and regulatory adherence (e.g., hygiene standards). | Moderate – Basic safety features; may not meet strict food-grade requirements without additions. | Strong – Can incorporate advanced compliance, but depends on engineering rigor. |
Analysis
-
Food Machinery Manufacturers (e.g., Peerless Food Equipment): Ideal for food processing companies prioritizing efficiency, hygiene, and minimal downtime. They offer unparalleled expertise in applications like dough mixing and cream deposition, as seen in Peerless’s 100+ years of experience serving bakeries. This option excels in regulated environments (USA FDA, EU food safety) where specialized, maintenance-free equipment reduces operational risks. Choose this for high-volume production needing quick, reliable results without in-house engineering burdens. Drawbacks include higher costs and less flexibility for non-standard needs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
General Industrial Equipment Suppliers: Best for budget-conscious firms with simpler requirements or those scaling from small to medium operations. These suppliers provide cost-effective, readily available hardware that can be adapted for basic food tasks, but often lack food-specific optimizations like sanitary designs or compliance with industry standards. In the USA and Europe, this may lead to higher retrofit expenses or regulatory hurdles. Opt for this alternative if your operation involves non-critical food processing and you have internal resources to handle customizations.
-
Custom Engineering Firms: Suitable for highly specialized or innovative food machinery needs where off-the-shelf solutions fall short. These firms deliver tailored engineering, such as unique depositors or mixers, but at a premium price and with longer timelines. They shine in complex projects requiring advanced features, yet may demand more client involvement for testing and validation. In Europe and the USA, this is preferable for R&D-driven companies or those with proprietary processes, though it risks delays and higher total costs compared to specialized manufacturers.
When selecting, consider your production scale, budget, and regulatory environment. Food machinery manufacturers generally provide the best balance of expertise and efficiency for dedicated food operations, while alternatives may suit cost-sensitive or highly customized scenarios. Consult experts to assess fit based on specific use cases, such as biscuit production or slurry mixing.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for food machinery manufacturers
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Food Machinery Manufacturers
This section outlines critical technical properties and trade terminology essential for B2B interactions in the food machinery sector, focusing on manufacturers targeting the USA and European markets. These elements ensure compliance with industry standards, operational efficiency, and smooth transactions. Content is informed by leading manufacturers like Peerless Food Equipment and Lyco MFG, emphasizing durability, sanitation, and customization.
Key Technical Properties
Food machinery must adhere to rigorous standards for safety, hygiene, and performance. Below are the primary properties, drawn from industry benchmarks:
- Durability: Equipment designed for continuous, high-volume production with materials resistant to wear, corrosion, and heavy use. Example: Peerless mixers offer virtually maintenance-free operations over decades, suitable for bakery and processing lines.
- Versatility: Adaptability for multiple applications, such as dough mixing, cream deposition, or batter handling, allowing manufacturers to serve diverse food sectors like bread, biscuits, and snacks.
- Sanitation: Compliance with hygiene standards (e.g., NSF, EHEDG) for easy cleaning and contamination prevention. Features include stainless steel construction, open frames for visibility, and sanitary seals to meet FDA and EU regulations.
- Innovation: Integration of advanced technologies like automated controls, energy-efficient motors, and customizable modules for optimized throughput and reduced downtime.
- Safety: Built-in safeguards, including overload protection, ergonomic designs, and compliance with OSHA and CE standards to minimize workplace hazards.
- Efficiency: High output with low energy consumption, often measured by throughput rates (e.g., mixers processing batches in minutes) and minimal waste.
These properties are critical for B2B buyers evaluating machinery for integration into production lines, ensuring long-term ROI and regulatory compliance.
Key Trade Terminology
Trade terms facilitate negotiations, orders, and logistics. The following table summarizes common acronyms and definitions relevant to food machinery manufacturers in USA and European contexts:
| Term | Definition | Relevance in Food Machinery |
|---|---|---|
| MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) | The smallest quantity of units a manufacturer requires for an order. | Often set at 1-10 units for custom machinery; higher for standardized equipment to cover production costs. |
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | A company that produces parts or equipment for integration into other products. | Manufacturers like Peerless offer OEM services for branded mixers or depositors customized for client specifications. |
| ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) | A company that designs and manufactures products as specified by another firm. | Applies to co-developed machinery, such as sandwiching equipment tailored for European bakery standards. |
| FOB (Free on Board) | Seller bears costs until goods are loaded onto the ship at the port of origin. | Common in USA exports; buyer handles shipping from origin, useful for international machinery shipments. |
| CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight) | Seller covers costs, insurance, and freight to the buyer’s port. | Prevalent in European imports; ensures machinery arrives at the destination with seller liability. |
| Incoterms | International commercial terms defining responsibilities of sellers and buyers. | Essential for cross-border deals; e.g., EXW for pickup or DDP for delivered duty paid. |
| SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) | A unique code for inventory tracking. | Used for parts like mixer blades or enrober systems to streamline orders and replacements. |
| Lead Time | The period from order placement to delivery. | Typically 4-12 weeks for custom food machinery; shorter for off-the-shelf items. |
| Warranty | Manufacturer’s guarantee on product performance. | Often 1-5 years, covering defects in durable equipment like Peerless mixers. |
| Customization (Bespoke) | Tailored modifications to standard products. | Key for sanitary or innovative features, such as integrating EU-specific hygiene protocols. |
Understanding these terms aids in drafting contracts, negotiating terms, and ensuring seamless B2B transactions. For specific applications, consult manufacturer guidelines or a consultant for tailored advice.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the food machinery manufacturers Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Food Machinery Manufacturers Sector
In the food machinery manufacturers sector, staying ahead requires a deep understanding of evolving market dynamics, strategic sourcing practices, and long-term sustainability goals. This section explores key trends, drawing from industry leaders like Peerless Food Equipment, which has delivered high-performance solutions for over a century.
Market Dynamics
The food machinery sector is shaped by increasing demands for efficiency, hygiene, and customization in food production. Key dynamics include:
-
Rising Automation and Digitization: Manufacturers are integrating advanced technologies to streamline operations. For instance, Peerless Food Equipment’s KleanVue mixers and continuous mixers emphasize virtually maintenance-free performance, reducing downtime and boosting productivity in bakeries and snack production.
-
Hygiene and Safety Standards: With global regulations tightening, equipment must meet stringent sanitary requirements. Peerless’s durable, versatile designs, such as their sandwiching machines and depositors, ensure compliance while supporting high-volume production for products like biscuits and tortillas.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Customization and Versatility: Demand for adaptable machinery has grown, driven by diverse food applications (e.g., bread, cakes, and snacks). Peerless’s history of pioneering solutions for world-class bakeries highlights how tailored equipment addresses specific needs, from enclosed frame mixers to slurry mixers.
-
Economic Pressures and Globalization: Fluctuations in raw material costs and supply chains influence pricing. In the USA and Europe, manufacturers navigate these through localized production and international partnerships, as seen in Peerless’s global support network.
| Key Market Trend | Impact on Manufacturers | Example from Peerless |
|---|---|---|
| Automation Adoption | Reduces labor costs and errors | Continuous mixers for precise batch mixing |
| Sustainability Focus | Meets eco-conscious consumer demands | Durable, long-lasting equipment minimizing waste |
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures product safety and market access | Sanitary designs for FDA/EU standards |
Sourcing Trends
Sourcing in the food machinery sector emphasizes reliability, cost-effectiveness, and ethical practices. Trends reflect a shift toward diversified, sustainable supply chains:
-
Global vs. Local Sourcing: Manufacturers balance global procurement for cost savings with local sourcing to reduce lead times and risks. Peerless Food Equipment leverages its century-long expertise to source high-quality components, ensuring durable machinery like their Pioneer medium-duty mixers.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Supplier Partnerships: Building long-term relationships with suppliers enhances innovation. Peerless’s collaborations, including with entities like Coperion, unify technology solutions, improving customer experience through enhanced brand identity and integrated equipment lines.
-
Material Innovation: Trends favor sustainable materials that withstand harsh environments. For example, Peerless’s equipment uses durable, sanitary materials to handle applications in bread, biscuit, and masa production, aligning with trends toward lightweight yet robust designs.
-
Supply Chain Resilience: Post-pandemic, there’s a push for resilient sourcing to mitigate disruptions. European and US manufacturers increasingly adopt predictive analytics for inventory, as evidenced by Peerless’s preventative maintenance programs.
Key sourcing strategies include:
– Prioritizing certified suppliers for compliance (e.g., ISO standards).
– Investing in digital tools for real-time tracking.
– Diversifying suppliers to avoid dependency on single sources.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability in Manufacturing
Sustainability is a core driver, with manufacturers focusing on eco-efficient designs to appeal to environmentally conscious buyers in the USA and Europe. Peerless Food Equipment exemplifies this through:
-
Energy-Efficient Operations: Equipment like their enrobers and depositors minimizes energy use while maintaining high output, reducing carbon footprints in food processing.
-
Waste Reduction: Durable, versatile machinery lowers the need for frequent replacements, cutting material waste. Peerless’s 100-year legacy underscores innovations that support sustainable production, such as their slurry mixers for efficient batter handling.
-
Circular Economy Practices: Trends include designing for recyclability and extending equipment life. In Europe, EU Green Deal initiatives influence manufacturers to adopt these practices, while US firms focus on reducing emissions through advanced materials.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Stakeholder Engagement: Companies engage customers and employees in sustainability efforts, as seen in Peerless’s customer testimonials praising reliable, low-maintenance solutions that align with green goals.
Historical Context
The food machinery sector has evolved from manual processes to sophisticated automation, with history informing current trends. Peerless Food Equipment, founded over a century ago, has pioneered innovations for bakeries, emphasizing sanitary and efficient designs. This legacy reflects broader industry shifts:
- Early 20th Century: Focus on basic mixing and handling equipment for staple foods.
- Mid-20th Century: Introduction of enclosed systems for hygiene, as seen in Peerless’s traditional enclosed frame mixers.
- Late 20th to Present: Integration of technology for versatility, driven by global food demands. Peerless’s role in major projects, like installations for brands such as MaMa Rosa’s Pizza and Parsons Nutritionals, illustrates how historical expertise enables modern, unstoppable production.
Understanding these historical roots helps manufacturers anticipate future dynamics, ensuring resilient, innovative sourcing and sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of food machinery manufacturers
Frequently Asked Questions for B2B Buyers of Food Machinery Manufacturers
Below are 8 common questions from B2B buyers in the USA and Europe, informed by industry standards from manufacturers like Peerless Food Equipment and Lyco MFG. Answers focus on practical considerations for selecting, purchasing, and maintaining industrial food processing equipment.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
1. What types of food machinery do manufacturers like Peerless offer, and how do they cater to different applications?
Peerless Food Equipment specializes in industrial mixers (e.g., KleanVue Open Frame, Traditional Enclosed Frame, Pioneer Medium Duty), sandwiching equipment (e.g., Peters Sandwiching Machine), creams and batters equipment (e.g., Continuous Mixer, Depositor, Enrober), and material handling systems. These are designed for applications in bread & roll production, biscuit & cracker manufacturing, masa & tortilla processing, and cake & snack lines. Customization ensures sanitary, efficient solutions tailored to your production needs, with expert designers collaborating on site-specific requirements.
2. How do food machinery manufacturers ensure compliance with sanitation and safety standards in the USA and Europe?
Manufacturers prioritize sanitary designs using durable, versatile materials that meet FDA, USDA, and EU regulations (e.g., EHEDG guidelines). Equipment like Peerless’s mixers features easy-clean surfaces and virtually maintenance-free operations to prevent contamination. B2B buyers should verify certifications, such as HACCP compliance, and inquire about built-in safety features like guards and automated shutoffs. Regular audits and preventive maintenance programs, as offered by Peerless, help maintain standards.
3. What service and support options are available for ongoing maintenance and parts?
Leading manufacturers provide global support with local reach, including 24/7 service, preventative maintenance programs, and on-site technicians. For example, Peerless offers superior service for equipment like mixers and depositors, with parts readily available to minimize downtime. B2B buyers benefit from contracts that include training, troubleshooting, and emergency repairs, ensuring production continuity in high-volume operations.
4. How customizable is the equipment, and what is the process for integrating it into existing production lines?
Equipment is highly customizable, with options for frame types, capacities, and integrations tailored to your workflow. Manufacturers like Peerless work directly with your team to design solutions, such as adapting mixers for specific dough or batter consistencies. The process involves consultation, prototyping, and testing; timelines vary by complexity, but expect 4-12 weeks for delivery and installation, including on-site setup and operator training.
5. What are the typical costs, ROI, and financing options for industrial food machinery?
Costs range from $10,000 for basic mixers to over $500,000 for integrated lines, depending on scale and features. ROI is driven by efficiency gains, reduced waste, and increased output—Peerless’s equipment often pays for itself within 1-3 years through lower maintenance and higher yield. Financing options include leasing, loans, or vendor credit; buyers should negotiate based on volume discounts and explore tax incentives in the USA (e.g., via USDA grants) or Europe (e.g., EU funding for sustainable equipment).
6. How do manufacturers handle delivery, installation, and training for international buyers in the USA and Europe?
Delivery is managed via global logistics partners, with lead times of 4-8 weeks post-order. Installation includes on-site assembly, testing, and calibration to ensure seamless integration. Training covers operation, safety, and maintenance, often provided in-person or virtually. For Europe, compliance with CE marking and customs regulations is standard; in the USA, FDA approvals are emphasized. Manufacturers like Lyco MFG offer turnkey solutions to minimize disruption.
7. What warranties and guarantees are provided, and how are they enforced?
Standard warranties cover 1-5 years on parts and labor, with options for extended coverage. Peerless guarantees performance for applications like biscuit cream delivery, focusing on durability and innovation. Enforcement involves on-site inspections and replacements for defects; disputes are resolved through manufacturer support teams or arbitration. B2B buyers should review terms for exclusions (e.g., misuse) and align with insurance policies.
8. How do food machinery manufacturers address energy efficiency and sustainability concerns?
Modern equipment incorporates energy-efficient motors, recyclable materials, and automated controls to reduce consumption by 20-30%. Peerless’s designs emphasize sanitary, innovative features that minimize water and energy use in operations like mixing and depositing. Sustainability reports and certifications (e.g., ISO 14001) are available; buyers can inquire about eco-friendly upgrades, which may qualify for incentives in Europe (e.g., green tech subsidies) or USA programs like EPA rebates, supporting long-term cost savings and environmental goals.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for food machinery manufacturers
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Food Machinery Manufacturers
In the competitive landscape of food machinery manufacturing, strategic sourcing from reputable suppliers like Peerless Food Equipment underscores the pivotal role of durable, versatile, and sanitary innovations in driving operational excellence. By prioritizing equipment that ensures virtually maintenance-free operations and high performance, manufacturers can achieve seamless production across applications such as dough mixing, sandwiching, and cream processing.
Key values derived from such partnerships include:
- Durability and Innovation: Equipment designed for unstoppable production, reducing downtime and enhancing efficiency.
- Sanitary Excellence: Compliance with stringent standards, minimizing contamination risks in food processing.
- Comprehensive Support: Global service networks offering preventative maintenance and expert consultations, as evidenced by successful installations for brands like Oreo.
- Versatility: Adaptable solutions for diverse sectors, from bakeries to snack production, fostering scalability.
Looking ahead, as demand for sustainable and efficient food machinery rises in the USA and Europe, manufacturers should focus on integrating advanced technologies and supplier collaborations to navigate evolving regulations and consumer trends. Embracing these strategies will position businesses for long-term growth, ensuring they remain at the forefront of the industry.
(Word count: 200)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.