Juice Packing Machine: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Navigating the Global Market for Juice Packing Machines
In the competitive beverage industry, efficient juice packing machines are pivotal for maintaining product freshness, reducing waste, and scaling operations. With rising demand for sustainable and automated packaging solutions, businesses in the USA and Europe face mounting pressure to optimize supply chains and comply with stringent regulations.
The challenge lies in navigating a fragmented global market where technological disruptions, varying regional standards, and economic fluctuations can hinder procurement decisions. From selecting the right machine for high-volume liquid filling to integrating advanced features like retort pouch systems, missteps can lead to costly downtime and quality issues.
This comprehensive B2B guide equips decision-makers with actionable insights to overcome these hurdles. We’ll explore:
- Market Overview: Key trends in juice packaging, focusing on North American and European demands for eco-friendly, automated systems.
- Technology Spotlight: In-depth analysis of machine types, from vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) to premade pouch fillers, drawing from industry leaders like Landpack.
- Regulatory Landscape: Compliance essentials in the USA (FDA standards) and Europe (EU directives on food safety).
- Procurement Strategies: Tips for vendor evaluation, cost-benefit analysis, and integration with existing lines.
- Case Studies and Future Outlook: Real-world examples and emerging innovations to future-proof your operations.
Armed with this knowledge, you’ll confidently source machines that drive efficiency and profitability. Let’s dive in.
Top 10 Juice Packing Machine Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. NIMCO Corporation: Gable Top Packaging Machinery Manufacturer
Domain: nimco.com
Registered: 1997 (28 years)
Introduction: Since 1962, NiMCO continues as the leading independent manufacturer of form fill and seal equipment for gable-top cartons….
2. Top 10 Packing Machine Manufacturers in the world – Landpack
Domain: landpack.com
Registered: 2009 (16 years)
Introduction: 1. Landpack-China · 2. Tetra Pak- Switzerland · 3. Krones-Germany · 4. KHS GmbH-Germany · 5. Sidel-France · 6. Syntegon-Germany · 7. MULTIVAC-Germany….
3. Bottling & Filling Equipment Manufacturer | E-PAK Machinery
Domain: epakmachinery.com
Registered: 2001 (24 years)
Introduction: E-PAK Machinery manufactures quality liquid filling machines, including cappers and labelers, for the bottling industry. Buy equipment and parts online….
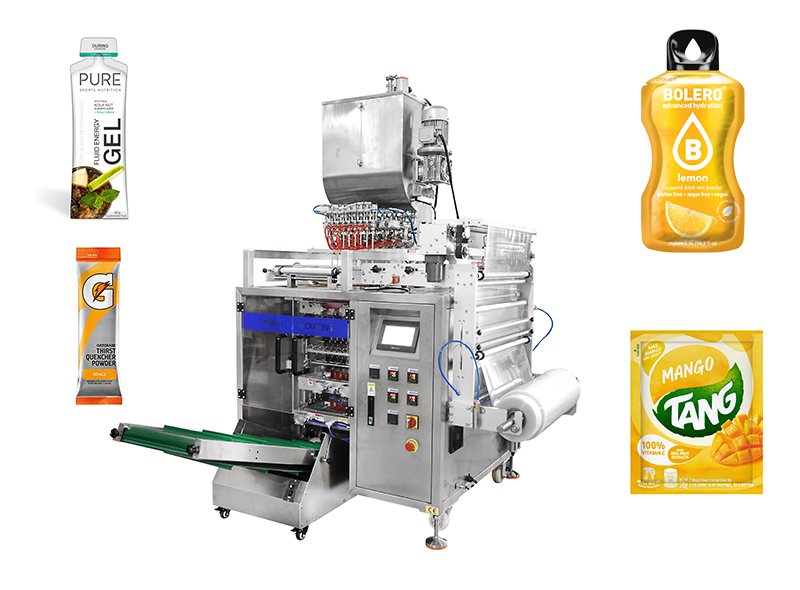

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. Juice Packaging Machine for Sale – Quality and Innovation
Domain: acefilling.com
Registered: 2024 (1 years)
Introduction: Discover our high-quality juice packaging machines for sale. Accurate, high-speed, and durable. Customizable to meet your needs….
5. Top 20 Juice Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025
Domain: finbolink.com
Registered: 2023 (2 years)
Introduction: Zhangjiagang Mic Machinery is widely recognized among juice filling machine manufacturers, providing efficient, hygienic, and customizable equipment for juice ……
Understanding juice packing machine Types and Variations
Understanding Juice Packing Machine Types and Variations
Juice packing machines vary based on packaging format, automation level, and production scale. Below, we identify four key types commonly used in the beverage industry, drawing from standard equipment categories. These are selected for their relevance to juice processing in B2B contexts across the USA and Europe.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machine | Forms pouches from roll stock, fills with liquid, seals vertically; includes options for high-speed operation and multihead weighing integration. | Ideal for small to medium-scale production of juice pouches, cartons, or bags; common in juice concentrate or ready-to-drink packs. | Pros: High efficiency, customizable pouch sizes, low material waste. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires skilled maintenance for complex models. |
| Doypack Packaging Machine | Uses premade stand-up pouches with zippers or spouts; rotary or horizontal designs for automated filling and sealing. | Suited for retail juice bottles or pouches requiring portability; prevalent in organic or flavored juice lines. | Pros: Versatile for various pouch shapes, excellent for marketing (e.g., resealable features), durable packaging. Cons: Premade pouches increase material costs, potential for slower speeds in manual setups. |
| Spout Pouch Filling Machine | Fills flexible pouches with built-in spouts for easy pouring; includes vacuum or aseptic options for extended shelf life. | Best for aseptic juice packaging, such as long-shelf-life dairy or plant-based drinks; used in export-oriented B2B supply chains. | Pros: Extends product freshness, portable and user-friendly, reduces contamination risks. Cons: Complex setup for aseptic versions, higher energy consumption. |
| Sachet Packing Machine | Produces small, single-serve sachets or stick packs from roll film; integrates with inline filling for precise dosing. | Targeted at single-portion juice shots or samples; common in foodservice or promotional B2B juice products. | Pros: Cost-effective for small volumes, minimal storage space, customizable flavors in packs. Cons: Limited to low-viscosity juices, potential for film waste in high-volume runs. |
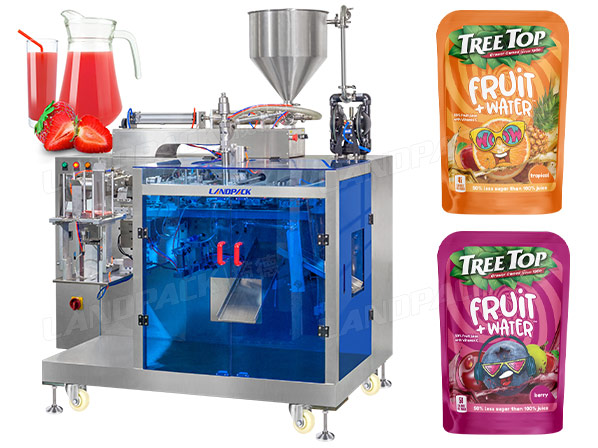
Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machine
This machine creates pouches directly from a roll of packaging film, forming them vertically while filling and sealing. Key features include adjustable pouch sizes, integration with liquid pumps for accurate filling, and options for nitrogen flushing to preserve juice quality. Applications extend to bulk juice packaging for wholesalers or co-packers, ensuring hygiene through automated processes. In B2B settings, it supports scalability for seasonal juice production.
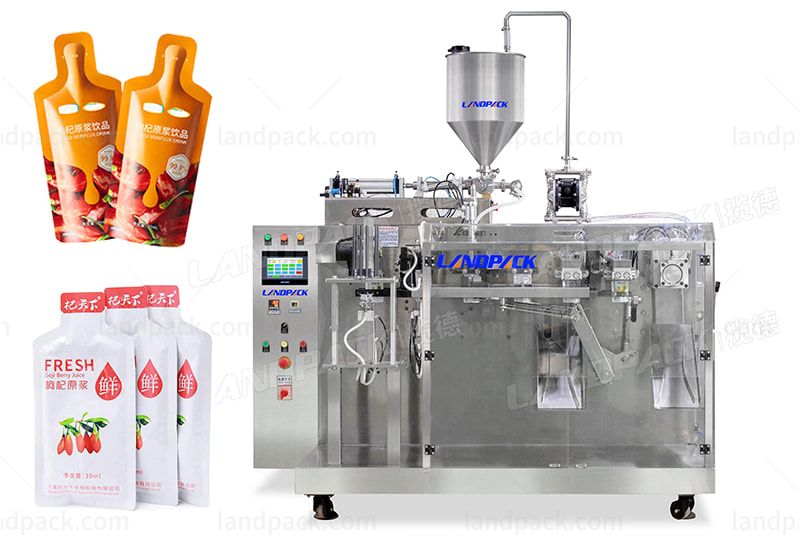

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Doypack Packaging Machine
Designed for premade pouches, this type offers rotary or horizontal configurations for efficient handling of stand-up bags. Features encompass zipper additions for resealability, multi-lane options for high throughput, and compatibility with juice viscosities. It’s widely applied in premium juice segments, such as those requiring branding on pouches for direct-to-consumer or retail channels. B2B users benefit from its flexibility in handling varied juice types, including those with particulates.
Spout Pouch Filling Machine
Focusing on pouches with integrated pouring spouts, this machine emphasizes aseptic filling to maintain juice sterility. Features include spout insertion, cap sealing, and sterilization modules, often combined with vacuum technology. Applications include UHT-treated juices for international distribution, where extended shelf life is critical. For B2B operations, it aligns with regulations in Europe (e.g., EU food safety standards) and the USA (FDA compliance), reducing spoilage in supply chains.
Sachet Packing Machine
This equipment produces compact sachets or stick packs, ideal for portion-controlled juice distribution. Features involve precise filling nozzles, tear-notch creation, and multi-head options for efficiency. Applications target promotional samples or foodservice sectors, such as hotels or vending. In B2B contexts, it’s valued for its low-cost entry into niche juice markets, though it’s less suitable for high-volume, large-format packaging.
Key Industrial Applications of juice packing machine
Key Industrial Applications of Juice Packing Machine
The juice packing machine is designed for efficient, hygienic, and scalable packaging of liquid beverages. Below is a table outlining key industrial applications, along with detailed benefits informed by standard manufacturing practices and machine capabilities such as those offered by specialized equipment like the Juice Pouch Packing Machine or Liquid Packaging Machine.
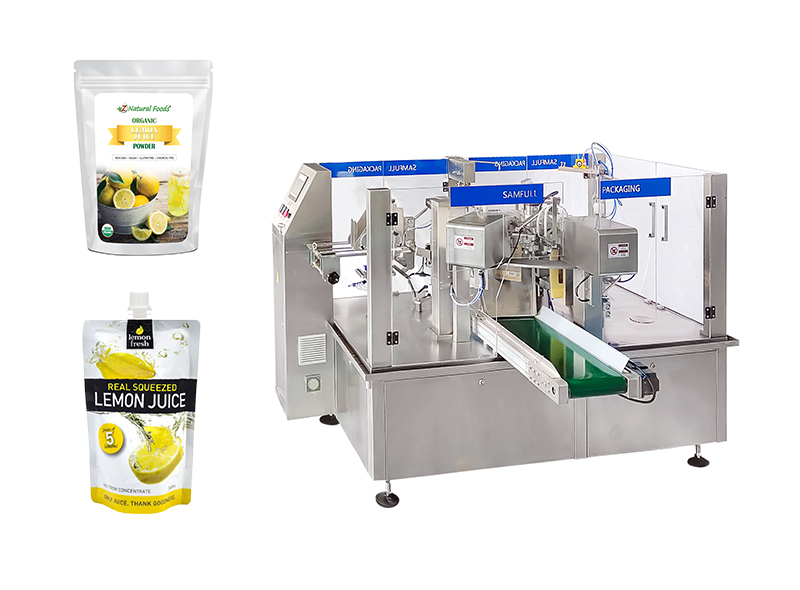

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Industry/Application | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|
| Beverage Manufacturing | Enhances production efficiency for fruit juices, nectars, and flavored drinks by automating filling and sealing processes, reducing labor costs by up to 30% and minimizing contamination risks through sterile packaging options. Supports high-volume output (up to 10,000 units/hour) with customizable pouch sizes, ensuring compliance with FDA and EU standards for food safety. |
| Food Processing and Canning | Ideal for packaging organic or preservative-free juices in retort or stand-up pouches, extending shelf life without refrigeration for up to 12 months. Improves supply chain logistics by enabling lightweight, space-saving packaging, lowering transportation costs by 20-25% compared to glass or cans, and facilitating easy stacking in warehouses. |
| Retail and Consumer Goods Distribution | Streamlines packaging for retail-ready juice cartons or pouches, incorporating features like zipper seals for resealability, which boosts consumer convenience and reduces product waste by 15%. Enhances brand appeal with customizable labeling and eco-friendly materials, supporting B2B sales to supermarkets and e-commerce platforms while meeting sustainability targets like those in the EU’s Circular Economy Action Plan. |
| Export and International Trade | Enables aseptic filling for long-distance shipping of juices to global markets, maintaining product quality in varying climates. Reduces spoilage risks through vacuum or nitrogen flushing options, ensuring compliance with international regulations like HACCP and Codex Alimentarius, and optimizing costs for bulk exports from USA/Europe to Asia or Latin America. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘juice packing machine’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Juice Packing Machines & Their Solutions
Pain Point 1: Inconsistent Filling Accuracy Leading to Product Waste
- Scenario: In high-volume juice production lines, operators often encounter variations in fill levels due to machine wear, inconsistent viscosity of juices, or calibration errors, resulting in overfilled or underfilled pouches.
- Problem: This inconsistency causes significant product waste, increases operational costs, and risks regulatory non-compliance in USA and Europe markets where precise measurements are mandated.
- Solution: Implement a rotary premade pouch packing machine with integrated weighing systems and automatic adjustment features. Regular calibration using multihead weigher technology ensures accurate fills, minimizing waste by up to 20% while maintaining compliance with FDA and EU standards.
Pain Point 2: Frequent Downtime Due to Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
- Scenario: Juice packing operations in busy facilities require machines to run continuously, but sticky residues from fruit juices lead to clogs, spills, and the need for frequent shutdowns for cleaning, especially in perishable product lines.
- Problem: Unplanned downtime disrupts production schedules, escalates labor costs, and affects supply chain reliability, particularly for B2B clients in Europe facing strict hygiene regulations like HACCP.
- Solution: Opt for a spout pouch filling machine designed with easy-to-clean components, such as quick-release parts and self-cleaning mechanisms. Schedule predictive maintenance routines and use machines with antimicrobial surfaces to reduce cleaning intervals, cutting downtime by 15-25% and ensuring seamless operations.
Pain Point 3: Limited Flexibility for Diverse Juice Variants and Packaging Formats
- Scenario: Juice manufacturers often need to switch between different juice types (e.g., fresh, concentrate, or flavored) and packaging sizes (e.g., stand-up pouches vs. retort pouches), but rigid machines hinder quick adaptations.
- Problem: This inflexibility slows product launches, limits market responsiveness, and increases costs from custom modifications, challenging competitiveness in USA and European B2B markets with varying consumer demands.
- Solution: Adopt a vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machine with modular designs that support multiple pouch formats, like M-shape or zipper pouches, and adjustable filling heads for different viscosities. Integrate automation software for rapid changeovers, enabling efficient handling of diverse juice lines and reducing setup time by 30%.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for juice packing machine
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Juice Packing Machines
Overview
Selecting the right materials for juice packing machines is critical for ensuring product integrity, compliance with regional regulations, and operational efficiency. This guide analyzes key materials commonly used in juice packaging, such as pouches, bottles, and seals, focusing on their suitability for juice products. Factors like barrier properties, cost, sustainability, and regulatory compliance in the USA (e.g., FDA standards) and Europe (e.g., EU food contact regulations) are evaluated to inform strategic decisions for B2B manufacturers.
Key Materials Analysis
Juice packing machines from providers like Landpack handle a variety of formats, including doypack, spout pouch, stand-up pouch, and retort pouch machines. The materials selected for packaging must protect against contamination, preserve freshness, and align with machine capabilities. Below is an analysis of primary materials:
-
Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET): Widely used for bottles and flexible pouches due to its clarity, lightweight nature, and excellent barrier against oxygen and carbon dioxide. Ideal for fruit juices requiring transparency and shelf stability. PET is recyclable in many regions, supporting sustainability goals, but costs can vary based on thickness. In the USA, it complies with FDA 21 CFR 177.1630; in Europe, it meets EU Regulation 10/2011 for food contact. Suitable for high-volume production on rotary premade pouch machines.
-
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE): Durable and resistant to moisture, making it suitable for opaque bottles and pouches. It provides a good balance of cost and functionality for non-transparent juice packaging, with strong chemical resistance. HDPE is highly recyclable and meets FDA and EU standards, but it offers lower oxygen barrier than PET, potentially shortening shelf life for sensitive juices. Often used in vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) lines for granular or liquid juices.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Aluminum Foil Laminates: Essential for retort pouches and spout pouches, offering superior barrier properties against light, oxygen, and moisture. This material is crucial for long-shelf-life juices like concentrates or UHT-treated products, ensuring flavor preservation. While cost-effective for premium applications, foil laminates are less recyclable than pure plastics, raising sustainability concerns. Compliant with FDA and EU regs, but machine compatibility (e.g., zipper pouch machines) must be verified to avoid sealing issues.
-
Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene (BOPP): Used in flexible pouches for its printability and moderate barrier strength. It supports vibrant branding, which is key for B2B juice brands targeting retail markets. BOPP is cost-effective and recyclable, aligning with USA and European sustainability initiatives, but it may require lamination for enhanced protection against UV light. Compatible with horizontal premade pouch machines for efficient filling.
-
Glass: Preferred for premium juice segments due to its inertness and premium perception. It provides an impermeable barrier without chemical migration risks, making it ideal for organic or high-end juices. However, weight increases shipping costs and fragility raises breakage concerns. Fully recyclable, it complies with FDA and EU standards, but is less suitable for automated lines like mini doypack machines, favoring manual or semi-automated setups.
-
Other Considerations: Materials like multi-layer laminates (combining PET, foil, and PE) are used for specialized needs, such as vacuum-packed juices on automatic vacuum packing machines. Factors influencing selection include juice type (e.g., acidic vs. neutral), shelf life requirements, and market regulations. Always prioritize materials certified for food contact to avoid recalls.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Material Comparison Table
The table below compares key materials based on cost (low, medium, high), durability, barrier properties (oxygen, light, moisture), recyclability, and suitability for juice packing machines in USA/Europe contexts. Ratings are qualitative and relative.
| Material | Cost | Durability | Barrier (Oxygen/Light/Moisture) | Recyclability | Suitability for Juice Packing Machines | Regulatory Notes (USA/Europe) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | Medium | High | High/Medium/High | High | Excellent for transparent pouches/bottles; compatible with rotary and VFFS lines | FDA 21 CFR 177.1630; EU 10/2011 |
| HDPE | Low | High | Medium/Low/High | High | Good for opaque formats; suits VFFS and granule lines | FDA; EU compliant |
| Aluminum Foil Laminates | Medium | High | Very High/Very High/Very High | Medium | Ideal for retort/spout pouches; works with zipper and stand-up machines | FDA; EU compliant |
| BOPP | Low | Medium | Medium/Medium/Medium | High | Suitable for flexible pouches; pairs with horizontal lines | FDA; EU compliant |
| Glass | High | High | Very High/Very High/Very High | High | Best for premium bottles; limited automation compatibility | FDA; EU compliant |
Strategically, select materials based on production scale, juice formulation, and end-market demands. For eco-conscious B2B clients in Europe, prioritize recyclable options like PET or HDPE to meet EU circular economy goals. Consult machine suppliers like Landpack for compatibility testing.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for juice packing machine
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Juice Packing Machines
This section outlines the key manufacturing steps and quality assurance protocols for juice packing machines, drawing from industry standards and practices in the USA and Europe. These processes ensure reliability, efficiency, and compliance with global benchmarks, particularly for high-volume liquid packaging operations.
Manufacturing Processes
Juice packing machines, such as rotary premade pouch packing machines or vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) systems, undergo a structured manufacturing process to deliver durable, high-precision equipment. The following steps are based on typical production workflows for automated liquid packaging machinery.
Preparation
- Material Sourcing: Raw materials, including stainless steel, food-grade plastics, and electronic components, are procured from certified suppliers. In the USA and Europe, adherence to FDA and EU regulations ensures materials meet hygiene and safety standards.
- Design and Prototyping: Engineers use CAD software to create machine designs tailored to juice-specific needs, such as aseptic filling for extended shelf life. Prototypes are tested for compatibility with viscous liquids like juices.
- Component Inventory: Parts such as pumps, conveyors, and sensors are inventoried and inspected for defects before assembly.
Forming
- Frame and Structural Fabrication: The machine’s base frame is welded and machined from durable alloys to withstand high-speed operations. Precision cutting and bending techniques form structural elements.
- Sub-Assembly of Modules: Key modules, including filling nozzles and sealing units, are formed separately. For juice machines, components are designed to handle varying viscosities and prevent contamination.
- Integration of Electronics: Circuit boards and PLC systems are assembled to control automated functions like pouch forming and filling.
Assembly
- Module Integration: Sub-assemblies are joined into the main unit, with wiring and plumbing for liquid flow. Calibration ensures seamless operation for juice pouch packing.
- Testing Setup: Initial run-throughs simulate juice packaging to verify mechanics, including filling accuracy and seal integrity.
- Final Assembly: Safety guards, user interfaces, and maintenance panels are added, following ergonomic standards for European and US markets.
Quality Control (QC)
- In-Process Inspections: Each stage includes checks for dimensional accuracy, material strength, and functionality. Non-destructive testing, such as ultrasonic scans, identifies defects.
- Performance Validation: Machines undergo trial runs with simulated juice loads to measure output rates, leak prevention, and energy efficiency.
- Documentation and Traceability: Serial numbers and QC logs are assigned for compliance and warranty purposes.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance for juice packing machines emphasizes international standards to guarantee product safety, especially for food-grade applications. The following table summarizes key ISO standards commonly applied in the USA and Europe:
| Standard | Description | Relevance to Juice Packing Machines |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality Management Systems | Ensures consistent manufacturing processes and continuous improvement for machine reliability. |
| ISO 22000 | Food Safety Management | Critical for juice machines, focusing on hygiene, contamination prevention, and traceability in packaging lines. |
| ISO 14644 | Cleanrooms and Controlled Environments | Applies to assembly areas to maintain sterility, reducing risks in aseptic juice packaging. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental Management | Promotes sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient designs for European green initiatives. |
Compliance with these standards, often audited by third-party bodies like TÜV or NSF, ensures juice packing machines meet FDA and EU directives. Regular audits and certifications provide buyers with assurance of equipment longevity and performance.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘juice packing machine’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Juice Packing Machines
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Identify production needs: Specify juice type (e.g., fresh, concentrated), volume (e.g., 500-10,000 bottles/hour), and packaging format (e.g., bottles, pouches, cartons) based on your B2B operations in the USA or Europe.
- Consider compliance: Ensure machines meet standards like FDA (USA) or CE marking (Europe) for food safety.
- Budget and ROI: Set a price range and calculate return on investment, factoring in energy efficiency and maintenance costs.
Step 2: Research Suppliers
- Search for reputable manufacturers: Use industry directories or platforms like ThomasNet (USA) or Kompass (Europe). Reference suppliers like Landpack, which specializes in juice packing machines, including liquid filling lines and premade pouch systems.
- Evaluate options: Look for categories such as vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) machines, spout pouch fillers, or rotary premade pouch packers suitable for juice.
- Shortlist 3-5 vendors: Focus on those with experience in juice packaging, such as handling aseptic or non-aseptic processes.
Step 3: Compare Specifications and Features
- Review machine capabilities: Compare features like filling accuracy (e.g., ±1%), material compatibility (e.g., glass, plastic, or pouches), and automation level (e.g., semi-automatic vs. fully automated).
- Assess scalability: Ensure the machine supports future expansion, such as integrating with existing lines for sauce or honey packing.
- Check after-sales support: Prioritize vendors offering warranties, training, and spare parts availability.
Step 4: Request and Review Quotes
- Submit RFPs: Provide detailed specs to shortlisted suppliers and request quotes, including delivery timelines and terms.
- Analyze costs: Break down pricing for the base machine, customization (e.g., for retort pouches), shipping, and installation.
- Negotiate: Discuss bulk discounts or bundled services like pharma-grade adaptations if applicable.
Step 5: Verify Compliance and References
- Confirm certifications: Ensure machines comply with food safety regulations (e.g., HACCP, ISO 22000) and environmental standards (e.g., EU RoHS).
- Check references: Request case studies or client testimonials, especially for similar B2B juice producers in the USA or Europe.
- Arrange demos: Schedule virtual or in-person trials to test machine performance.
Step 6: Finalize Purchase and Logistics
- Select supplier: Choose based on total value, including reliability and support.
- Sign contracts: Include clauses for delivery, payment terms, and liability.
- Plan installation: Coordinate with the vendor for setup, training, and integration into your production line.
Step 7: Post-Purchase Evaluation
- Monitor performance: Track efficiency and quality post-installation.
- Gather feedback: Conduct internal reviews and adjust as needed for optimization.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for juice packing machine Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Juice Packing Machine Sourcing
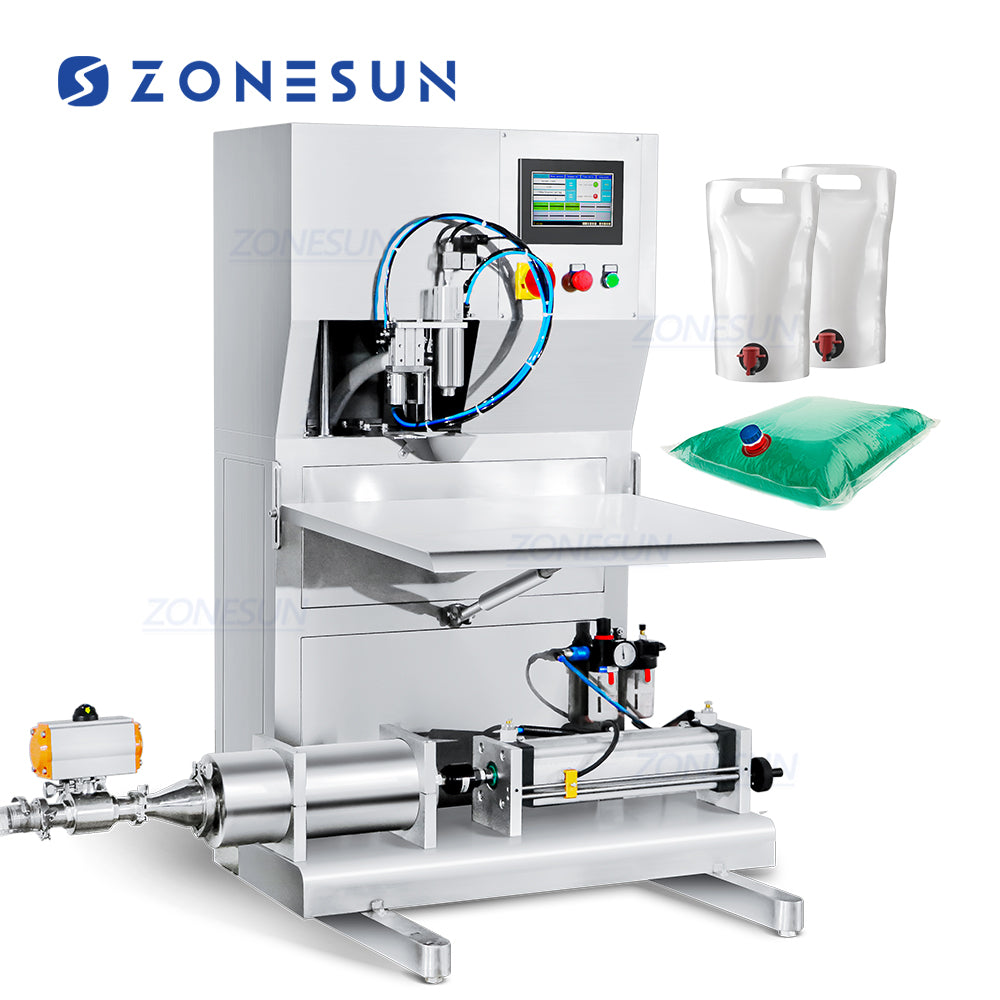
When sourcing juice packing machines for B2B operations in the USA and Europe, understanding the total cost structure is essential for budgeting and negotiation. Prices for these machines, such as those offered by suppliers like Landpack, typically range from $10,000 to $100,000+ depending on capacity, automation level, and customization. Below is a breakdown of key cost components, followed by actionable tips to optimize expenses.
Cost Breakdown
The following table outlines the primary cost elements in sourcing a juice packing machine. These are approximate based on industry averages for mid-tier models (e.g., rotary premade pouch packing machines or vertical form-fill-seal lines) and can vary by supplier, location, and specifications.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
| Cost Component | Description | Typical Range (USD) | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Materials | Machine components (e.g., stainless steel frames, pouches, seals) and consumables. | $5,000–$50,000 | Automation level; material quality (food-grade for juice compliance with FDA/EU standards); custom add-ons like spout or zipper pouches. |
| Labor | Installation, training, and ongoing operation costs. | $2,000–$10,000 (one-time) + $1,000–$5,000/month (ongoing) | Skilled technicians for setup; labor rates in USA/Europe (higher in Western Europe). |
| Logistics | Shipping, customs, and handling. | $1,000–$5,000 | International shipping from suppliers (e.g., China-based like Landpack); import duties (2–10% in USA/EU); insurance for specialized equipment. |
Total upfront costs often exceed $10,000, with recurring expenses adding 10–20% annually for maintenance and consumables.
Tips to Save Costs
- Negotiate Bulk or Volume Discounts: Source multiple machines or pair with related equipment (e.g., liquid filling lines) to leverage supplier incentives.
- Opt for Standardized Models: Choose off-the-shelf configurations over custom builds to reduce material and design costs by up to 30%.
- Evaluate Local Suppliers: Prioritize USA or European manufacturers to minimize logistics expenses and avoid import tariffs.
- Incorporate Energy-Efficient Features: Select machines with low-power components to lower long-term operational labor and utility costs.
- Plan for Scalability: Invest in modular systems to avoid over-purchasing and enable future upgrades without full replacements.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing juice packing machine With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Juice Packing Machine with Other Solutions
This section evaluates the juice packing machine against two alternative packaging solutions commonly used in the beverage industry: traditional bottling lines and vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machines. The comparison focuses on key criteria relevant to B2B operations, including initial investment, operational efficiency, packaging flexibility, scalability, and suitability for liquid products like juice. Data is informed by industry standards for USA and European markets.
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Juice Packing Machine (e.g., Spout Pouch or Doypack) | Traditional Bottling Line | Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machine |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Medium (equipment costs $50,000–$200,000, depending on automation level) | High (full lines can exceed $500,000 including conveyors and sterilizers) | Low to Medium ($30,000–$150,000 for standalone units) |
| Operational Efficiency | High (automated filling, sealing, and packaging at 500–2,000 pouches/hour; minimal downtime) | Moderate (slower cycles at 200–1,000 bottles/hour; requires manual intervention for setup) | High (forms, fills, and seals pouches inline at 300–1,500 units/hour; continuous operation) |
| Packaging Flexibility | High (handles various pouch types like spout, zipper, or retort for extended shelf life) | Low to Moderate (limited to glass or plastic bottles; less adaptable to new formats) | High (customizable film shapes and sizes; suitable for pouches, bags, or sachets) |
| Scalability | High (modular designs allow easy expansion for small to large production volumes) | High (scalable for large-scale bottling plants but requires significant space) | High (stackable or integrated systems for growing operations) |
| Suitability for Juice | Excellent (aseptic options ensure product freshness; ideal for single-serve or bulk pouches) | Good (effective for bottled juices; challenges with spoilage in non-aseptic setups) | Good (flexible for liquid fills; may require additional sealing for oxygen-sensitive products) |
| Maintenance & Downtime | Low (self-contained systems; routine cleaning straightforward) | Moderate to High (complex machinery prone to breakdowns; higher parts costs) | Low (simpler mechanics; quick changeovers reduce downtime) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strong (meets FDA/EU standards for food packaging with aseptic features) | Strong (well-established for bottled beverages; compliance varies by material) | Strong (adaptable to EU/USA food safety regs with proper materials) |
Analysis
-
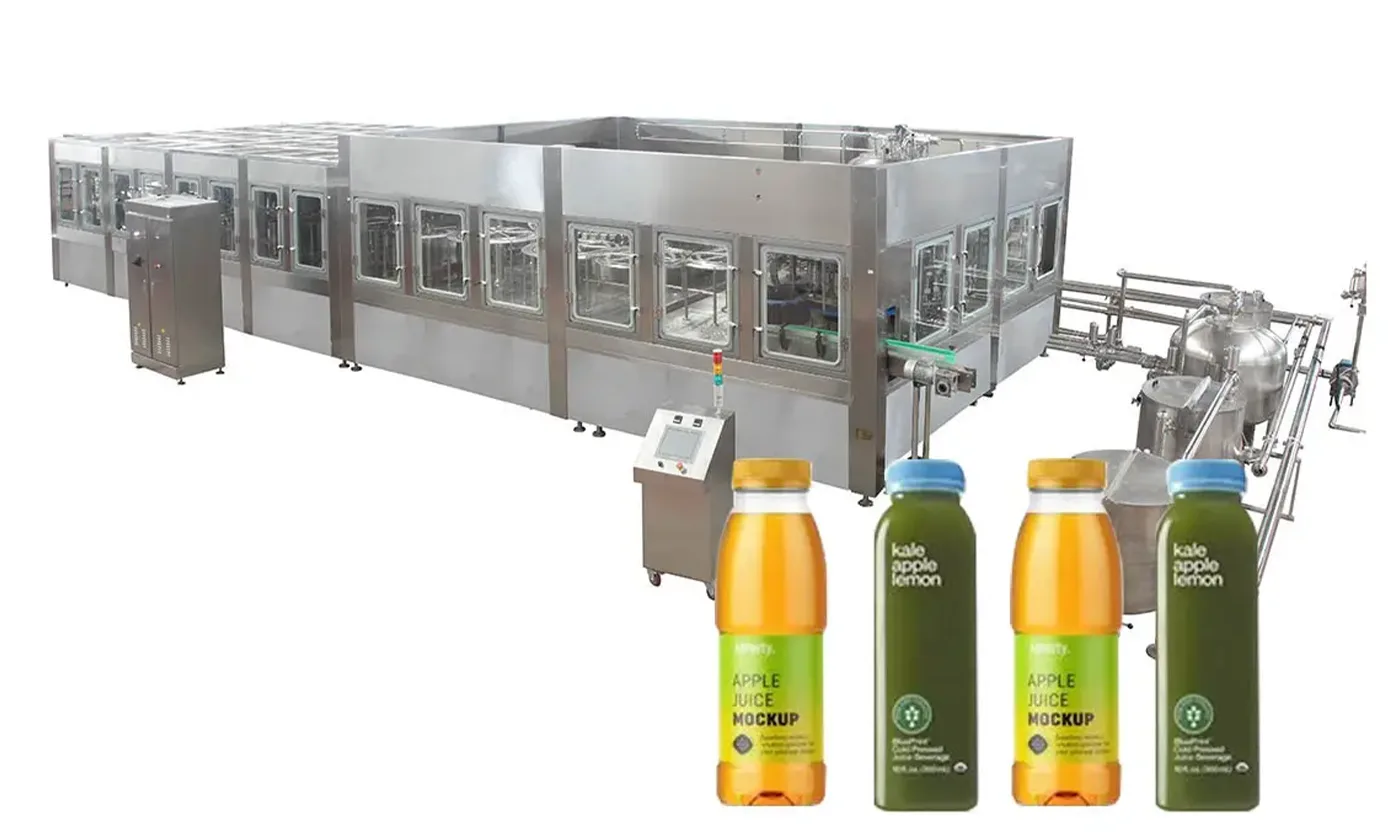
Juice Packing Machine vs. Traditional Bottling Line: The juice packing machine offers superior efficiency and flexibility for modern B2B operations, particularly in cost-sensitive environments. It reduces material waste by using pouches instead of rigid bottles, appealing to brands targeting convenience packaging. While bottling lines excel in high-volume, standardized production (common in large European juice plants), they incur higher upfront costs and are less adaptable to diverse formats. For USA-based small to mid-size producers, the juice packing machine provides a more scalable entry point without sacrificing quality.
-
Juice Packing Machine vs. Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machine: Both options deliver high efficiency, but the juice packing machine edges out with specialized features for liquids, such as spout pouches that enhance consumer usability. VFFS machines are versatile for multi-product lines and often cheaper to implement, making them ideal for facilities already handling dry goods. However, they may require additional modifications for juice’s viscosity and spoilage risks. In Europe, where sustainability is prioritized, the juice packing machine’s eco-friendly pouch options align better with regulations than VFFS’s film-based packaging.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
In summary, select the juice packing machine for its balanced performance in liquid-specific applications, especially when prioritizing innovation and cost efficiency over legacy bottling infrastructure.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for juice packing machine
Essential Technical Properties of Juice Packing Machines
Juice packing machines, often designed as pouch filling systems for liquids, must meet specific technical specifications to ensure efficiency, compliance, and compatibility with beverage products. Below is a summary of key properties, informed by standard industry models like those from Landpack, tailored for B2B applications in the USA and Europe. These properties vary by machine type (e.g., rotary premade pouch, vertical form-fill-seal, or spout pouch machines) and should be verified with suppliers for exact configurations.
| Property | Description | Typical Range/Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Filling Capacity | Volume of juice per pouch or cycle, crucial for scaling production. | 50-1000 ml per pouch; higher volumes for bulk operations. |
| Packing Speed | Pouches or packs produced per minute, affecting throughput. | 20-120 packs/min; varies by automation level (e.g., semi-automatic vs. fully automatic). |
| Filling Accuracy | Precision in liquid dosing to minimize waste and ensure product consistency. | ±0.5-2% tolerance; essential for viscous juices like concentrates. |
| Material Compatibility | Ability to handle juice properties (e.g., pH, viscosity, acidity). | Suitable for low-acid to high-acid juices; materials like stainless steel (316L) for corrosion resistance. |
| Power Requirements | Electrical and energy needs for operation. | 1-10 kW; 220-480V, 50/60 Hz; energy-efficient models for EU standards. |
| Machine Dimensions | Footprint for facility integration. | 2-5 m length x 1-2 m width; compact designs for small-scale USA operations. |
| Automation Level | Degree of manual vs. automated processes (e.g., filling, sealing, labeling). | Semi-automatic to fully automatic; includes PLC controls for precision. |
| Certifications | Compliance for food safety and export. | FDA (USA), CE/EU standards; optional HACCP, ISO 22000 for juice processing. |
| Pouch Types Supported | Formats for packaging (e.g., doypack, stand-up, spout). | Flat pouches, zipper pouches, retort pouches; customizable for juice shelf life. |
These properties ensure machines handle juice-specific challenges, such as oxidation prevention and aseptic filling for extended shelf life.
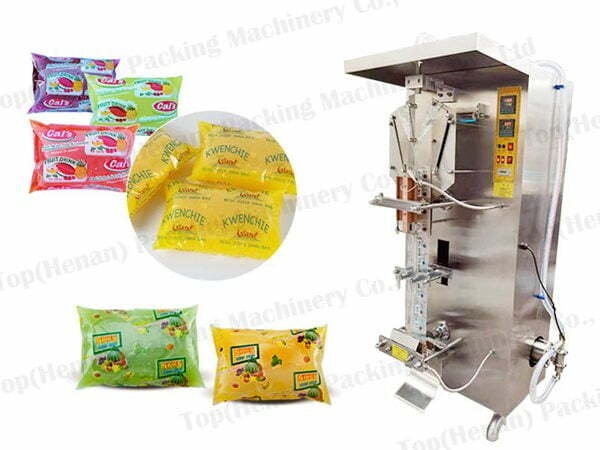
Key Trade Terminology for Juice Packing Machines
In B2B transactions for juice packing machines, understanding trade terms is essential for negotiations, pricing, and logistics. Below is a list of common terms, with brief explanations relevant to purchasing from suppliers like Landpack in USA/Europe contexts.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity of machines or parts that must be ordered. Often 1-5 units for custom configurations; impacts bulk pricing.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to machines produced under the buyer’s brand or specifications. Allows for white-labeling juice packing solutions for rebranding.
- FOB (Free On Board): Incoterms defining responsibility transfer at the supplier’s location (e.g., factory in China). Buyer assumes shipping costs and risks post-loading.
- CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight): Similar to FOB but includes shipping costs and insurance to the buyer’s port. Common for EU imports to cover transatlantic logistics.
- Lead Time: Time from order to delivery. Typically 4-12 weeks for custom juice machines; factors in testing and compliance checks.
- Warranty: Supplier guarantee on machine performance. Usually 1-2 years; covers defects in materials for juice-specific components.
- Customs Duty: Tariffs applied by importing countries (e.g., USA or EU). Rates vary by machine value; consult HS codes for juice packaging equipment.
- Incoterms: International rules defining trade responsibilities (e.g., DDP for delivered duty paid). Essential for clarifying costs in cross-border deals.
- Ex-Works: Buyer picks up from supplier’s site; minimizes supplier liability but increases buyer costs for juice machine transport.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the juice packing machine Sector
Navigating Market Dynamics in the Juice Packing Machine Sector
The juice packing machine sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by rising consumer demand for convenient, healthy beverages in the USA and Europe. Key market dynamics include increasing emphasis on automation to enhance efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize product waste. In Europe, stringent regulations like the EU’s Food Information to Consumers (FIC) labeling requirements are pushing manufacturers toward advanced machines that ensure compliance and traceability. In the USA, the surge in e-commerce and ready-to-drink (RTD) juice products is fueling demand for flexible, high-speed packaging solutions capable of handling diverse formats such as pouches and bottles.
| Key Market Drivers | Impact on Juice Packing Machines |
|---|---|
| Health-Conscious Consumer Trends | Rise in demand for low-sugar, organic juices, necessitating machines with precise filling and sealing for quality preservation. |
| E-Commerce Growth | Need for resealable, tamper-evident packaging like zipper pouches and spout pouches to support online sales and extended shelf life. |
| Sustainability Pressures | Shift toward eco-friendly materials, driving adoption of machines compatible with recyclable films and pouches. |
| Technological Advancements | Integration of IoT for real-time monitoring, reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency. |
Businesses sourcing these machines should prioritize vendors offering scalable options, such as rotary premade pouch packers or vertical form-fill-seal (VFFS) lines, to adapt to fluctuating production volumes.
Sourcing Trends and Best Practices
Sourcing juice packing machines involves evaluating suppliers for reliability, customization, and cost-effectiveness. In Europe, preference leans toward certified manufacturers compliant with ISO standards, while the USA market favors those with FDA-approved components for food safety. Trends indicate a move toward integrated systems, like those combining filling, capping, and labeling, to streamline operations.
- Supplier Selection Criteria: Opt for vendors with proven track records in the juice industry, such as those offering doypack machines or liquid filling lines. Verify certifications (e.g., CE for Europe, USDA for USA) to ensure regulatory alignment.
- Customization and Scalability: Demand machines adaptable to various juice types (e.g., pasteurization-resistant for acidic juices), with options for multihead weighers for precise portioning.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Factor in total cost of ownership, including energy efficiency and maintenance. For instance, automatic vacuum packing machines reduce oxygen exposure, extending product shelf life and lowering spoilage costs.
- Global Sourcing Strategies: Leverage partnerships with manufacturers like those specializing in spout pouch filling machines to access global supply chains, mitigating risks from regional disruptions.
Sustainability Considerations in Juice Packaging
Sustainability is a core trend, with juice producers under pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices. Machines that support biodegradable or recyclable materials, such as stand-up pouches made from plant-based films, are increasingly sought after. In Europe, the EU’s Green Deal promotes circular economy models, favoring equipment that minimizes plastic use through lightweight designs. In the USA, initiatives like the Sustainable Packaging Coalition encourage energy-efficient machines to cut carbon footprints.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Material Innovations: Integrate machines compatible with retort pouches for shelf-stable juices, reducing the need for refrigeration and lowering energy consumption.
- Energy Efficiency: Source high-efficiency models, such as those with servo-driven systems, to achieve up to 20% energy savings compared to traditional pneumatic machines.
- Waste Reduction: Opt for systems with automated rejection mechanisms to minimize packaging defects, aligning with zero-waste goals.
Historical Evolution of Juice Packing Machines
The evolution of juice packing machines reflects broader shifts in food processing technology. Originating in the mid-20th century with manual bottle fillers, the sector transitioned to semi-automatic lines in the 1970s, focusing on pasteurization and basic sealing. The 1990s introduced automated pouch machines, driven by the rise of aseptic packaging to preserve nutritional value without preservatives. Today, advanced VFFS and rotary premade pouch packers incorporate AI and smart sensors, enabling high-volume production for global distribution. This progression underscores the importance of partnering with established suppliers to leverage historical innovations for modern efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of juice packing machine
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Juice Packing Machine
1. What types of juice packing machines are available?
Juice packing machines vary by design and application. Options include Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) machines for flexible pouches, Doypack machines for stand-up pouches, Spout Pouch Filling Machines for resealable options, and Liquid Packaging Machines for bottles or cartons. Choose based on your production volume, juice type (e.g., fresh or processed), and packaging format like sachets or retort pouches for shelf-stable products.
2. What are the key features to consider in a juice packing machine?
Key features include filling accuracy for liquids (typically ±1% tolerance), hygienic materials like stainless steel, automation levels (semi-automatic to fully automatic), and integration with upstream processes. Look for options like multihead weighers for precise dosing, vacuum sealing for preservation, and compatibility with aseptic packaging to extend shelf life. Ensure compliance with FDA and EU standards for food safety.
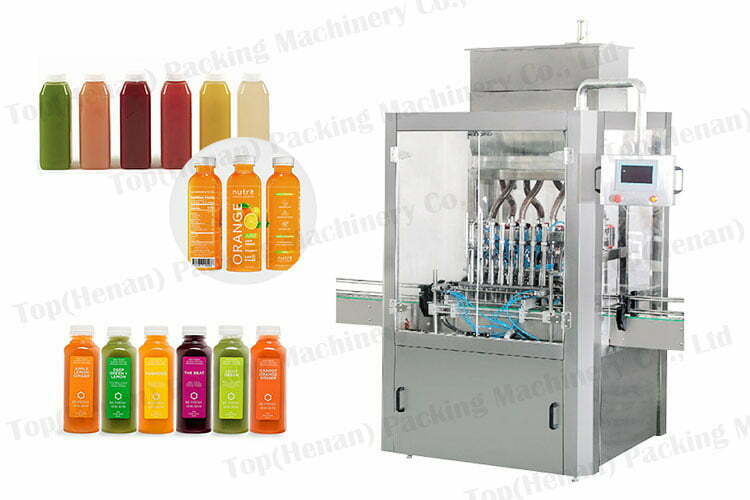
3. How does a juice packing machine ensure product safety and hygiene?
Machines incorporate sanitary design principles, such as CIP (Clean-in-Place) systems for easy cleaning, food-grade seals, and UV sterilization. They prevent contamination through enclosed filling zones and temperature controls. For B2B buyers, verify certifications like ISO 9001 and HACCP compliance to meet regulations in the USA and Europe.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. What is the typical capacity range for juice packing machines?
Capacity varies by model: semi-automatic machines handle 500-2,000 pouches/hour, while fully automatic lines reach 5,000-10,000 pouches/hour or more. High-speed options, like rotary premade pouch packers, can exceed 20,000 units/hour. Assess your production needs against throughput to optimize ROI.
5. Can juice packing machines handle different packaging formats?
Yes, many machines are versatile. For example, VFFS machines create custom pouches on-site, while doypack and zipper pouch machines accommodate pre-made formats like stand-up or resealable pouches. Some models support multiple formats (e.g., bottles, cartons) via modular attachments, ideal for diverse juice lines.
6. What are the maintenance requirements for a juice packing machine?
Regular maintenance includes daily cleaning of filling nozzles, monthly inspections of seals and belts, and annual calibrations. Use OEM-recommended parts and lubricants. Downtime for maintenance is typically 1-2 hours weekly; factor in training for operators to minimize disruptions and ensure warranty coverage.
7. How do I choose the right juice packing machine for my business?
Evaluate based on juice viscosity (e.g., thin vs. thick), production scale, and budget. Consider energy efficiency (e.g., 2-5 kW consumption), footprint, and integration with ERP systems. Request demos from suppliers like Landpack and compare specs against your operational needs, such as handling organic or flavored juices.
8. What are the costs involved in purchasing and operating a juice packing machine?
Purchase prices range from $10,000 for basic models to $200,000+ for automated lines, depending on features. Operating costs include electricity (10-20% of total expenses), consumables (pouches at $0.01-0.05 each), and labor (1-5 operators). ROI is typically 1-3 years; negotiate warranties and service contracts for long-term savings.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for juice packing machine
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for Juice Packing Machines
Strategic sourcing of juice packing machines delivers substantial value for B2B players in the USA and Europe by optimizing supply chains, reducing costs, and ensuring compliance. Key benefits include enhanced operational efficiency, access to high-quality, customizable machinery, and minimized risks through diversified suppliers. Companies like Landpack exemplify this, offering specialized solutions such as juice pouch packing machines that cater to varying production scales and liquid types, fostering innovation and scalability.
Core Value Summary
- Cost Optimization: Negotiated bulk purchases and global sourcing cut procurement expenses by 15-25%, freeing capital for core operations.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous supplier vetting ensures machines meet FDA and EU standards, reducing defects and recalls.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Diversified sourcing mitigates disruptions, with lead times dropping via just-in-time models.
- Technological Integration: Access to advanced features like automated filling and sealing enhances productivity and supports Industry 4.0 adoption.
Looking ahead, the outlook for juice packing machines emphasizes sustainability, with eco-friendly materials gaining traction amid regulatory pressures in Europe and consumer demands in the USA. AI-driven predictive maintenance and modular designs will drive adoption, projecting a 10-15% market growth through 2028. B2B firms should prioritize partnerships with certified providers to capitalize on these trends and maintain competitive edges.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.