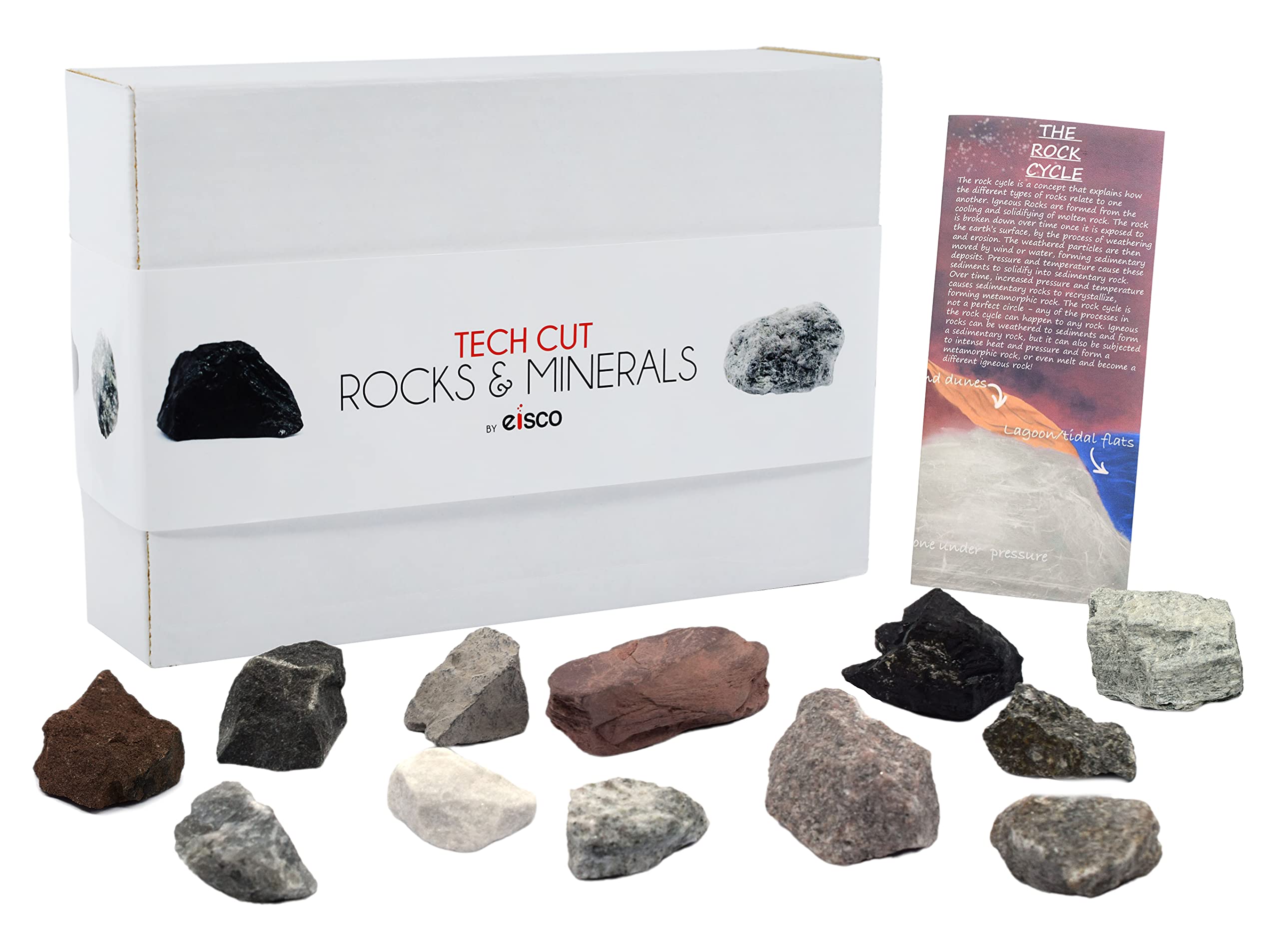
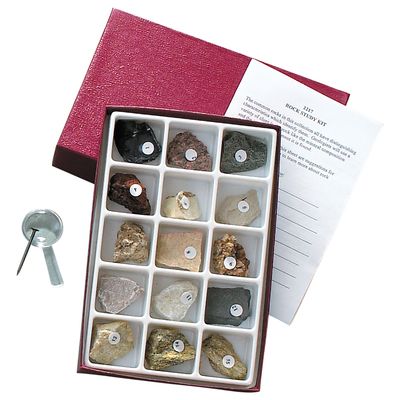
Geology Kit Rocks Guide: Type,Cost,Material…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for geology kit rocks
Navigating the global market for geology kit rocks presents a unique challenge for B2B buyers, particularly those operating in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Sourcing high-quality geology kits that meet educational and professional needs can be daunting, especially with varying standards and availability across different markets. This guide aims to demystify the complexities of purchasing geology kits by providing a comprehensive overview of the types available, their applications in educational and professional settings, and strategies for effective supplier vetting.
In this guide, you will discover insights into the different categories of geology kits, including mineral collections, rock samples, and specialized educational resources. Additionally, we will delve into factors influencing cost, ensuring that you can budget effectively while maximizing value. By equipping international buyers with the knowledge to assess suppliers and products critically, this guide empowers informed purchasing decisions. Whether you are a school in Nigeria looking to enhance your curriculum or a geological firm in Saudi Arabia needing reliable resources for fieldwork, understanding these dynamics is crucial for success in the global marketplace.
With actionable insights and expert guidance, you will be well-prepared to navigate the intricate landscape of geology kit sourcing, ensuring your organization benefits from high-quality educational tools and materials.
Understanding geology kit rocks Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Igneous Rocks Collection | Formed from cooled magma or lava; includes basalt, granite, and obsidian. | Geology education, construction materials, and geological surveys. | Pros: Durable, diverse applications. Cons: Limited aesthetic appeal. |
| Sedimentary Rocks Collection | Composed of particles from other rocks or organic materials; includes sandstone and limestone. | Oil and gas exploration, environmental studies, and sediment analysis. | Pros: Valuable for resource extraction. Cons: Can be less durable than igneous rocks. |
| Metamorphic Rocks Collection | Formed under heat and pressure; includes marble and schist. | Construction, sculpture, and geological research. | Pros: Unique textures and patterns. Cons: Often more expensive due to processing. |
| Mineral Specimens Collection | Individual minerals showcasing various properties; includes quartz and calcite. | Educational kits, geological studies, and mineral identification. | Pros: Great for hands-on learning. Cons: Requires knowledge for proper identification. |
| Rock Cycle Educational Kits | Comprehensive kits covering all rock types with interactive elements. | Educational institutions, training programs, and public outreach. | Pros: Engaging and informative. Cons: Higher initial investment for comprehensive kits. |
What Are Igneous Rocks and Their B2B Relevance?
Igneous rocks, formed from the cooling and solidification of magma or lava, are characterized by their crystalline texture and mineral composition. Common examples include basalt and granite. In B2B contexts, they are widely used in construction and engineering due to their durability and strength. When purchasing igneous rock collections, buyers should consider the geological context of their projects, as well as the specific applications, such as road construction or decorative stonework.
How Do Sedimentary Rocks Serve Various Industries?
Sedimentary rocks are formed from the accumulation of mineral and organic particles, showcasing layers that often tell a story of Earth’s history. Key examples include sandstone and limestone, which are crucial in the oil and gas industries for reservoir studies. Buyers looking to acquire sedimentary rock collections should focus on the quality and provenance of the specimens, as these factors can significantly influence their applicability in geological surveys and educational settings.
What Makes Metamorphic Rocks Unique for Businesses?
Metamorphic rocks result from the alteration of existing rocks under heat and pressure, leading to distinctive textures and structures. Examples include marble and schist, which are not only used in construction but also in artistic applications such as sculpture. For B2B buyers, understanding the sourcing and processing of these rocks is essential, as quality and aesthetic appeal can impact their market value.
Why Are Mineral Specimens Important for Educational Purposes?
Mineral specimens are individual samples that highlight the unique properties of various minerals, such as hardness, luster, and color. These collections are invaluable for educational institutions and researchers, providing hands-on learning experiences. Buyers should evaluate the quality and diversity of the specimens included in a mineral collection, ensuring that they meet educational standards and provide comprehensive insights into mineral identification.
How Do Rock Cycle Educational Kits Enhance Learning?
Rock cycle educational kits are designed to illustrate the processes of rock formation, transformation, and erosion. These kits typically include samples of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, along with interactive elements that engage learners. For B2B buyers, investing in these kits can enhance educational programs and outreach initiatives, fostering a deeper understanding of geology among students and the general public. However, the initial investment may be higher compared to basic rock collections, so evaluating long-term benefits is crucial.
Key Industrial Applications of geology kit rocks
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of geology kit rocks | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Education & Training | Geology education programs using rock specimens for practical labs | Enhances student engagement and understanding of geology | Ensure kits include diverse rock types and educational materials. |
| Mining & Exploration | Training kits for mineral identification and geological surveys | Improves accuracy in mineral exploration and resource assessment | Source kits that reflect local geology for relevant training. |
| Environmental Consulting | Rock and mineral analysis for environmental impact assessments | Supports informed decision-making for sustainable practices | Consider kits with comprehensive testing capabilities and documentation. |
| Construction & Engineering | Geotechnical investigations using geology kits for site assessments | Increases project safety and compliance with regulations | Ensure kits meet industry standards and include necessary testing tools. |
| Hobby & Retail | Retail sales of geology kits for educational and recreational use | Expands product offerings and caters to growing interest in geology | Look for kits that appeal to various age groups and skill levels. |
How Are Geology Kit Rocks Used in Education and Training?
In educational settings, geology kit rocks are utilized to provide hands-on learning experiences for students studying earth sciences. These kits typically include a variety of rock and mineral specimens, which are essential for practical lab exercises. They help students understand geological concepts such as the rock cycle and mineral identification, enhancing their engagement and retention of knowledge. For international buyers, especially in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing kits that align with local geological contexts can significantly improve educational outcomes.
What Role Do Geology Kit Rocks Play in Mining and Exploration?
In the mining and exploration sector, geology kit rocks serve as crucial training tools for professionals involved in mineral identification and geological surveys. By using these kits, companies can train their teams to accurately assess mineral deposits, which is vital for effective resource extraction. For buyers in regions like the Middle East, where mineral exploration is growing, it is important to source kits that include specimens reflective of local geology to ensure relevance and effectiveness in training.
How Are Geology Kit Rocks Applied in Environmental Consulting?
Environmental consultants leverage geology kit rocks for conducting detailed analyses during environmental impact assessments. These kits facilitate the understanding of soil and rock composition, which is essential for evaluating potential impacts on ecosystems. For B2B buyers in Europe, sourcing kits that come with comprehensive testing capabilities and thorough documentation can support more informed decision-making, leading to sustainable practices in various projects.
Why Are Geology Kit Rocks Important for Construction and Engineering?
In construction and engineering, geology kit rocks are integral to geotechnical investigations, helping assess site conditions before construction begins. These assessments ensure that projects comply with safety regulations and mitigate potential risks associated with geological hazards. Buyers in regions with diverse geological conditions, such as Africa and South America, should prioritize sourcing kits that meet industry standards and include necessary testing tools to support their projects effectively.
How Can Hobby and Retail Sectors Benefit from Geology Kit Rocks?
The hobby and retail sectors can capitalize on the growing interest in geology by offering geology kits designed for educational and recreational purposes. These kits appeal to a wide range of customers, from children to adults, fostering a love for earth sciences. For retailers, selecting kits that cater to different age groups and skill levels can enhance customer engagement and expand product offerings, particularly in regions like Europe, where educational toys and science kits are increasingly popular.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘geology kit rocks’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Inadequate Customization Options for Geology Kits
The Problem: Many B2B buyers, especially educational institutions and research organizations, face a challenge when the geology kits available on the market do not fully meet their specific curriculum needs. These buyers often require kits that align with particular educational standards or focus on certain geological concepts. When kits are too generic or lack specific rock types and minerals relevant to their studies, it leads to dissatisfaction and ineffective teaching methods. This disconnect can hinder learning experiences and limit students’ understanding of geological processes.
The Solution: To address this issue, B2B buyers should seek suppliers that offer customizable geology kits. Engaging with manufacturers who allow for the selection of specific rock types, minerals, and educational resources can significantly enhance the relevance of the kits. Additionally, buyers can collaborate with suppliers to design a kit that includes supplementary materials, such as instructional videos, interactive manuals, and lab exercises tailored to their curriculum. By leveraging these partnerships, buyers can ensure the geology kits are not only educational but also engaging and practical for their students.
Scenario 2: Concerns About the Quality and Authenticity of Geological Samples
The Problem: B2B buyers often struggle with the authenticity and quality of geological samples included in geology kits. In regions like Africa and South America, where local geology may vary significantly, buyers need assurance that the rocks and minerals provided are not only authentic but also representative of the geological features found in their areas. Low-quality or poorly sourced samples can lead to misinformation and a lack of trust in educational materials, ultimately affecting the learning outcomes.
The Solution: To mitigate these concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing geology kits from reputable suppliers who provide detailed provenance for their samples. This includes documentation that verifies the origin and quality of each rock and mineral included in the kit. Buyers can also request samples before making bulk purchases to evaluate quality firsthand. Additionally, suppliers who conduct regular quality control checks and provide certifications of authenticity can build trust with their customers. Establishing long-term relationships with these suppliers can lead to better product offerings and more reliable service.
Scenario 3: Limited Support for Educators Using Geology Kits
The Problem: Educators often encounter difficulties when integrating geology kits into their teaching due to a lack of instructional support and resources. Many kits come with minimal guides or no supplementary materials, which can leave educators feeling unprepared to effectively teach the content. This limitation can detract from the educational experience, as teachers may struggle to engage students or explain complex geological concepts without adequate support.
The Solution: Buyers should look for suppliers that provide comprehensive educational resources alongside their geology kits. These resources can include detailed activity guides, lesson plans, and access to online platforms with instructional videos or interactive content. Additionally, suppliers that offer training sessions or workshops for educators can empower teachers to utilize the kits more effectively. By ensuring that educators have the necessary tools and support, buyers can enhance the overall teaching experience and improve student engagement in geology.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for geology kit rocks
What Are the Key Materials Used in Geology Kit Rocks?
When selecting materials for geology kit rocks, understanding the properties, advantages, and limitations of various rock types is crucial for B2B buyers. This section analyzes common materials used in geology kits, focusing on their performance, cost, and suitability for international markets, particularly in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
What Are the Key Properties of Igneous Rocks in Geology Kits?
Igneous rocks, formed from cooled magma or lava, are often included in geology kits due to their diverse textures and mineral compositions. Key properties include high durability and resistance to weathering, making them suitable for educational purposes. They can withstand a range of temperatures and pressures, which is vital for practical demonstrations in geology.
Pros: Igneous rocks are generally abundant and cost-effective, providing a wide array of specimens for educational use. Their hardness and structural integrity make them ideal for hands-on activities.
Cons: The variability in mineral composition can lead to inconsistencies in appearance and texture, which may affect the educational experience. Additionally, sourcing specific types may incur higher costs.
Impact on Application: Igneous rocks are compatible with various educational activities, including rock cycle demonstrations and mineral identification exercises. They are particularly useful in regions with volcanic activity, where local specimens can be sourced.
How Do Sedimentary Rocks Contribute to Geology Kits?
Sedimentary rocks, formed from the accumulation of mineral and organic particles, offer a different educational perspective. Their layered structure provides insights into geological processes such as erosion and sedimentation.
Pros: Sedimentary rocks are often readily available and can be collected easily, making them a cost-effective choice. They also exhibit unique features such as fossils, enhancing the educational value.
Cons: While generally durable, sedimentary rocks can be more susceptible to weathering compared to igneous rocks. This may limit their longevity in a kit if not properly stored or handled.
Impact on Application: These rocks are particularly valuable for teaching concepts related to stratification and fossilization. In regions where sedimentary formations are prevalent, local sourcing can reduce costs and support community engagement.
What Role Do Metamorphic Rocks Play in Geology Kits?
Metamorphic rocks, created under heat and pressure from existing rock types, provide critical insights into geological transformations. Their unique textures and mineral alignments make them essential for demonstrating metamorphic processes.
Pros: Metamorphic rocks are often visually striking, which can enhance student engagement. They are also durable and can withstand various environmental conditions.
Cons: The complexity of their formation can make them more challenging to source consistently. Additionally, some metamorphic rocks may be more expensive due to their rarity.
Impact on Application: These rocks are essential for illustrating concepts of metamorphism and tectonic activity. Buyers in regions with significant geological activity may find local options that are both educational and cost-effective.
What Are the Specific Considerations for International B2B Buyers?
For international B2B buyers, especially in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, compliance with local standards such as ASTM, DIN, or JIS is crucial. Understanding regional preferences for educational materials can influence purchasing decisions. For instance, countries with a strong emphasis on geology education may prefer kits that include a diverse range of rock types and detailed instructional materials.
Moreover, considerations around shipping costs, import regulations, and potential tariffs should be factored into purchasing strategies. Establishing relationships with local suppliers can also enhance supply chain efficiency and reduce costs.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Geology Kit Rocks
| Material | Typical Use Case for geology kit rocks | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Igneous Rocks | Rock cycle demonstrations | High durability and availability | Variability in mineral composition | Low |
| Sedimentary Rocks | Fossil studies and stratification | Cost-effective and easy to source | Susceptible to weathering | Low |
| Metamorphic Rocks | Demonstrating metamorphism | Visually striking and durable | More challenging to source | Med |
This analysis provides B2B buyers with actionable insights into the strategic selection of materials for geology kits, ensuring they can meet educational needs while considering regional market dynamics.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for geology kit rocks
What Are the Main Stages of Manufacturing Geology Kit Rocks?
The manufacturing process for geology kit rocks involves several key stages, ensuring that the final products are of high quality and suitable for educational and research purposes. Understanding these stages can help B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing geology kits.
Material Preparation: How Are Raw Materials Sourced and Processed?
The first step in the manufacturing process is material preparation, where raw geological specimens are sourced. This often involves mining or collecting rocks from specific geological locations known for their educational value. Suppliers typically focus on diverse types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—to provide a comprehensive educational experience.
Once collected, the rocks undergo initial processing, which may include cleaning to remove impurities and categorization based on type and characteristics. This preparation is crucial as it affects the quality of the final product. Suppliers often establish partnerships with local mining operations to ensure a consistent supply of high-quality materials.
Forming: What Techniques Are Used to Shape and Size Rocks?
The forming stage involves shaping and sizing the geological specimens to meet the specific requirements of educational kits. Techniques can vary widely depending on the type of rock and its intended use. For instance, some rocks may require cutting or grinding to achieve specific dimensions, while others are left in their natural state.
Manufacturers often employ advanced machinery for precision cutting and polishing, which enhances the aesthetic appeal of the rocks. Additionally, techniques such as sieving are used to ensure uniformity in size and weight, making it easier for educational institutions to use these kits in a classroom setting.
Assembly: How Are Geology Kits Organized and Packaged?
After the rocks are prepared and formed, they are assembled into kits. This stage involves selecting a diverse range of specimens to provide a well-rounded educational experience. Manufacturers often include instructional materials, such as activity guides and testing kits, to enhance the usability of the kits.
Packaging is another critical aspect of the assembly process. Kits are typically designed to be visually appealing and informative, often featuring clear labeling and protective casings to prevent damage during transport. This attention to detail not only protects the product but also adds value for the buyer.
Finishing: What Final Touches Are Applied to Ensure Quality?
The finishing stage is where the final touches are applied to the geology kits. This may include additional cleaning, polishing, or applying protective coatings to enhance the durability of the specimens. Manufacturers also conduct final inspections to ensure that each kit meets predefined quality standards.
At this stage, suppliers may package the kits in bulk for distribution or prepare individual kits for direct sale to educational institutions and businesses. The branding and labeling also play a crucial role, as they communicate the quality and educational value of the products.
What Quality Assurance Measures Are Commonly Implemented in Geology Kit Manufacturing?
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of geology kit rocks, as the educational value of these kits relies heavily on the integrity and quality of the specimens included. Implementing rigorous QA measures helps ensure that products meet international standards and customer expectations.
Which International Standards Guide Quality Control in Geology Kits?
Many manufacturers adhere to international quality standards, such as ISO 9001, which focuses on quality management systems. This certification is critical as it demonstrates a commitment to consistent quality and customer satisfaction. Compliance with these standards is often a prerequisite for B2B buyers looking to source products from reputable suppliers.
In addition to ISO standards, other certifications may apply, depending on the target market. For instance, CE marking is essential for products sold in the European Union, indicating compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
What Are the Key Quality Control Checkpoints in Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integrated throughout the manufacturing process to identify and rectify potential issues early on. Key checkpoints typically include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified criteria before processing begins.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the manufacturing stages, random samples are taken to evaluate whether the production processes are yielding products that meet quality standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the kits are packaged and shipped, they undergo a final inspection to ensure they meet all quality and specification requirements.
These checkpoints are essential in maintaining the integrity of the products and ensuring that the final kits are ready for educational use.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify the Quality Control of Their Suppliers?
For B2B buyers, especially those in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial for ensuring product reliability and educational value.
What Auditing and Reporting Methods Are Available?
Buyers can conduct supplier audits to assess the quality management systems in place. This involves a thorough review of the supplier’s processes, documentation, and quality assurance practices. Additionally, suppliers may provide quality control reports that detail the results of inspections and tests performed during manufacturing.
Third-party inspections can also serve as an effective means of verifying quality. Engaging an independent organization to assess the manufacturing facility can provide unbiased insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
What Are the Specific Quality Control Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers should be aware of specific quality control nuances that may affect their purchasing decisions. For example, regulations and standards can vary significantly between regions. Buyers should ensure that suppliers are familiar with local regulations in their target markets, such as specific environmental or safety standards.
Moreover, cultural differences may influence how quality assurance is perceived and implemented. Building strong relationships with suppliers and maintaining open lines of communication can help mitigate misunderstandings and foster a collaborative approach to quality assurance.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for geology kit rocks are crucial for delivering high-quality educational products. By understanding these processes and the associated quality control measures, B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing geology kits, ensuring they meet their specific educational and operational needs.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘geology kit rocks’
This guide serves as a practical checklist for B2B buyers looking to procure geology kit rocks. The objective is to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that buyers make informed decisions that align with their educational or research needs.
Step 1: Define Your Technical Specifications
Begin by outlining the specific requirements for your geology kits. Consider the types of rocks and minerals needed—whether igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic—as well as the quantity and quality of each specimen. Clear specifications help in identifying the right suppliers and ensure that the kits meet educational or research objectives.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify potential suppliers that specialize in geology kits. Use online platforms, trade shows, and industry associations to gather a list of reputable companies. Look for suppliers with a strong track record, positive reviews, and experience in your target regions, such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Verify the certifications and quality standards of potential suppliers. Check for compliance with international quality management standards (e.g., ISO 9001) and any relevant environmental regulations. Certifications not only ensure product quality but also demonstrate the supplier’s commitment to sustainable practices, which is increasingly important in global procurement.
Step 4: Request Product Samples
Before making a bulk purchase, request samples of the geology kits. This step allows you to assess the quality, variety, and educational value of the materials provided. Pay attention to the accuracy of rock and mineral specimens, as well as the accompanying instructional materials or kits that enhance the learning experience.
Step 5: Assess Pricing and Payment Terms
Compare pricing structures among different suppliers to ensure competitive rates. Consider the total cost of ownership, which includes shipping, customs duties, and potential import taxes. Additionally, clarify payment terms, such as deposit requirements and credit options, to align with your budgetary constraints.
Step 6: Check for After-Sales Support
Inquire about the level of after-sales support offered by suppliers. Reliable suppliers should provide assistance with any product-related issues, including replacement parts or additional resources for educational purposes. Strong after-sales support ensures a positive long-term relationship and enhances the overall value of your investment.
Step 7: Finalize the Order and Review Terms
Once you’ve selected a supplier, finalize the order details and review the terms of the contract. Ensure that delivery timelines, return policies, and warranty information are clearly stated. A well-defined agreement protects both parties and sets expectations for the transaction, fostering a smoother procurement process.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing geology kit rocks effectively, ensuring that they make informed decisions that support their educational and research goals.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for geology kit rocks Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Geology Kit Rocks?
Understanding the cost structure of geology kits is essential for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margins.
-
Materials: The choice of rocks and minerals significantly influences costs. Standard geology kits typically use common specimens, while specialized kits featuring rare minerals or custom collections can escalate expenses. The sourcing of ethically mined or certified materials can also affect the overall price.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary depending on the complexity of the kits and the expertise required for assembly and quality checks. Kits that include interactive components or educational manuals may necessitate higher skilled labor.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to utilities, equipment maintenance, and facility costs. Suppliers with advanced manufacturing processes may pass on these costs to buyers, affecting the final pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific tooling may be required for creating unique kits or customizations, adding to initial costs. Buyers should inquire about tooling fees, especially for low-volume orders.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of rocks and minerals through rigorous testing can lead to increased costs. Buyers should consider the value of QC in maintaining educational standards and user satisfaction.
-
Logistics: Shipping costs can vary widely based on the origin of materials, destination, and chosen Incoterms. International shipments may incur additional customs duties or tariffs, impacting the total cost.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin that varies based on their target market and competition. Understanding the margin can provide insights into negotiation strategies.
What Factors Influence the Pricing of Geology Kits?
Several factors can influence pricing beyond just the cost components. These include:
-
Volume/MOQ: Minimum order quantities (MOQ) can significantly impact pricing. Higher volumes often lead to discounts, while smaller orders may incur higher per-unit costs.
-
Specifications/Customization: Customized kits tailored to specific educational needs or regional geological features may come at a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the costs.
-
Materials: The quality and sourcing of materials directly affect pricing. Kits utilizing high-quality specimens or unique geological features will typically command higher prices.
-
Quality/Certifications: Kits that come with certifications or educational endorsements may be priced higher. This is especially relevant for institutions seeking to meet specific educational standards.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can influence pricing. Established suppliers with a proven track record may charge more due to perceived value.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the chosen Incoterms is crucial for predicting total costs. Different terms can shift responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and customs, which can impact the overall expense.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Costs When Sourcing Geology Kits?
B2B buyers can employ several strategies to optimize costs and enhance value when sourcing geology kits:
-
Negotiation: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate pricing, especially for large orders. Don’t hesitate to ask for discounts based on volume or long-term commitments.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership (TCO) rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes considering shipping costs, potential import tariffs, and future maintenance or replacement costs.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and regional pricing strategies. Understanding local market dynamics can aid in negotiating better deals.
-
Research: Conduct thorough market research to compare prices and offerings from multiple suppliers. This can provide leverage in negotiations and help identify the best value for specific needs.
-
Bulk Purchasing: If feasible, consider bulk purchasing to take advantage of lower per-unit costs. Group purchases among institutions can also lead to significant savings.
By taking a comprehensive approach to understanding the cost structure, pricing influences, and negotiation strategies, international B2B buyers can make well-informed decisions when sourcing geology kits tailored to their educational or research needs.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing geology kit rocks With Other Solutions
Introduction to Alternatives in Geology Education Solutions
When considering geology education solutions, businesses often seek alternatives to traditional geology kit rocks. These alternatives may include digital resources, virtual lab simulations, or specialized educational programs. Each solution has its unique advantages and challenges, making it essential for B2B buyers to assess which option best fits their educational objectives and operational needs.
Comparison Table
| Comparison Aspect | Geology Kit Rocks | Digital Rock and Mineral Kits | Interactive Geology Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Provides hands-on experience and tangible specimens for study. | Offers virtual simulations and extensive resources, but lacks physical interaction. | Highly interactive with diverse learning modules, yet may not cater to all learning styles. |
| Cost | Ranges from $20 to $300+ depending on the collection. | Typically between $50 to $200 per license. | Subscription models may range from $100 to $500 annually. |
| Ease of Implementation | Simple to implement in classroom settings; requires minimal setup. | Requires digital devices and internet access, which may not be universally available. | Installation can be complex; requires tech support and training. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance; requires occasional cleaning and proper storage. | No physical maintenance; updates are managed digitally. | Regular updates needed; tech support required for troubleshooting. |
| Best Use Case | Ideal for tactile learning environments and hands-on activities. | Best for remote learning and institutions with strong tech infrastructure. | Suitable for institutions seeking comprehensive digital resources and interactive learning. |
Detailed Breakdown of Alternatives
Digital Rock and Mineral Kits
These kits provide a virtual experience with images and descriptions of various rocks and minerals. They are particularly beneficial for institutions that may not have the budget or space for physical kits. The primary advantage is accessibility; however, the lack of tactile interaction may hinder some students’ learning experiences. Institutions in regions with reliable internet can benefit greatly from this solution, but in areas with limited access, it may not be practical.
Interactive Geology Software
This alternative offers a comprehensive digital approach to geology education, incorporating simulations, quizzes, and interactive lessons. It serves as an excellent tool for institutions looking to integrate technology into their curriculum. The software can engage students through gamification and immersive experiences. However, it can be costly, and the complexity of installation and maintenance may pose challenges, particularly for smaller institutions or those with limited IT support.
Conclusion: How to Choose the Right Solution for Your Needs
When selecting the most suitable geology education solution, B2B buyers should consider their specific needs, including budget constraints, technological infrastructure, and learning objectives. Geology kit rocks are ideal for hands-on learning environments, while digital kits and interactive software provide flexible, technology-driven alternatives. Ultimately, the right choice will align with the institution’s educational philosophy and the needs of its learners, ensuring an effective and engaging geology education experience.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for geology kit rocks
What Are the Key Technical Properties of Geology Kit Rocks?
In the procurement of geology kits, understanding critical technical properties is essential for ensuring quality and suitability for educational or professional applications. Below are some vital specifications to consider:
1. Material Grade
Material grade refers to the quality and type of rocks and minerals included in the kit. This specification impacts both the educational value and the durability of the specimens. Higher-grade materials often provide more accurate representations of geological features, making them suitable for advanced studies or professional training.
2. Rock Type Distribution
A well-balanced geology kit should feature a mix of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. This distribution is crucial as it allows users to study the rock cycle comprehensively. Buyers should verify that kits include a representative sample of each rock type to facilitate a more thorough educational experience.
3. Specimen Size and Weight
The size and weight of the rocks included in a kit can affect handling and usability in educational settings. For example, smaller specimens may be easier for students to manipulate, while larger specimens can demonstrate geological features more effectively. Buyers should consider the intended use when evaluating these dimensions.
4. Packaging and Storage Conditions
Proper packaging ensures that geological specimens remain undamaged during transit and storage. Kits should come in durable containers that prevent breakage and facilitate easy organization. Understanding packaging standards can help buyers avoid issues related to specimen loss or degradation.
5. Educational Content and Resources
Many geology kits include manuals, activity guides, or digital resources to enhance the learning experience. The presence of these educational materials is vital for effective teaching and should be evaluated when making purchasing decisions. Buyers should ensure that the included resources are relevant and accessible for the intended audience.
6. Certifications and Standards Compliance
Certification indicates that the rocks and minerals comply with specific educational and safety standards. For B2B buyers, especially in regulated markets, ensuring that products meet these standards is crucial for avoiding legal complications and ensuring customer satisfaction.
What Are Common Trade Terms in the Geology Kit Industry?
Familiarity with industry terminology can significantly streamline the procurement process and enhance communication with suppliers. Here are several key terms:
1. OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of geology kits, buyers might work with OEMs to customize kits according to specific educational requirements or regional geological features.
2. MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQs is crucial for budgeting and inventory management, particularly for educational institutions or companies looking to purchase kits in bulk.
3. RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that a buyer sends to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. In the geology kit market, an RFQ can help buyers gather competitive pricing, ensuring they make informed purchasing decisions.
4. Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, defining the responsibilities of sellers and buyers. Familiarity with Incoterms is essential for international transactions, as they clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs.
5. Lead Time
Lead time refers to the amount of time between placing an order and receiving it. Understanding lead times is critical for planning, especially for educational institutions that may need kits ready for specific academic schedules.
6. Warranty and Return Policy
The warranty and return policy outline the conditions under which products can be returned or replaced. Buyers should review these terms carefully to ensure they have recourse in case of defects or dissatisfaction with the geology kits.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with their educational or professional needs in the geology sector.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the geology kit rocks Sector
What Are the Current Market Trends Affecting Geology Kit Rocks?
The global geology kit rocks market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing educational initiatives and an expanding interest in earth sciences across diverse regions, particularly in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. In Africa, countries like Nigeria are investing in science education, leading to a surge in demand for geology kits as tools for both students and professionals. Similarly, in the Middle East, nations such as Saudi Arabia are emphasizing STEM education as part of their Vision 2030 initiative, creating opportunities for suppliers of educational geology kits.
Emerging technologies are transforming how B2B buyers source geology kits. The rise of e-commerce platforms allows for streamlined procurement processes, offering buyers the ability to compare products and suppliers effortlessly. Additionally, virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) tools are increasingly being incorporated into geology education, enhancing the user experience and engagement levels for both students and professionals. This trend presents a unique opportunity for suppliers who can integrate these technologies into their offerings, providing a competitive edge in the market.
Furthermore, the need for localized sourcing is gaining traction among international buyers. As logistical challenges persist, particularly in regions with underdeveloped infrastructure, there is a growing preference for suppliers who can provide quick turnaround times and localized support. Buyers are also looking for customized kits tailored to specific educational curricula or research needs, enhancing the relevance and applicability of the products they procure.
How Important Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing for Geology Kit Rocks?
Sustainability and ethical sourcing are becoming critical considerations for B2B buyers in the geology kit rocks sector. The environmental impact of raw material extraction, particularly for minerals and rocks, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. Buyers are increasingly scrutinizing their supply chains to ensure that materials are sourced responsibly, minimizing ecological footprints and promoting biodiversity.
Ethical supply chains not only mitigate risks associated with environmental degradation but also enhance brand reputation. Suppliers who prioritize sustainability and can provide certifications such as Fair Trade or Eco-Certified are more likely to attract discerning buyers. These certifications assure customers that the products they are purchasing meet specific environmental and social standards.
In addition, the growing awareness of climate change and its implications is prompting buyers to seek out products made from renewable resources or those that utilize sustainable manufacturing processes. By investing in geology kits that are designed with eco-friendly materials and packaging, businesses can align themselves with the values of their customers and contribute positively to the environment.
How Has the Geology Kit Rocks Market Evolved Over Time?
The geology kit rocks market has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from basic collections of rocks and minerals to comprehensive educational tools that incorporate advanced learning methodologies. Initially, geology kits were primarily aimed at hobbyists and young students, offering simple rock specimens and minimal instructional materials. However, as education systems worldwide have increasingly recognized the importance of hands-on learning, the market has expanded to include kits that are integrated into formal curricula, complete with lab exercises and digital resources.
In recent years, the introduction of technology into educational geology kits, such as interactive digital manuals and online resources, has further transformed the market. This evolution reflects a broader trend toward experiential learning, where students engage with materials in ways that enhance their understanding of geological concepts. Today’s geology kits are not just educational tools; they are vital components of modern geoscience education, reflecting the dynamic nature of the field and the growing demand for effective teaching resources.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of geology kit rocks
-
How do I choose the right geology kit for educational purposes?
Selecting the right geology kit involves assessing your educational objectives and the age group of your students. Look for kits that include a variety of rock types—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—as well as educational resources such as activity guides and instructional videos. Ensure that the kit aligns with your curriculum and offers hands-on activities that promote engagement. Additionally, consider the quality and durability of the materials, as well as any certifications that may be relevant for educational use in your region. -
What are the most common components included in geology kits?
Most geology kits typically include a selection of rock and mineral specimens, tools for identification (like magnifying glasses or streak plates), and educational manuals or guides. Some kits also come with interactive elements such as digital resources or experiments related to the rock cycle and mineral properties. When sourcing kits, verify the variety and number of specimens included, as well as any supplementary materials that enhance the learning experience. -
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for geology kits?
When vetting suppliers, check their reputation, experience, and the quality of their products. Look for suppliers that provide detailed product descriptions, including the origins of their specimens and any educational content included. Request samples if possible, and inquire about their quality assurance processes. Additionally, verify their compliance with international trade regulations and standards, especially if you are importing kits into regions like Africa or the Middle East. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for geology kits?
Minimum order quantities can vary widely among suppliers. Some may offer kits in small quantities suitable for individual classrooms, while others may have higher MOQs for bulk purchases intended for institutions or educational programs. Always discuss your specific needs with the supplier to see if they can accommodate smaller orders or if there are discounts available for larger purchases. This information is crucial for budgeting and planning your procurement strategy. -
What payment terms are commonly offered by suppliers of geology kits?
Payment terms can vary significantly depending on the supplier and your location. Common options include upfront payments, net 30 or net 60 days, and installment plans for larger orders. It’s essential to negotiate terms that align with your financial capabilities and purchasing schedule. Additionally, inquire about accepted payment methods, as some suppliers may offer flexible options such as credit cards, bank transfers, or letters of credit. -
How can I ensure the quality of geology kits before purchase?
To ensure quality, request product specifications and certifications from the supplier. Look for suppliers that have undergone third-party quality audits or those that provide detailed descriptions of their sourcing processes. Consider asking for customer testimonials or case studies that showcase the effectiveness of their kits in educational settings. Finally, if possible, acquire samples or conduct a trial order to assess the quality firsthand before committing to a larger purchase. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when importing geology kits?
When importing geology kits, consider shipping costs, customs duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure your supplier has experience with international shipping and can provide necessary documentation to facilitate customs clearance. Also, evaluate the reliability of their logistics partners and inquire about tracking options for shipments. Understanding these factors will help you plan effectively and mitigate potential delays or additional costs during the import process. -
Can geology kits be customized to meet specific educational needs?
Many suppliers offer customization options for geology kits to better fit specific educational requirements or curriculum goals. This may include selecting particular rock types, adding unique instructional materials, or bundling kits with additional tools. Discuss your needs with the supplier to see what customization options are available and whether there are any additional costs associated with these modifications. Customization can enhance the educational value of the kits and provide a tailored learning experience for students.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 10 Geology Kit Rocks Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Cornerstone – Geology Kits
Domain: cornerstone-edsupply.com
Registered: 2015 (10 years)
Introduction: This company, Cornerstone – Geology Kits, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
2. Carolina – Earth Science Supplies
Domain: carolina.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: This company, Carolina – Earth Science Supplies, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
3. eScience Labs – Rocks and Minerals Kit
Domain: esciencelabs.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Rocks and Minerals Kit – Physical Geology 2nd Edition”, “price”: “$93.00”, “components”: {“minerals”: 9, “rocks”: 18}, “features”: {“labs”: 5, “exercises”: 5, “topics”: [“plate tectonics”, “rock identification”, “mineral identification”]}, “support”: {“manual”: “interactive”, “videos”: “instructional”, “digital_assets”: [“Google Earth TM exercises”], “accessibility”: “ADA compati…
4. Home Science Tools – Rocks & Minerals Kits
Domain: homesciencetools.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Rocks & Minerals for Kids: Collection Kits & Tools from HomeScienceTools. Explore geology by collecting rocks and minerals. Purchase mineral sets for testing color streak, hardness, and magnetism. Use rock pick and safety goggles with geodes to reveal mineral deposits. Learn about the rock cycle: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks. Gifts available include complete sets of rocks and minera…
5. UARK – Digital Rock Kit for GEOS 11101L
Domain: uark.libguides.com
Registered: 2007 (18 years)
Introduction: Rock Kit for GEOS 11101L: Physical Geology Lab includes digital rock and mineral kits. The kit is divided into three sections: Igneous Rocks, Sedimentary Rocks, and Metamorphic Rocks. Each section features pictures and important characteristics of various rock specimens. A full digital rock kit album with additional pictures is available. The content is licensed under a Creative Commons Attributio…
6. Pasco – Basic Rock and Mineral Kit
Domain: pasco.com
Registered: 1994 (31 years)
Introduction: Basic Rock and Mineral Kit – PS-2347
– U.S. Educator Price: $52
– Includes 15 species of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks.
– Additional kit with 15 common minerals.
– Identification guide for rocks and minerals included.
– Mineral identification by hardness, luster, streak, color, cleavage, and other properties.
– Includes streak plate and hand lens.
– Compatible with SPARKvue software …
7. Good and Beautiful – Geology Rocks and Minerals Kit
Domain: goodandbeautiful.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Geology: Rocks and Minerals Kit
8. GeoCentral – Earth Science Kit: Rocks
Domain: geocentral.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Earth Science Kit: Rocks – GeoCentral
– Focus: Exploration of geological world with a variety of rocks.
– Includes: 6 Earth Science Kits.
– Each kit contains:
– 15 igneous rocks
– 1 magnifier
– 1 streak plate
– 1 instructional guide
– Designed to spark interest in Science, Technology, Engineering, Art, or Math (STEAM).
– Categories: STEAM, Toy.
– Tags: adventure faves, retail 20 and below…
9. SciPlus – Geodes and Magnetic Hematite
Domain: sciplus.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: 1. BREAK YOUR OWN GEODES CLASSROOM PKG(15): 1-1/4″ dia stones, MSRP: $24.50. 90% have beautiful white crystals inside. 2. MAGNETIC HEMATITE SPECIMEN PKG(12): Potential healing powers, MSRP: $6.15, on sale for $6.95 (12% OFF). 3. BREAK YOUR OWN GEODES PKG(2): 1-1/4″ dia stones, MSRP: $2.63, on sale for $5.25 (50% OFF).
10. Thomas Scientific – Rock & Mineral Kit
Domain: thomassci.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Rock & Mineral Kit, 1″ x 12 Specimens. Set includes twelve different rocks and minerals: Crystal Quartz, Basalt, Breccia, Biotite Gneiss, Fluorite, Granite, Conglomerate, Marble, Apatite, Scoria, Sandstone, and Slate. Each specimen measures approximately 1″. Useful for testing mineral hardness, streak color, magnetic properties, appearance, and effervescence. Packaged in a protective box for stora…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for geology kit rocks
Effective strategic sourcing in the realm of geology kit rocks is vital for international buyers looking to enhance educational offerings and professional development in geoscience. Understanding the diverse range of products, from introductory kits to specialized mineral collections, allows organizations to tailor their purchases to meet specific educational goals and regional needs. The value derived from these kits extends beyond mere acquisition; they foster engagement and understanding of geological processes, critical for cultivating the next generation of geoscientists.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, strategic sourcing presents a unique opportunity to invest in high-quality educational resources that can significantly impact local educational standards and workforce development. By prioritizing quality, sustainability, and supplier reliability, organizations can ensure they are well-equipped to support both current and future geoscience initiatives.
As the global demand for geological education continues to rise, now is the time to act. Evaluate your sourcing strategies, engage with reputable suppliers, and consider how geology kits can elevate your educational programs. The future of geology education is bright—seize the opportunity to be at the forefront of this vital field.