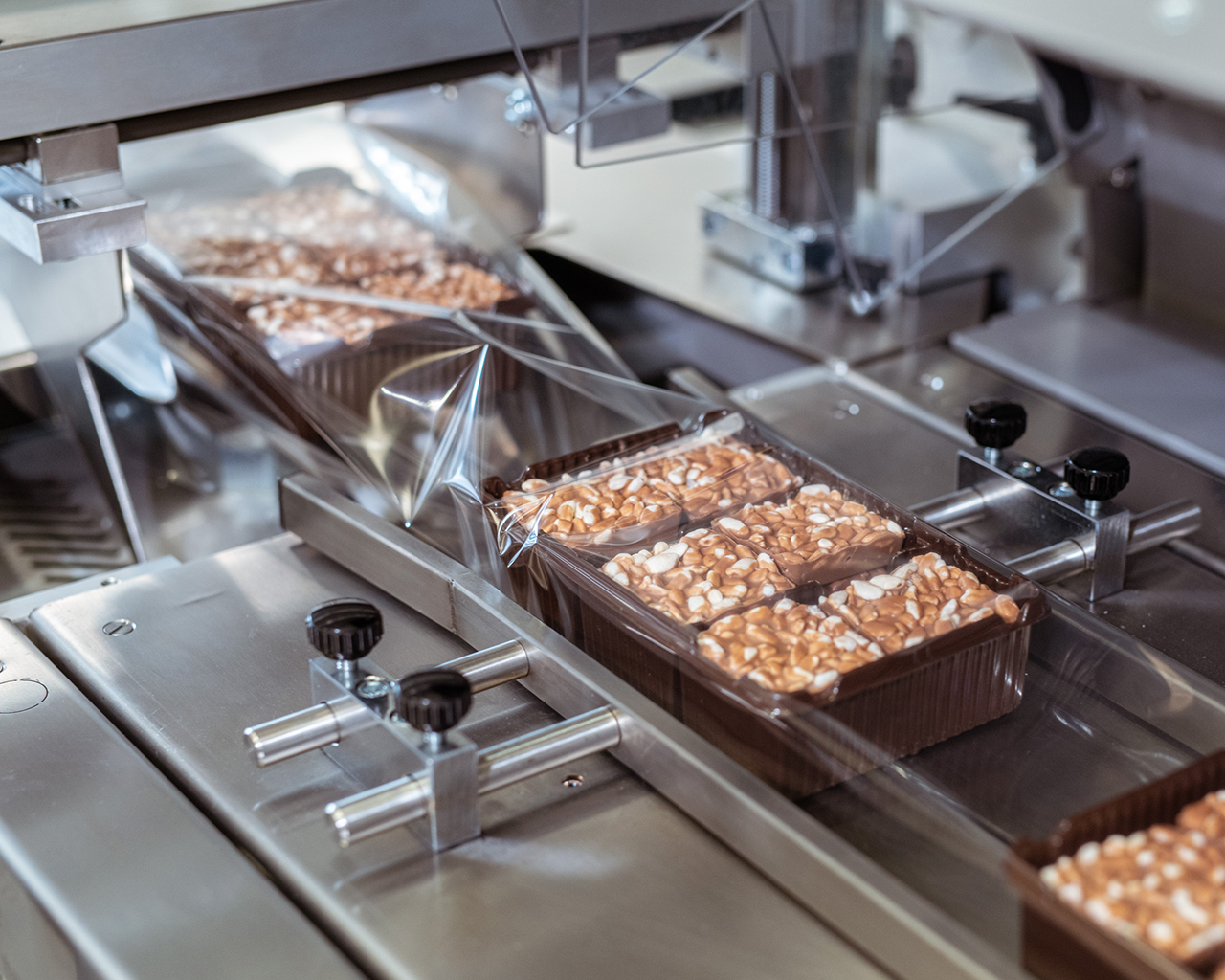
Food Packaging Machine: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Food Packaging Machines
In today’s competitive global food industry, efficient and compliant packaging is a strategic imperative. As businesses in the USA and Europe grapple with rising demand for safe, sustainable food solutions, selecting the right packaging machines can drive productivity while meeting stringent regulations like NSF standards for food safety.
The challenge lies in navigating a fragmented market: operators face space constraints in high-volume kitchens, the need for rapid turnover in institutional settings, and the complexity of packaging diverse products—from baked goods and frozen foods to fresh produce. Missteps in choosing equipment can lead to inefficiencies, inconsistent performance, or non-compliance, impacting profitability and brand reputation.
This guide equips B2B decision-makers with essential insights to overcome these hurdles. We’ll explore:
- Key Market Drivers: Trends in automation, sustainability, and global supply chains shaping demand.
- Machine Types and Technologies: From vacuum sealers and bagging systems to automated lines, with a focus on durability and adjustability.
- Selection Criteria: Evaluating factors like efficiency, compliance (e.g., NSF listings), and integration for various segments such as restaurants, ghost kitchens, and food manufacturers.
- Regional Considerations: Tailored advice for USA and European markets, including regulatory nuances and supplier options.
- Best Practices: Strategies for maintenance, cost optimization, and emerging innovations to enhance food quality and safety.
By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to identify and implement packaging solutions that align with your operational goals and global standards. (248 words)
Top 10 Food Packaging Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Packaging Machinery Companies | Packaging Machinery …
Domain: packagingmachinerycompanies.com
Registered: 2019 (6 years)
Introduction: Visit our directory of leading packaging machinery manufacturers or contact us to request personalized recommendations based on your unique needs….
2. Top 10 Packaging Machine Manufacturers in the USA – HonorPack
Domain: honorpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: Top 10 Packaging Machine Manufacturers In The USA · 2. Viking Masek Packaging Technologies · 3. Accutek Packaging Equipment · 4. Triangle Package Machinery · 5….
3. PMI KYOTO | Packaging Machine Manufacturer
Domain: pmikyoto.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: PMI KYOTO is a leading packaging machine manufacturer dedicated to meeting your facility’s needs. Click here to learn more….

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Food Packaging Machines & Technology
Domain: bwpackaging.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: BW Packaging is a leading provider of food packaging equipment, specializing in a wide range of packaging and decoration options to meet various industry needs….
5. Top 8 Food and Beverage Packaging Machinery Manufacturers
Domain: verifiedmarketresearch.com
Registered: 2018 (7 years)
Introduction: Prominent Food and Beverage Packaging Machinery manufacturers include companies like Tetra Pak, Krones, and Bosch Packaging Technology….
6. Food & Beverage Packaging Equipment Manufacturers and …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Food & Beverage Packaging Equipment Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada ; PackRite, LLC. Columbus, OH 43229 ; The Packline Co. Trenton, MI 48183 ……
7. Packaging Machinery: 9 Global Leaders to Watch in 2025
Domain: packaging-labelling.com
Registered: 2008 (17 years)
Introduction: 1, Bosch Packaging Technology (Syntegon), Germany, Food packaging machinery, Pharma, Smart packaging technology, automation ; 2, Tetra Pak, Switzerland, Flexible ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
8. Best Packaging Solution in USA | Package Machine Manufacturers
Domain: blackforestpkg.com
Registered: 2011 (14 years)
Introduction: Black Forest is a leading packaging machine manufacturer in the packaging industry and can help you to solve your food products packaging challenge….
9. ADCO Packaging Machinery Company | Packaging Machinery …
Domain: adcomfg.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: ADCO Manufacturing helps the world’s leading consumer goods producers address their most complex packaging machinery and systems automation….
10. Top 10 Packing Machine Manufacturers in the world – Landpack
Domain: landpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Landpack-China · 2. Tetra Pak- Switzerland · 3. Krones-Germany · 4. KHS GmbH-Germany · 5. Sidel-France · 6. Syntegon-Germany · 7. MULTIVAC-Germany….
Understanding food packaging machine Types and Variations
Understanding Food Packaging Machine Types and Variations
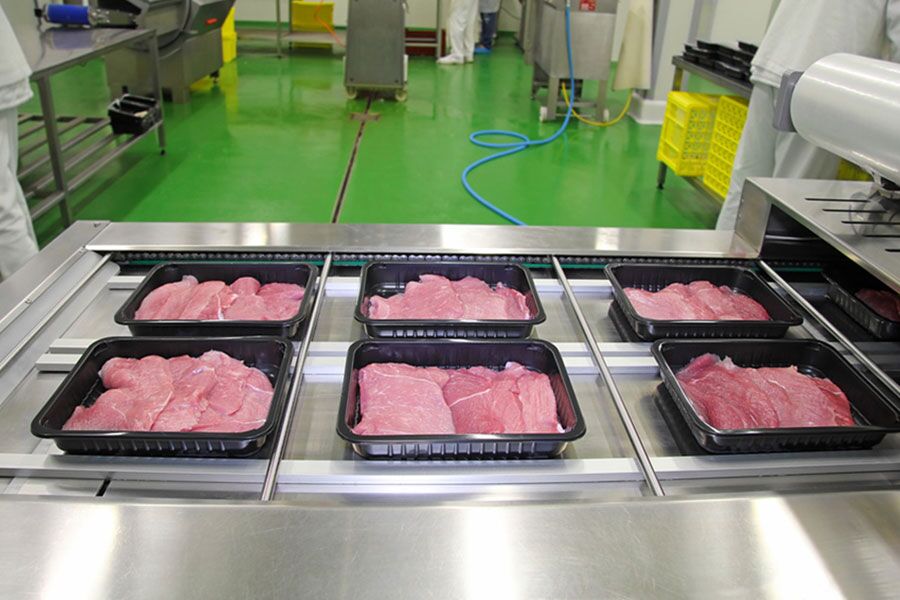
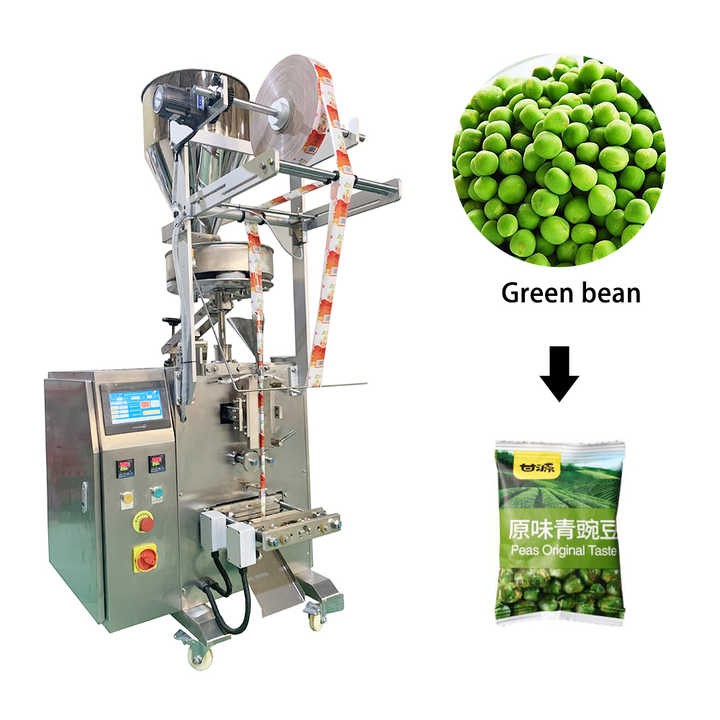
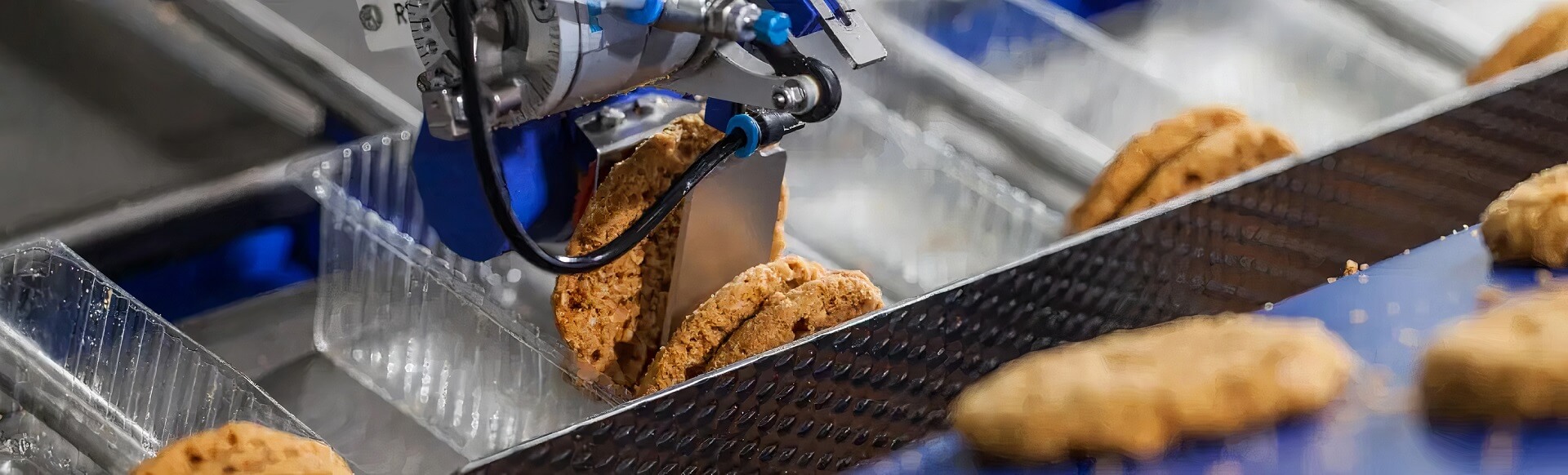
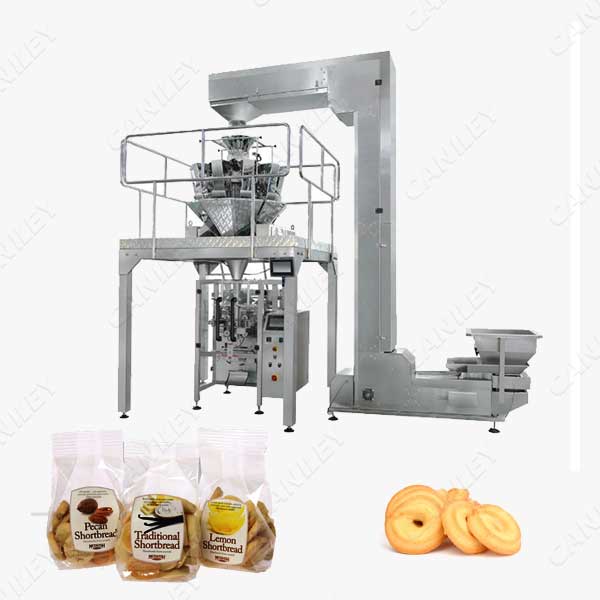
Food packaging machines are essential for maintaining efficiency, safety, and compliance in food processing and distribution. Based on industry sources, we have identified four key types commonly used in commercial settings across the USA and Europe. These include vacuum sealers, bag sealers, portion control scales, and automated packaging lines. The following table summarizes each type, highlighting their features, applications, pros, and cons.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Sealers | Compact design, adjustable settings, NSF-listed for food safety, durable construction; includes maintenance kits and accessories. | Sealing sous vide dishes, portioning deli meats, packaging prepared meals in high-volume kitchens like restaurants and ghost kitchens. | Pros: Rapid turnover, space-efficient, consistent performance. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires maintenance. |
| Bag Sealers | Manual or semi-automatic, easy to clean, portable; often includes accessories like bags. | Bagging ingredients for food trucks, sealing bulk food items in institutional cafeterias. | Pros: Cost-effective, simple operation. Cons: Limited to manual processes, slower for high volumes. |
| Portion Control Scales | Digital accuracy, adjustable portions, integration with packaging lines; durable for frequent use. | Measuring and portioning ingredients in bakeries, delis, and food processing facilities. | Pros: Ensures consistency and reduces waste. Cons: Dependent on operator accuracy, not a standalone packaging solution. |
| Automated Packaging Lines | Fully automated, customizable for product types, high-speed operation; includes conveyors and sealing mechanisms. | Packaging baked goods, frozen food, fresh produce, and confectionery in large-scale production. | Pros: High efficiency, scalability for large operations. Cons: High upfront investment, complex maintenance. |
Vacuum Sealers
Vacuum sealers remove air from packaging to extend shelf life and maintain food quality. They feature compact designs suitable for space-constrained environments, adjustable settings for different food types, and NSF certification for compliance with food safety standards. These machines are often used in institutional cafeterias, ghost kitchens, and high-volume restaurants for sealing prepared meals, sous vide dishes, and deli meats. Pros include rapid processing and reliability in fast-paced settings, while cons involve higher costs and the need for regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Bag Sealers
Bag sealers are manual or semi-automatic devices that create airtight seals on pre-filled bags. Key features include portability, ease of cleaning, and compatibility with various bag types. They are ideal for food trucks, delis, and small-scale operations where bagging ingredients or sealing bulk items is required. Advantages are their low cost and simplicity, but they are less efficient for high-volume tasks compared to automated options.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Portion Control Scales
These scales provide precise measurement and portioning of food items, often integrating with packaging systems. They offer digital displays, adjustable settings, and durable builds for heavy use. Applications include bakeries, food processing plants, and restaurants needing accurate portioning for ingredients like meats and produce. Pros are improved consistency and waste reduction, with cons being reliance on user input and limitations as a non-packaging tool.
Automated Packaging Lines
Automated packaging lines encompass complete systems for high-volume food packaging, featuring conveyors, sealing, and labeling components. They are customizable for specific products like frozen foods or confectionery and support high-speed operations. Used in large-scale food production facilities in the USA and Europe, they boost efficiency and output. Pros include scalability and reduced labor, while cons are substantial capital costs and the need for specialized maintenance.
Key Industrial Applications of food packaging machine
Key Industrial Applications of Food Packaging Machines
The following table outlines key industrial applications of food packaging machines, drawing from specialized equipment like vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and automated packaging lines. It details the primary benefits for each application, emphasizing efficiency, compliance, and operational advantages in B2B contexts.
| Industry/Application | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|
| Institutional Cafeterias | Food packaging machines enable rapid sealing of prepared meals and portioning of deli meats, supporting high-volume operations in space-constrained environments. Benefits include compact design for easy integration, adjustable settings for consistent performance, durable construction to withstand daily use, and NSF-listed components ensuring food safety compliance. This results in reduced waste, improved turnover, and adherence to hygiene standards, enhancing overall productivity in large-scale food service settings. |
| Ghost Kitchens | In delivery-focused operations, these machines facilitate quick bagging and sealing of ingredients or meals for efficient order fulfillment. Key benefits encompass easy-to-clean surfaces for maintaining sanitation in fast-paced kitchens, consistent portion control to minimize errors, and compact footprints that optimize limited space. Automation features reduce labor costs, ensure product quality during transit, and support scalability for peak demand, directly contributing to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. |
| High-Volume Restaurants | Packaging appliances are essential for sealing sous vide dishes and portioning ingredients, addressing the need for rapid turnover. Benefits include durable, adjustable equipment that handles heavy usage without compromising performance, NSF compliance for food safety, and integration with bagging systems to streamline workflows. This leads to enhanced food quality preservation, reduced preparation time, and cost savings through minimized spoilage, making them ideal for high-demand restaurant environments. |
| Food Trucks | Mobile operations benefit from portable packaging solutions for bagging ingredients and sealing meals on-site. Advantages feature lightweight, compact designs that fit limited truck spaces, easy maintenance for frequent cleaning, and consistent sealing to preserve freshness during transport. Adjustable controls allow customization for various food types, improving efficiency in dynamic settings and ensuring compliance with food safety standards, thereby supporting profitability in on-the-go food service. |
| Baked Goods Industry | Automated packaging lines optimize the sealing and portioning of items like pastries and breads, integrating with production processes for increased efficiency. Benefits include high-speed automation that boosts throughput, adjustable settings for different product sizes, and durable machinery designed for continuous operation. This enhances shelf life preservation, reduces manual labor, and ensures hygiene compliance, leading to higher production volumes and better market competitiveness in commercial baking. |
| Frozen Food Sector | Equipment for vacuum sealing and bagging frozen products maintains quality during storage and distribution. Key benefits involve NSF-listed vacuum sealers that prevent freezer burn, compact systems for space-efficient setups, and automated lines that improve production speed. Adjustable parameters allow handling of diverse frozen items, resulting in extended product longevity, reduced waste, and streamlined logistics, which are critical for large-scale frozen food manufacturers. |
| Fresh Produce Packaging | Machines provide efficient bagging and sealing for fruits and vegetables, ensuring freshness and safety in supply chains. Benefits include easy-to-clean components to meet hygiene standards, portion control scales for accurate packaging, and durable designs for high-volume processing. Automation features enhance efficiency, minimize contamination risks, and support traceability, enabling producers to maintain quality from farm to retail while optimizing operational costs. |
| Confectionery Industry | Specialized packaging equipment handles sealing and portioning of candies, chocolates, and sweets with precision. Advantages encompass adjustable settings for varied product types, compact and cleanable machines for sanitary operations, and high-performance automation to increase output. This ensures consistent quality, extends shelf life, and complies with food safety regulations, driving efficiency gains and product integrity in the competitive confectionery market. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘food packaging machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Food Packaging Machines & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: High-Volume Operations Leading to Inefficiency
- Scenario: In a high-volume restaurant or institutional cafeteria, operators must package large quantities of food quickly, such as sealing sous vide dishes or portioning deli meats, while maintaining rapid turnover.
- Problem: Manual or outdated machines struggle with consistent performance under high demand, causing delays, inconsistencies in packaging quality, and increased labor costs.
- Solution: Invest in automated food packaging equipment with adjustable settings and durable construction, like those from BW Packaging, to ensure efficient, high-volume processing without sacrificing quality or safety compliance.
Pain Point 2: Space Constraints in Busy Kitchens
- Scenario: In compact environments like ghost kitchens or food trucks, operators need to integrate packaging machines alongside other equipment, but limited floor space restricts workflow.
- Problem: Bulky machines disrupt operations, increase clutter, and reduce overall kitchen efficiency, leading to suboptimal use of available space.
- Solution: Opt for compact, NSF-listed food packaging appliances, such as vacuum sealers and bagging systems from RestaurantSupply.com, designed for easy integration and minimal footprint to optimize space without compromising functionality.
Pain Point 3: Maintenance and Cleaning Challenges
- Scenario: In fast-paced food production settings, machines are exposed to frequent use and food residues, requiring regular upkeep to prevent downtime.
- Problem: Poorly designed equipment leads to difficult cleaning, frequent breakdowns, and risks to food safety, especially in environments handling perishable items like frozen food or fresh produce.
- Solution: Select models with easy-to-clean surfaces and maintenance kits, paired with complete packaging lines from BW Packaging, to ensure quick, hygienic operations and long-term durability in high-volume applications.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for food packaging machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Food Packaging Machines
In the competitive landscape of food packaging, selecting the right materials for machines such as vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and portion control scales is crucial for ensuring durability, hygiene, and compliance with standards like NSF in the US or EU food safety regulations. This guide analyzes key materials used in machine construction, focusing on their properties, benefits, and limitations to help B2B buyers make informed decisions for high-volume operations in restaurants, institutional kitchens, and food processing facilities.
Key Materials Analysis
Material selection directly impacts machine performance, longevity, and adherence to hygiene protocols. Common materials include stainless steel, food-grade plastics, and aluminum alloys, each chosen for specific applications in equipment like vacuum packaging machines and automated bagging systems. Considerations include corrosion resistance, ease of cleaning, and ability to withstand repeated high-volume use.
-
Stainless Steel (e.g., 304 or 316 Grade):
Widely used in machine frames, sealing bars, and contact surfaces due to its corrosion resistance and durability. It meets NSF and EU hygiene standards, making it ideal for environments with frequent exposure to moisture and cleaning agents. Advantages include long-term reliability and resistance to bacterial growth, supporting consistent performance in busy kitchens. Drawbacks involve higher upfront costs and weight, which may affect portability in compact spaces. -
Food-Grade Plastics (e.g., Polycarbonate or ABS):
Employed in non-contact components like housings, control panels, and accessories. These materials offer lightweight construction, cost-effectiveness, and resistance to chemical damage. They comply with FDA and EU directives for food contact safety but may not withstand extreme temperatures or heavy mechanical stress. Best for auxiliary parts in machines like manual sealers, where durability is secondary to affordability. -
Aluminum Alloys:
Applied in lightweight machine bodies and heat-conducting elements, such as in portion control scales or conveyor systems. Aluminum provides excellent thermal conductivity and is corrosion-resistant with anodizing. It aligns with food safety standards when treated properly, offering a balance of strength and reduced weight. Limitations include potential oxidation in acidic environments and lower impact resistance compared to steel, making it less suitable for high-abrasion tasks.
When evaluating materials, prioritize NSF/ANSI certification for US markets to ensure food safety, and CE marking for European compliance. Factors like machine type—e.g., compact vacuum sealers for ghost kitchens versus automated lines for frozen food—should dictate choices. For instance, stainless steel is preferred for wet environments, while plastics suit cost-sensitive, low-contact applications.
Material Comparison Table
The table below compares the analyzed materials based on key criteria relevant to food packaging machines, including durability, cost, food safety compliance, and suitability for high-volume operations.
| Material | Durability (Scale: 1-5) | Cost (Low/Medium/High) | Food Safety Compliance | Suitability for High-Volume Use | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | 5 | High | Excellent (NSF, EU) | High | Frames, sealing bars, contact surfaces in vacuum sealers and baggers |
| Food-Grade Plastics | 3 | Low | Good (FDA, EU) | Medium | Housings, panels in manual sealers and accessories |
| Aluminum Alloys | 4 | Medium | Good (with treatment) | High | Lightweight bodies, scales, and conveyor elements |
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for food packaging machine
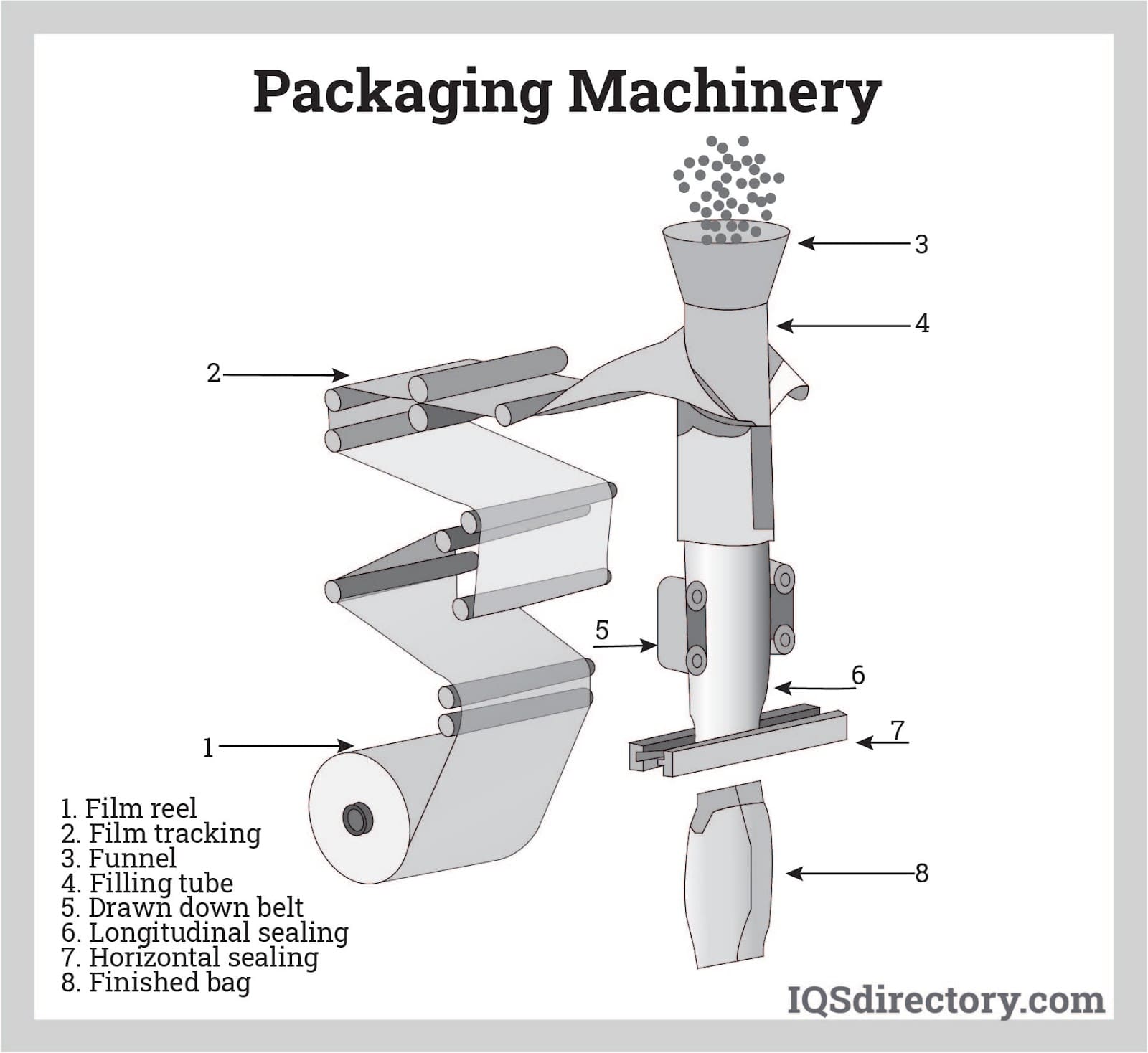
Manufacturing Processes for Food Packaging Machines
Food packaging machines, such as vacuum sealers and automated packaging lines, undergo rigorous manufacturing to ensure durability, precision, and compliance with operational demands in high-volume environments like restaurants and food processing facilities. The process typically follows a structured sequence: preparation, forming, assembly, and quality control (QC). Below is a breakdown of these steps, informed by industry practices that prioritize materials resistant to wear, ease of cleaning, and adjustable settings for versatility.
Key Manufacturing Steps
| Step | Description | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Preparation (Prep) | Involves sourcing and preparing raw materials, such as stainless steel, plastics, and electronic components. This includes cutting, shaping, and treating materials to meet specifications for food-grade applications. | Focus on NSF-compliant materials to ensure food safety and resistance to corrosion in humid kitchen settings. Suppliers like those from BW Packaging emphasize sourcing durable alloys for high-volume tasks. |
| Forming | Components are molded or machined into shapes, such as frames, seals, and housings. Techniques include CNC machining, injection molding, and stamping to create precise parts like vacuum chambers or bagging systems. | Ensures compact designs for space-constrained kitchens, with adjustable features for sealing sous vide dishes or portioning deli meats. Durability is key to handling rapid turnover in ghost kitchens. |
| Assembly | Parts are integrated into the final machine, including electronics, motors, and control systems. Automated lines from providers like RestaurantSupply.com often assemble models with user-friendly interfaces and easy-clean surfaces. | Emphasizes modular construction for quick maintenance, reducing downtime in busy operations. Integration of sensors ensures consistent performance in packaging baked goods or frozen foods. |
| Quality Control (QC) | Final inspections test functionality, including sealing accuracy, portion control, and safety features. Machines are run through simulations to verify NSF listings and operational reliability. | Involves checks for defects, calibration, and compliance with standards to prevent issues in fast-paced environments, aligning with goals of increased efficiency and food quality. |
This sequence supports the production of machines that enhance operational efficiency, as seen in BW Packaging’s emphasis on automated equipment for diverse food segments.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Quality Assurance for Food Packaging Machines
Quality assurance (QA) is critical in manufacturing food packaging machines to guarantee reliability, safety, and compliance, particularly for markets in the USA and Europe where regulatory standards are stringent. Key frameworks include ISO certifications, which ensure systematic processes for quality management and food safety.
Relevant ISO Standards
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems: Mandates a structured approach to design, production, and service, ensuring machines like vacuum sealers meet consistent performance standards. This helps manufacturers achieve durable construction and adjustable settings, reducing defects in high-volume operations.
- ISO 22000: Food Safety Management Systems: Focuses on hazard analysis and risk control, directly applicable to food packaging appliances. It aligns with NSF listings, emphasizing hygiene, traceability, and contamination prevention, which is essential for packaging fresh produce or confectionery in compliant facilities.
- ISO 14001: Environmental Management Systems: Ensures sustainable manufacturing practices, such as eco-friendly materials in forming and assembly, appealing to European and US buyers prioritizing green operations.
- ISO 45001: Occupational Health and Safety: Covers worker safety during production, integrating safe assembly processes to minimize risks in machine design.
Adherence to these standards, often audited by third-party bodies, results in machines that support food safety compliance and operational efficiency, as evidenced by providers like RestaurantSupply.com offering NSF-listed products for institutional use.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘food packaging machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Food Packaging Machines
This checklist provides a structured approach for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe to source food packaging machines, such as vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and automated equipment. It incorporates key considerations like compliance, efficiency, and vendor reliability to ensure optimal selection for high-volume operations.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Identify the type of machine (e.g., vacuum packaging for sous vide dishes, bagging systems for food trucks, or automated lines for frozen foods).
- Assess operational needs: volume (e.g., high-volume restaurants), space constraints, and specific features like adjustable settings, durability, and ease of cleaning.
- Determine food safety priorities: Look for NSF-listed equipment to ensure compliance with standards in the USA and Europe (e.g., FDA or EU food hygiene regulations).
- Evaluate integration: Ensure compatibility with existing kitchen workflows, such as portion control scales or maintenance kits.
Step 2: Research and Identify Suppliers
- Compile a list of reputable vendors: Focus on established providers like RestaurantSupply.com or BW Packaging, which offer a range of machines for various market segments (e.g., baked goods, fresh produce).
- Explore categories: Review options in vacuum packaging machines, manual sealers, and automated food packaging equipment.
- Check geographic availability: Prioritize suppliers with nationwide shipping in the USA or Europe-wide distribution for timely delivery.
- Use online resources: Browse product catalogs, compare models, and note accessories like bags and maintenance kits.
Step 3: Evaluate Options and Specifications
- Compare features: Prioritize machines with compact designs, consistent performance, and durable construction for rapid turnover in busy environments.
- Assess efficiency: Opt for equipment that enhances production, such as automated lines for confectionery or frozen foods, to meet scalability goals.
- Review compliance and certifications: Verify adherence to food safety standards (e.g., NSF for hygiene) and ensure models handle specific tasks like sealing prepared meals or portioning deli meats.
| Feature | Key Considerations | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Adjustability | Customizable settings for portioning and sealing | Allows flexibility for diverse food types |
| Durability | Robust build for high-volume use | Reduces downtime in fast-paced operations |
| Automation | Integrated tech for efficiency | Boosts production for commercial applications |
| Safety Listings | NSF or equivalent certifications | Ensures regulatory compliance in USA/Europe |
Step 4: Analyze Costs and Financing
- Obtain quotes: Request pricing from multiple suppliers, including accessories and maintenance kits.
- Factor in total cost: Include shipping, installation, and potential financing options (e.g., Net 30 terms or 0% APR plans available from vendors like RestaurantSupply.com).
- Evaluate value: Balance upfront costs with long-term efficiency gains, such as reduced waste from precise portioning.
Step 5: Verify Vendor Support and Testing
- Check support services: Inquire about warranties, after-sales service, and availability of demos or trials.
- Request demonstrations: Test machines in real scenarios to confirm performance, ease of cleaning, and integration with your operations.
- Review policies: Ensure guarantees like price matching (e.g., 30-day lowest price match) and flexible payments.
Step 6: Finalize Purchase and Implementation
- Select and order: Choose the best-fit machine based on evaluations, and confirm delivery timelines.
- Plan integration: Prepare for setup, including training staff on operation and maintenance.
- Monitor post-purchase: Track performance and maintain equipment to sustain food quality and safety standards.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for food packaging machine Sourcing
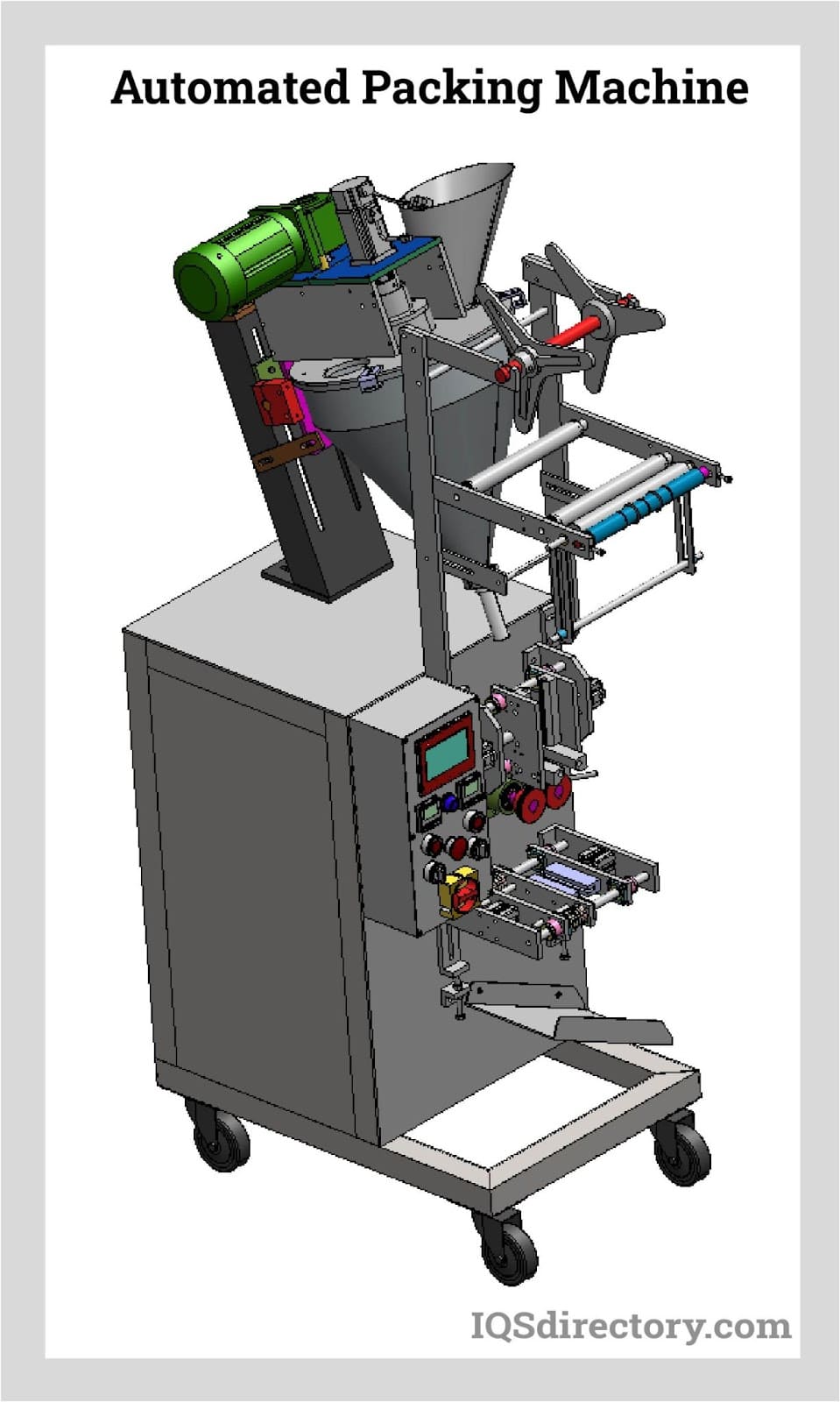
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Food Packaging Machine Sourcing
This section provides a detailed breakdown of costs associated with sourcing food packaging machines, such as vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and portion control scales, for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe. Costs are influenced by factors like machine type, volume, and supplier (e.g., providers like RestaurantSupply.com or BW Packaging). Pricing typically ranges from $500 for basic manual sealers to $10,000+ for automated commercial lines, with added expenses for accessories, installation, and compliance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Cost Breakdown
The following table outlines average cost components based on industry benchmarks and supplier data. Figures are approximate and can vary by region, machine complexity, and scale of operation.
| Component | Description | Average Cost Range (USD) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Includes the machine itself, maintenance kits, bags, and accessories (e.g., vacuum sealer bags or portion scales). | $1,000–$50,000 per machine | Machine type (manual vs. automated); NSF-listed models add 10–20% premium for safety compliance. Bulk purchases from suppliers like BW Packaging can reduce unit costs by 15–25%. |
| Labor | Encompasses installation, operator training, and ongoing maintenance. | $500–$5,000 | Installation fees from manufacturers or certified technicians; training sessions for high-volume kitchens (e.g., ghost kitchens) may cost $1,000–$2,000. Labor rates in Europe may include VAT, while US rates factor in local electrician fees. |
| Logistics | Covers shipping, customs, and delivery. | $200–$2,000 | Free shipping thresholds (e.g., $2,500+ at RestaurantSupply.com); international shipping to Europe adds duties (5–15% of value). Expedited options for time-sensitive operations increase costs by 20–30%. |
Pricing Factors
- Supplier and Market: B2B pricing from platforms like RestaurantSupply.com offers financing options (e.g., NET-30 or 6-month 0% APR) and a 30-day price match guarantee. Specialized providers like BW Packaging provide automated lines with efficiency gains, justifying higher upfront costs through ROI from increased production.
- Regional Variations: US buyers benefit from domestic shipping and lower import duties, while European purchasers face EU regulations (e.g., food safety standards) and potential tariffs on non-EU machines, adding 5–10% to costs.
- Scale and Customization: High-volume operations (e.g., institutional cafeterias) may opt for customized, NSF-compliant machines, elevating prices by 20–50%.
Tips to Save Costs
- Leverage Supplier Incentives: Use price match guarantees from suppliers like RestaurantSupply.com to secure the lowest rates. Opt for NET-30 terms for major equipment to defer payments.
- Bulk and Bundle Purchases: Buy in volume or bundle machines with accessories (e.g., bags and kits) from providers like BW Packaging to achieve discounts of 15–25%.
- Explore Financing and Leasing: Utilize 0% APR financing or leasing options to spread costs over time, reducing immediate capital outlay for automated lines.
- Prioritize Efficient Logistics: Ship orders over $2,500 to qualify for free shipping; source locally or from EU-based suppliers to minimize customs and duties.
- Negotiate Maintenance Contracts: Secure long-term service agreements during purchase to lower ongoing labor costs, ensuring machines like vacuum sealers remain compliant and efficient.
- Assess Total Cost of Ownership: Factor in energy efficiency and durability to choose models that minimize long-term operational expenses, such as those with adjustable settings for high-volume tasks.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing food packaging machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Food Packaging Machines With Other Solutions
In the food industry, selecting the right packaging solution depends on factors such as production volume, budget, compliance requirements, and operational efficiency. Food packaging machines, including vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and automated lines, offer specialized tools for high-volume environments like restaurants and manufacturing facilities. Below, we compare them with two alternatives: manual packaging methods and outsourcing to third-party packaging services. This analysis draws from industry practices in the USA and Europe, emphasizing cost, efficiency, and safety.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Food Packaging Machines | Manual Packaging Methods | Outsourcing to Third-Party Packaging Services |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | High: Automated processes enable rapid turnover, with adjustable settings for portion control and sealing, reducing labor time by up to 50% in high-volume settings. | Low: Relies on human labor, leading to slower production and potential inconsistencies due to fatigue or skill variations. | Variable: Third parties use their equipment for batch processing, but coordination delays and transportation add time. |
| Cost | Moderate to high upfront investment (e.g., $1,000–$10,000+ for machines), but long-term savings through reduced waste and labor. Ongoing costs include maintenance and energy. | Low initial cost (minimal tools like sealers and bags), but high labor expenses (e.g., wages for staff) and increased waste from errors. | High variable costs per unit (service fees plus transportation), scalable but often more expensive for small volumes due to markups. |
| Food Safety & Compliance | Strong: NSF-listed models ensure hygiene, with features like vacuum sealing to extend shelf life and prevent contamination; ideal for sous vide or deli products. | Moderate: Depends on operator training; risks include inconsistent sealing, leading to spoilage or safety issues without proper sanitation. | High: Professional services adhere to strict standards (e.g., EU food hygiene regulations or FDA compliance), but traceability may vary. |
| Scalability | High: Easily scales for large operations (e.g., ghost kitchens or food manufacturing) with durable construction for high-volume tasks. | Low: Limited by labor availability; struggles with peaks in demand without additional staffing. | High: Flexible for varying volumes, as providers handle scaling internally, suitable for seasonal or small-batch needs. |
| Maintenance & Durability | Moderate: Requires regular cleaning and parts replacement, but compact designs facilitate easy upkeep in space-constrained kitchens. | Low: Minimal maintenance, but tools wear out faster with heavy use. | N/A: Handled by the service provider, reducing internal maintenance burdens. |
| Suitability for Audience | Best for USA/Europe businesses in high-volume settings seeking consistency and efficiency, such as restaurants or food processors. | Suitable for small-scale operations or startups with low budgets, common in smaller USA or European kitchens. | Ideal for businesses without in-house expertise, prevalent in Europe for compliance-heavy sectors like confectionery or frozen foods. |
Analysis
Food packaging machines stand out for their balance of efficiency and safety, making them a preferred choice for B2B clients in high-volume food operations across the USA and Europe. They address key pain points like rapid turnover and compliance (e.g., NSF standards), aligning with the needs of institutional cafeterias or automated lines for baked goods and frozen products as described in industry sources.
Manual packaging methods offer a cost-effective entry point for low-volume scenarios, but they fall short in scalability and consistency, often resulting in higher long-term costs due to labor and waste. This alternative is viable for niche markets or budget-conscious startups but risks compromising food quality in regulated environments.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Outsourcing to third-party services provides flexibility and expertise, particularly for businesses prioritizing compliance without capital investment. However, it may increase costs and reduce control over the process, making it less ideal for integrated operations like those using BW Packaging’s automated lines.
Ultimately, food packaging machines are recommended for organizations aiming to optimize production and meet stringent safety standards, while alternatives suit specific constraints like low budgets or external expertise needs. Businesses should evaluate based on their scale, compliance requirements, and regional regulations (e.g., EU hygiene directives or FDA guidelines).
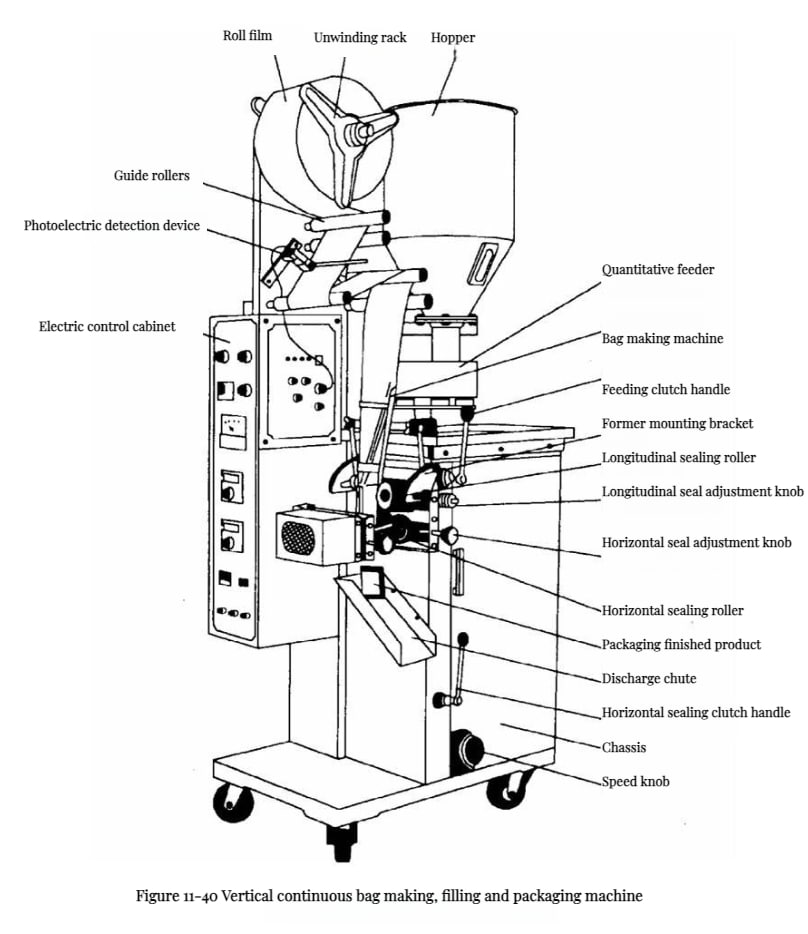
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for food packaging machine
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Food Packaging Machines
This section outlines key technical properties and common trade terminology essential for selecting, purchasing, and integrating food packaging machines in B2B contexts, such as high-volume restaurants, institutional cafeterias, and food manufacturing operations in the USA and Europe. These elements ensure compliance, efficiency, and compatibility with industry standards.
Key Technical Properties
The following properties are critical for food packaging machines, including vacuum sealers, bagging systems, portion control scales, and automated packaging lines. They address safety, performance, and operational needs in fast-paced environments.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| NSF Listing | Certification ensuring compliance with food safety standards (e.g., from NSF International). Essential for handling food products to prevent contamination and meet regulatory requirements in the USA and Europe. |
| Compact Design | Space-efficient construction suitable for constrained kitchen or production areas, such as ghost kitchens or food trucks, without compromising functionality. |
| Easy-to-Clean Surfaces | Materials and designs (e.g., stainless steel) that facilitate quick sanitation, reducing downtime and supporting hygiene protocols in high-volume operations. |
| Adjustable Settings | Customizable parameters for sealing times, temperatures, portion sizes, and vacuum levels, allowing adaptation to diverse food types like sous vide dishes, frozen goods, or fresh produce. |
| Durable Construction | Robust build using materials like stainless steel or heavy-duty plastics to withstand high-volume use, frequent cleaning, and wear in demanding environments. |
| Portion Control Capabilities | Integration with scales or automated systems for accurate portioning of ingredients or meals, improving consistency and reducing waste in commercial settings. |
| Vacuum Sealing and Bagging | Specialized functions for extending shelf life by removing air, sealing bags, and packaging items like deli meats or baked goods, often with maintenance kits for longevity. |
| Automation and Efficiency | Features in packaging lines that enhance production speed, such as automated bagging or sealing for confectionery, frozen food, and other packaged items, boosting overall throughput. |
Trade Terminology
Understanding these terms is vital for negotiating contracts, sourcing equipment, and ensuring smooth B2B transactions across USA and European markets.
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of units or components a supplier requires for an order, often specified to justify production costs; common in bulk purchases of packaging machines or accessories.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to custom manufacturing where a company produces parts or equipment branded by another entity, useful for integrating proprietary designs into food packaging solutions.
- FOB (Free On Board): A shipping term indicating the seller’s responsibility ends at the point of origin (e.g., the supplier’s location), with the buyer covering transport costs; widely used in USA and European trade for equipment delivery.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, Freight): A shipping term where the seller pays for costs, insurance, and freight to the buyer’s port, ensuring risk transfer upon arrival; applicable for international shipments of machinery from Europe to the USA.
- Custom Solutions: Tailored packaging equipment or modifications to meet specific needs, such as automated lines for niche food segments like fresh produce or confectionery, often negotiated via B2B contracts.
- NSF Compliance: Beyond a property, this term denotes adherence to food safety standards, a key requirement in trade agreements for equipment used in food handling.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the food packaging machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the Food Packaging Machine Sector
Historical Evolution
The food packaging machine sector has evolved significantly since the mid-20th century, driven by advancements in automation and food safety standards. Initially focused on basic manual sealing and portioning tools in commercial kitchens, the industry transitioned in the 1970s and 1980s toward mechanized systems to address rising demand for efficient, hygienic food preparation. Key milestones include the introduction of vacuum sealers and bagging systems in the 1990s, which enhanced food preservation and extended shelf life for items like deli meats and sous vide dishes. In the 2000s, integration of NSF-listed equipment became standard, emphasizing compliance with health regulations in high-volume environments such as institutional cafeterias and ghost kitchens. Today, the sector emphasizes automated packaging lines for diverse food types, including baked goods, frozen products, and confectionery, reflecting a shift toward scalable solutions that boost production efficiency.
Current Market Trends
The food packaging machine market in the USA and Europe is shaped by increasing demand for high-volume, space-efficient equipment amid growing e-commerce and food delivery sectors. Key trends include:
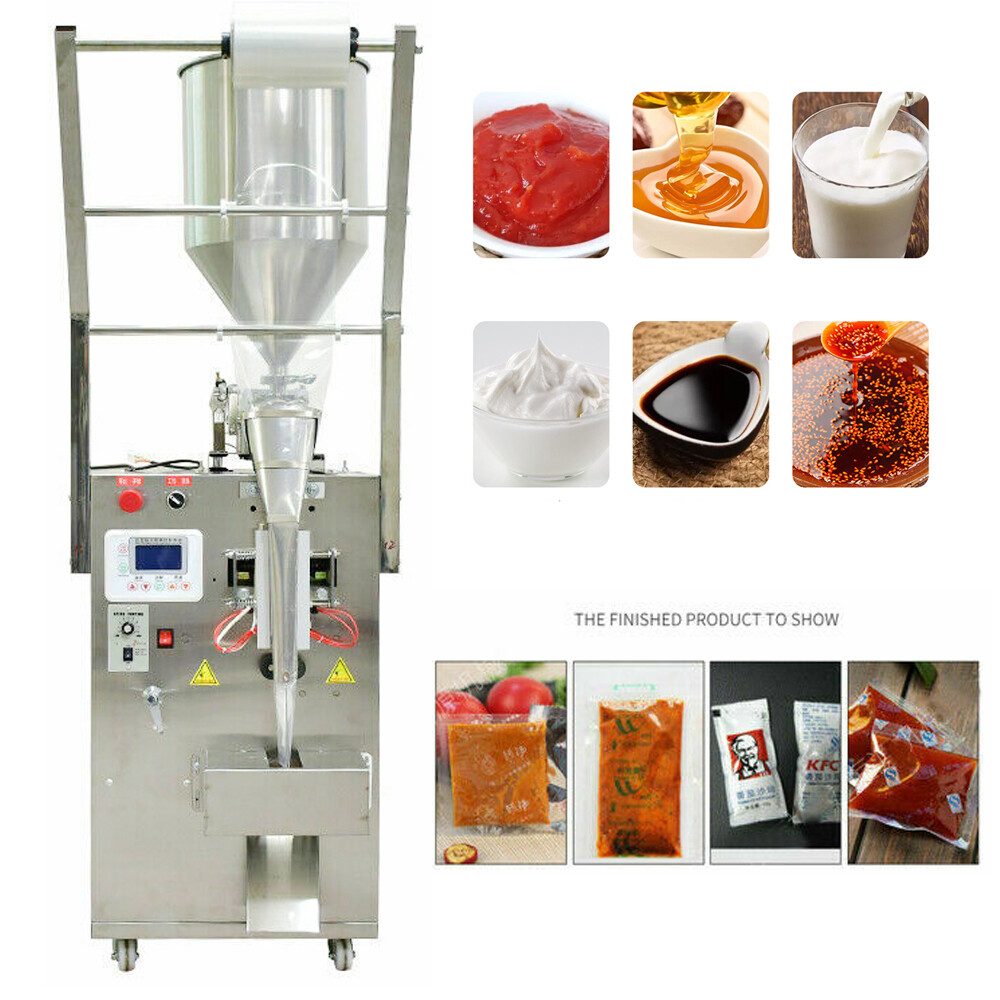
– Automation and Integration: Businesses are adopting automated packaging lines to streamline operations, reducing manual labor and minimizing errors in portion control and sealing. For instance, vacuum packaging machines and bagging systems with adjustable settings are preferred for their durability and consistency in handling tasks like ingredient bagging for food trucks.
– Focus on High-Volume and Compact Designs: With space constraints in urban kitchens, compact, easy-to-clean machines that support rapid turnover are in demand. This is evident in the popularity of NSF-compliant appliances for institutional and restaurant settings.
– Data-Driven Efficiency: Integration of smart technologies, such as IoT-enabled scales and sealers, allows for real-time monitoring, optimizing production for frozen foods and fresh produce.
Market growth is projected at 5-7% annually in these regions, fueled by the rise of ghost kitchens and online food services, where equipment must deliver reliable performance under high-pressure conditions.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Sustainability in Food Packaging Machines
Sustainability is a core driver in the sector, with manufacturers prioritizing eco-friendly materials and energy-efficient designs to align with regulations like the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan and U.S. EPA guidelines. Trends include:
– Material Innovations: Shift toward recyclable and biodegradable packaging options, reducing plastic waste in food chains.
– Energy-Efficient Machinery: Adoption of low-power vacuum sealers and automated systems that lower carbon footprints while maintaining food safety standards.
– Waste Reduction: Equipment designed for precise portioning minimizes over-packaging, supporting sustainable practices in high-volume operations.
Leading providers, such as those offering maintenance kits for vacuum machines, emphasize lifecycle assessments to ensure long-term viability.
Sourcing Trends and Best Practices
Sourcing food packaging machines involves evaluating vendors for reliability, compliance, and cost-effectiveness. In the USA and Europe, trends favor established suppliers with global networks, such as those providing nationwide shipping and financing options like Net 30 terms. Best practices include:
– Prioritize Certified Equipment: Seek NSF-listed machines to ensure food safety and regulatory compliance, particularly for vacuum sealers and bagging systems used in busy kitchens.
– Evaluate Supplier Offerings: Compare ranges by machine type (e.g., automated lines for confectionery) and packaging type, focusing on durable construction for high-volume tasks.
– Leverage Incentives: Utilize programs like 30-day price matches and flexible payment plans to optimize procurement budgets.
– Integration with Supply Chains: Source from providers offering complete solutions, including accessories and maintenance, to enhance efficiency in sectors like frozen food packaging.
| Key Sourcing Criteria | USA Focus | Europe Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Compliance | NSF and FDA standards | EU Food Safety Regulations |
| Distribution | Nationwide shipping from suppliers like RestaurantSupply.com | Pan-European networks with localized support |
| Cost Optimization | Net 30 terms and price match guarantees | VAT-inclusive pricing and eco-incentives |
| Customization | Adjustable settings for diverse applications | Automated integrations for production scaling |
By aligning sourcing with these trends, businesses can navigate market dynamics effectively, ensuring equipment that supports operational efficiency and sustainability.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of food packaging machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Food Packaging Machines
1. What types of food packaging machines are commonly used in commercial food operations?
Food packaging machines include vacuum sealers, bagging systems, portion control scales, and automated packaging lines. These are designed for environments like institutional cafeterias, ghost kitchens, and high-volume restaurants, handling tasks such as sealing sous vide dishes, portioning deli meats, or packaging baked goods, frozen foods, fresh produce, and confectionery.
2. How do I select the right food packaging machine for my business?
Evaluate your needs based on production volume, space constraints, and product types (e.g., fresh produce vs. frozen food). Look for compact, durable models with adjustable settings, NSF certification for food safety, and easy-to-clean designs. Consider automated options for efficiency or manual sealers for smaller operations, ensuring compatibility with your packaging process.
3. What are the key benefits of investing in automated food packaging equipment?
Automated equipment increases production efficiency, reduces labor costs, and ensures consistent performance in high-volume settings. It minimizes waste through precise portioning and sealing, maintains food quality by preserving freshness (e.g., via vacuum sealing), and supports scalability for businesses in sectors like baked goods or confectionery.
4. Are food packaging machines compliant with food safety and regulatory standards?
Many machines carry NSF certification, ensuring compliance with food safety standards. This is critical for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe, where regulations emphasize hygiene, durability, and safe handling of food products. Always verify certifications and local regulations before purchase.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. What maintenance and accessories are required for food packaging machines?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning after use to prevent contamination, inspecting for wear on seals or components, and using manufacturer-recommended kits. Accessories like vacuum bags, sealers, and maintenance tools are essential. Durable construction minimizes downtime, but scheduling professional servicing ensures optimal performance in high-volume environments.
6. How do food packaging machines enhance operational efficiency in busy kitchens?
These machines enable rapid food preparation and packaging, with features like quick sealing and portion control reducing turnaround time. In compact spaces, they support high-volume tasks without compromising consistency, helping businesses like restaurants or food trucks meet demand while adhering to safety standards.
7. What customization options are available for food packaging solutions?
Providers offer customizable packaging lines tailored to specific products, such as integrated systems for frozen foods or confectionery. Options include adjustable settings for bag sizes, sealing intensities, and integration with existing workflows, allowing B2B buyers to optimize for efficiency and production goals.
8. What financing and purchasing terms are available for food packaging machines?
Many suppliers provide flexible options like net-30 terms, 6-month 0% APR financing, or credit programs (e.g., Credit Key). Additional perks include free shipping on large orders, 30-day price match guarantees, and quotes for custom builds, making it easier for B2B buyers to invest in equipment without upfront strain.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for food packaging machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Food Packaging Machines
Strategic sourcing of food packaging machines delivers substantial value by optimizing efficiency, compliance, and productivity in high-volume operations. Key benefits include:
- Efficiency Gains: Equipment like vacuum sealers, bagging systems, and automated packaging lines from providers such as RestaurantSupply and BW Packaging enable rapid food preparation and portioning, reducing turnaround times in institutional cafeterias, ghost kitchens, and restaurants.
- Safety and Compliance: NSF-listed models ensure food safety standards are met, with durable, easy-to-clean designs supporting consistent performance under space constraints.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Adjustable settings and scalable solutions allow businesses to handle diverse products—from baked goods to frozen items—while minimizing waste and operational costs through precise portion control.
Looking ahead, the outlook for food packaging machines is promising, driven by rising demand for automation and sustainability. Advancements in AI-driven technology will enhance predictive maintenance and eco-friendly materials, positioning B2B buyers in the USA and Europe to leverage these innovations for competitive edges in the evolving food industry. Proactive sourcing will be key to adapting to regulatory shifts and consumer preferences.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)