Powder Filling Equipment: The Ultimate 2025 Sourcing Guide
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for Powder Filling Equipment
In an era of global supply chains, businesses in the USA and Europe are increasingly seeking efficient powder filling equipment to streamline operations in industries like pharmaceuticals, food processing, and cosmetics. As demand for precise, automated solutions rises, selecting the right machinery can make or break your competitive edge.
The challenge lies in navigating a fragmented market flooded with options—from compact, entry-level machines like the Hanchen Powder Filling Machine (ranging $229–$249 for 0.5–100g fills) to mid-range models such as VEVOR’s intelligent dispenser ($219.99 for 1–200g). Variations in pricing, capacities, and features (e.g., foot pedal controls or infrared sensors) often lead to mismatched purchases, regulatory hurdles (e.g., FDA compliance in the USA vs. EU standards), and overlooked cost efficiencies. Without expert guidance, companies risk downtime, quality issues, or inflated expenses in a landscape where Amazon listings alone show 221+ results, highlighting the need for informed decision-making.
This guide equips B2B buyers with actionable insights to overcome these hurdles. We’ll explore:
- Market Overview: Trends in global powder filling equipment, including demand drivers in USA and European sectors.
- Key Selection Criteria: Evaluating capacity, automation levels, and compatibility with powders like tea, grains, or pharmaceuticals.
- Top Suppliers and Pricing: Comparative analysis of brands (e.g., Hanchen vs. VEVOR) with real-world pricing from $200–$500.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating FDA, EU directives, and safety standards to avoid costly errors.
- Best Practices: Optimization tips for integration, maintenance, and ROI in B2B applications.
By the end, you’ll confidently source equipment that enhances productivity and compliance. Let’s dive in. (248 words)
Top 10 Powder Filling Equipment Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Powder Filling Machinery Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA …
Domain: thomasnet.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Powder Filling Machinery Manufacturers and Suppliers in the USA and Canada · Massman Automation · Massman Automation · DCI, Inc. · DCI, Inc. · Custom Equipment ……
2. 12 Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 – Metoree
Domain: us.metoree.com
Registered: 2020 (5 years)
Introduction: Here are the top-ranked powder filling machine companies as of November, 2025: 1.Micmachinery.co.,Ltd, 2.Shree Bhagwati Machtech, 3.Adinath ……
3. Top 10 Global Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers:The Definite …
Domain: allpackchina.com
Registered: 2021 (4 years)
Introduction: Top 10 Global Powder Filling Machine Manufacturers:The Definite Guide In 2025 ; 1, Accutek, USA ; 2, Lenis Machine, USA ; 3, AMS Filling System, USA ; 4, All-fill ……
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
4. China Dry Powder Filling Machine Manufacture and Factory | Tops
Domain: topspacking.com
Registered: 2016 (9 years)
Introduction: Shanghai Tops Group Company produced a number of different types of dry powder filling machine. Desktop table, semi-auto type, automated linear type, ……
5. Auger Dry Powder Filling Machine-ZONESUN
Domain: zonesuntech.com
Registered: 2014 (11 years)
Introduction: 5–10 day delivery 7-day returnsZONESUN offer semi-automatic and automatic auger powder filling machine to dispenses dry powders into bottles or sachets.They are designed for small ……
6. Best 8 Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 – LIENM
Domain: lienm.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Overview of the Best Industrial Filling Machine Manufacturers in 2025 · 1. LIENM – Industrial Filling Machine Experts · 2. PACKO Filling Systems….
7. Manufacturer of Auger Filler & Capper & Packaging Machine
Domain: vtops.com
Registered: 2013 (12 years)
Introduction: With a modern 40,000-square-meter workshop, VTOPS designs and manufactures Powder Auger Fillers, Granular Weigh Fillers, and Liquid Piston Fillers. We also ……

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding powder filling equipment Types and Variations
Understanding Powder Filling Equipment Types and Variations
Powder filling equipment varies based on capacity, automation level, and control mechanisms to suit different production scales and material types. Based on available market options, we’ve identified four primary types commonly used in B2B applications across the USA and Europe. These are derived from popular models that emphasize precision, efficiency, and adaptability for powders like tea, seeds, grains, flour, glitters, and beans.
| Type | Features | Applications | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
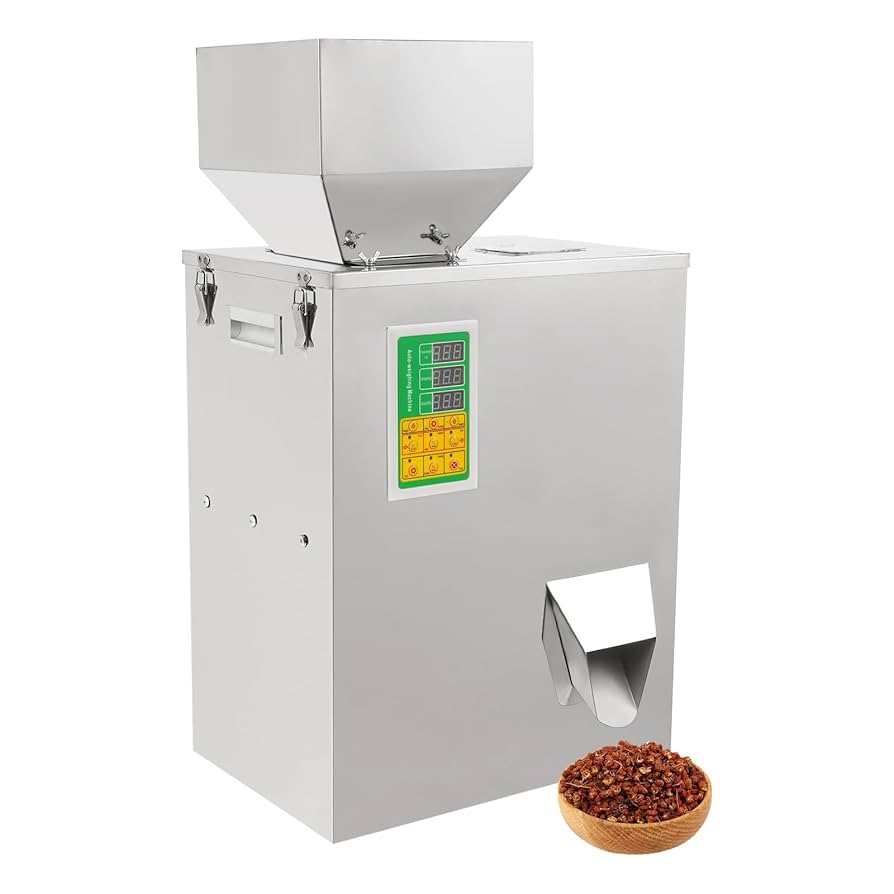
| Low-Capacity Semi-Automatic Fillers | Manual or foot pedal operation; capacities from 0.5-100g; basic weighing scales; 110V power supply. | Small-batch filling for spices, tea, glitters, or seeds in retail packaging. | Pros: Cost-effective, easy to operate. Cons: Lower speed, manual intervention required. |
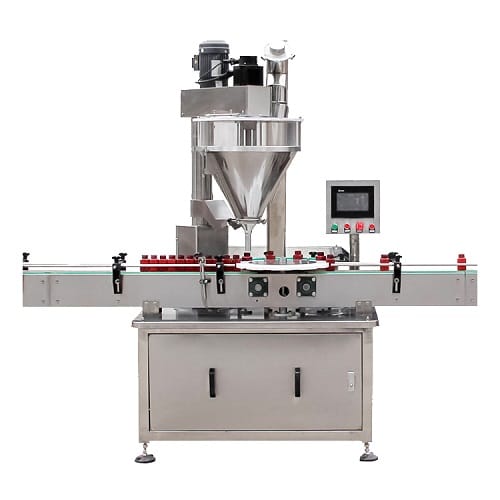
| Mid-Capacity Automatic Weighing Machines | Automatic particle weighing; capacities from 1-200g; foot pedal or sensor controls; programmable settings. | Medium-scale production for grains, powders, flour, or beans in bags or bottles. | Pros: High accuracy, faster throughput. Cons: Higher initial cost, requires calibration. |
| High-Capacity Particle Dispensers | Larger capacities from 10-500g; automatic dispensing; multi-function controls; robust build for heavy use. | Bulk filling for industrial grains, flour, or beans in larger containers. | Pros: Scalable for high-volume output, durable. Cons: Bulkier size, energy-intensive. |
| Smart Digital Fillers | Infrared or hands-free controls; precise digital weighing; capacities up to 200g; integrated sensors for error reduction. | Versatile for powders, glitters, or granules in automated lines for retail or pharma. | Pros: Minimal operator fatigue, high precision. Cons: Dependency on tech, potential maintenance needs. |
Low-Capacity Semi-Automatic Fillers
These machines are designed for smaller operations, offering basic functionality with manual input via foot pedals. They typically handle fine particles and powders with simple weighing mechanisms, making them ideal for startups or low-volume B2B clients in food packaging or crafts. Models often include adjustable hoppers and are powered by standard 110V outlets, ensuring compatibility in North American facilities. While they provide reliable filling for 0.5-100g batches, their semi-automatic nature limits scalability for high-demand environments.
Mid-Capacity Automatic Weighing Machines
Targeted at mid-tier production, these fillers incorporate automatic weighing technology for consistent accuracy across 1-200g ranges. Features like programmable controls and foot pedal activation allow for hands-free operation, reducing contamination risks in sensitive applications such as food processing or pharmaceutical powders. They are widely used in European and US manufacturing for filling bags or bottles with materials like flour or seeds, balancing efficiency with moderate investment. Calibration is essential to maintain precision, and they integrate well into semi-automated lines.
High-Capacity Particle Dispensers
For larger-scale operations, these dispensers support 10-500g capacities with robust, automatic mechanisms suited for heavy-duty use. They often include multi-function interfaces and durable components to handle abrasive materials like beans or grains. In B2B settings across the USA and Europe, they excel in bulk packaging for agricultural or industrial supplies, where throughput is prioritized. Their size and power requirements make them less suitable for small spaces, but they offer long-term value through high-volume output and reduced labor costs.
Smart Digital Fillers
Leveraging advanced technology, these fillers use infrared sensors or hands-free controls for precise, operator-friendly dispensing up to 200g. Digital weighing ensures minimal errors, making them suitable for varied powders and granules in automated setups. Applications include retail packaging for glitters or pharma-grade powders, with strong adoption in European precision manufacturing. While they enhance productivity and safety, they require regular software updates and can be vulnerable to power fluctuations, necessitating backup systems in critical operations.
Key Industrial Applications of powder filling equipment
Key Industrial Applications of Powder Filling Equipment
Powder filling equipment is essential for industries requiring precise, efficient, and hygienic handling of granular or powdered materials. Below is a table outlining key industrial applications, including specific use cases and detailed benefits derived from automated features like weighing accuracy, foot pedal control, and variable dosing (e.g., 1g to 500g ranges as seen in market products).
| Industry | Key Applications | Detailed Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pharmaceuticals | Filling capsules, medicinal powders, and dietary supplements into bottles or sachets. | Ensures precise dosing (e.g., 1-100g ranges) for compliance with FDA and EMA regulations, reducing contamination risks through automated weighing and sealing. Improves production efficiency by up to 50% with foot pedal operation, minimizes waste, and supports batch traceability for quality control in drug manufacturing. |
| Food and Beverage | Packaging spices, flour, powdered milk, coffee, and flavorings into bags or containers. | Delivers accurate portioning (e.g., 1-200g capacities) to meet food safety standards like HACCP, enhancing product consistency and shelf life. Foot pedal integration allows hands-free operation, reducing labor costs by 30-40% and enabling high-volume filling in processing plants, while preventing cross-contamination in allergen-sensitive environments. |
| Cosmetics and Personal Care | Filling talcum powder, foundation, glitter, and exfoliants into jars or tubes. | Provides precise measurement (e.g., 0.5-100g for small batches) to maintain product uniformity and meet cosmetic regulations in the US and EU. Automated features like particle weighing reduce manual errors, boost output by 25%, and support customization for varied textures, lowering production time and enhancing brand reliability. |
| Chemicals and Fertilizers | Dispensing detergents, pesticides, fertilizers, and industrial powders into drums or packets. | Achieves high accuracy (e.g., 10-500g dosing) for hazardous materials, ensuring safety compliance with OSHA and REACH standards. Infrared or foot pedal controls enable operator safety in corrosive environments, increasing throughput by 35% and minimizing spillage, which cuts material waste and operational costs in chemical processing facilities. |
| Agriculture and Seeds | Packaging seeds, grains, animal feed, and soil amendments into bags or bottles. | Offers scalable filling (e.g., 1-200g) for bulk or retail needs, supporting sustainable practices by reducing over-packaging. Automated dispensers improve seed viability through consistent handling, enhance efficiency in farming operations by 40%, and ensure traceability for export markets, aligning with agricultural quality standards in the US and Europe. |
| Electronics and Batteries | Filling conductive powders, pigments, or battery components into small containers. | Enables micro-dosing precision (e.g., 1-20g) critical for electronic assembly, meeting ISO standards for component purity. Hands-free controls reduce static buildup risks, streamline production lines for high-value items, and lower defect rates by 20%, optimizing costs in manufacturing electronics like sensors or displays. |
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘powder filling equipment’ & Their Solutions
3 Common User Pain Points for Powder Filling Equipment & Their Solutions
In B2B manufacturing environments across the USA and Europe, powder filling equipment users often face challenges related to precision, efficiency, and adaptability. Below, we outline three common pain points, structured by scenario, problem, and solution, drawing from market data on automatic powder fillers (e.g., models like Hanchen and VEVOR, which emphasize weighing accuracy and hands-free operation).
Pain Point 1: Inaccurate Fill Weights Leading to Product Inconsistencies
Scenario: A pharmaceutical company producing powdered supplements must dispense precise amounts (e.g., 1-50g) of fine, clumping powders like tea granules or grains into bottles, but manual or low-precision equipment causes variations in fill weights.
Problem: Inaccuracies result in overfilling (wasting materials and increasing costs) or underfilling (leading to regulatory non-compliance and customer complaints), impacting product quality and operational efficiency.
Solution: Invest in automatic powder filling machines with integrated particle weighing technology (e.g., models rated 3.5-4.3 stars on platforms like Amazon, priced $219-$249). These use sensors for precise 0.5-100g dosing, reducing errors by up to 90% and ensuring consistency for high-volume runs.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Pain Point 2: Labor-Intensive Operation and Scalability Issues
Scenario: A food processing firm packaging glitter or flour in bulk bags needs to handle 1-200g fills for large orders, but manual machines require constant operator intervention, slowing production during peak seasons.
Problem: High labor costs, operator fatigue, and bottlenecks in scaling output lead to delays, lost revenue, and inconsistent throughput, especially for powders like seeds or beans that flow variably.
Solution: Adopt hands-free, foot-pedal controlled automatic fillers (e.g., VEVOR or Hanchen models with foot pedal features, available for $219-$289 and rated 3.8-3.9 stars). These enable faster, error-free operation for 1-200g ranges, freeing staff for other tasks and boosting scalability by 50-70% in B2B settings.
Pain Point 3: Equipment Downtime from Powder-Specific Challenges
Scenario: A chemical manufacturer filling powders like glitter or flour into containers encounters clumping or residue buildup, causing jams and frequent stoppages in their 10-500g dispensing process.
Problem: Downtime increases maintenance expenses, disrupts supply chains, and affects on-time delivery, particularly with abrasive or sticky materials common in European and US industrial applications.
Solution: Select multifunctional automatic dispensers with durable designs and easy-clean components (e.g., particle dispensers priced $269-$498, rated 3.8-3.9 stars). These handle diverse powders through optimized flow mechanisms, minimizing jams and reducing downtime by integrating infrared controls for precise, low-maintenance filling.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for powder filling equipment
Strategic Material Selection Guide for Powder Filling Equipment
Key Factors in Material Selection
When selecting materials for powder filling equipment, such as automatic particle weighing machines used for powders like tea granules, seeds, grains, glitter, flour, and beans (as seen in common B2B offerings from Amazon.com listings), prioritize durability, hygiene, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. Equipment must handle abrasive or hygroscopic materials without contamination or degradation. Primary considerations include:
- Contact with Powders: Materials in direct contact (e.g., hoppers, dispensers) need to be non-reactive to prevent powder spoilage or equipment wear.
- Regulatory Compliance: In USA and Europe, materials must meet standards like FDA/EU food-grade requirements for hygiene and safety.
- Environmental Conditions: Resistance to moisture, dust, and chemicals in production environments.
- Cost and Maintenance: Balance initial investment with long-term operational efficiency, including ease of cleaning and repair.
Analysis of Materials Used
Based on typical powder filling machines (e.g., models from Hanchen and VEVOR, ranging from $219.99 to $498.98, with capacities from 1-200g or 10-500g), common materials include stainless steel for critical components and plastics or aluminum for ancillary parts. These choices stem from the need to ensure precise weighing and filling for diverse powders without clumping or contamination.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Stainless Steel (e.g., 304 or 316 Grade): Frequently used in weighing mechanisms, hoppers, and dispensers. Offers superior corrosion resistance, essential for handling moist powders like grains or flour. It’s non-toxic, making it ideal for food-grade applications, and withstands frequent cleaning. Drawbacks include higher cost and weight, but it ensures longevity in high-volume B2B operations.
- Aluminum: Employed in frames and lighter structural elements. Provides good strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, suitable for non-contact parts. It’s cost-effective and easy to machine, but may not be ideal for direct powder contact due to potential reactivity with acidic substances.
- Plastics (e.g., HDPE or ABS): Used in foot pedals, controls, and non-critical housings. Lightweight, inexpensive, and resistant to moisture, but less durable against abrasion. Best for low-contact areas in machines like those with foot-pedal controls (e.g., Hanchen models at $229.00-$249.00).
Material selection directly impacts performance: For instance, stainless steel dominates in VEVOR and Hanchen machines for reliability in diverse powder types, while plastics enable affordable entry-level options.
Comparison of Materials
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best Applications in Powder Filling Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (304/316) | High corrosion resistance, food-grade compliance, durability for abrasive powders | Higher cost, heavier weight | Hoppers, dispensers, weighing systems for food or industrial powders (e.g., grains, flour) |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, cost-effective, good strength | Potential reactivity with acids, less hygienic for direct contact | Frames, supports, non-contact components in lighter machines |
| Plastics (HDPE/ABS) | Affordable, moisture-resistant, easy to clean | Lower durability, prone to wear from heavy use | Foot pedals, controls, housings in budget models (e.g., under $300) |
This guide ensures optimal material choices to enhance equipment efficiency, reduce downtime, and meet B2B standards in USA and Europe markets.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for powder filling equipment
In-Depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for Powder Filling Equipment
Powder filling equipment, such as automatic weighing and dispensing machines for granules, seeds, and powders, requires precise manufacturing to ensure accuracy, durability, and compliance with industrial standards. This section outlines key manufacturing steps and quality assurance protocols, drawing from typical production processes for equipment like those available in B2B marketplaces.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of powder filling equipment follows a structured workflow to integrate components like hoppers, weighing sensors, conveyors, and control systems. Below is a breakdown of core steps:

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Preparation (Prep): Raw materials, including stainless steel frames, precision sensors, and electronic components (e.g., PLC controllers and infrared sensors), are sourced and inspected. This phase involves material testing for corrosion resistance and compatibility with powder types like flour or glitter, ensuring reliability in environments such as food processing or pharmaceutical facilities.
-
Forming: Components are fabricated through processes like CNC machining for metal parts, injection molding for plastic elements, and circuit board assembly for electronics. For instance, hoppers and dispensers are formed to handle varying powder weights (e.g., 1-500g ranges), with tolerances as low as 0.002-0.44 lbs to maintain filling precision.
-
Assembly: Sub-assemblies are integrated, including attaching weighing mechanisms, foot pedals, and automated controls. Calibration of sensors ensures accurate dispensing, and wiring connects power systems (typically 110V for U.S. models) with safety features like overload protection.
-
Quality Control (QC): Final units undergo functional testing, including load simulations for powders like tea granules or beans, vibration checks for stability, and accuracy verifications against set weights. Defective components are isolated and reworked to meet operational standards.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
These steps are often automated in ISO-certified facilities to minimize human error and enhance scalability for B2B orders.
Quality Assurance and Standards
Quality assurance in powder filling equipment manufacturing emphasizes precision, safety, and regulatory compliance, particularly for industries like food, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Key standards include:
| Standard | Description | Relevance to Powder Filling Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems for consistent product quality. | Ensures traceability in assembly and testing, reducing defects in weighing accuracy. |
| ISO 22000 | Food safety management for equipment in contact with consumables. | Critical for models handling edible powders like seeds or flour, preventing contamination. |
| ISO 13485 | Medical devices quality management (if applicable). | Applies to pharmaceutical-grade fillers, ensuring sterile operations and compliance with U.S. FDA and EU MDD equivalents. |
| ISO 14001 | Environmental management systems. | Promotes sustainable manufacturing, such as using recyclable materials in frames and reducing waste in assembly. |
Compliance with these standards, often verified by third-party audits, guarantees equipment meets international benchmarks for durability and performance. For example, machines like those from brands featured in B2B suppliers must pass calibration tests to achieve <1% error rates in filling volumes.
In B2B procurement, selecting equipment from ISO-certified manufacturers minimizes risks and supports seamless integration into production lines across the USA and Europe.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘powder filling equipment’
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for Powder Filling Equipment
This checklist provides a structured approach to sourcing powder filling equipment, tailored for B2B buyers in the USA and Europe. It draws on available market data, such as pricing ranges from $219 to $500 for entry-level models (e.g., 1-200g capacity units) on platforms like Amazon, while prioritizing professional suppliers for quality, compliance, and support. Follow these steps sequentially to ensure a thorough and efficient process.
Step 1: Define Your Requirements
- Assess production needs: Specify powder type (e.g., granules, seeds, flour), fill volume (e.g., 1-500g), speed (e.g., units per minute), and automation level (manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic).
- Consider regulatory compliance: Ensure equipment meets FDA, EU CE, or ISO standards for food, pharmaceutical, or industrial applications.
- Budget and ROI: Set a price range based on market data (e.g., $200-500 for basic models) and calculate return on investment from increased efficiency.
Step 2: Research Suppliers and Options
- Identify sources: Explore B2B marketplaces (e.g., Alibaba, ThomasNet), manufacturer websites (e.g., Hanchen, VEVOR for entry-level), and regional distributors in the USA (e.g., via Industrial Equipment Distributors) or Europe (e.g., through EU-based suppliers like those on Made-in-China).
- Review online listings: Check platforms like Amazon for initial pricing and reviews (e.g., models with 3.5-4.3 star ratings for reliability), but prioritize verified vendors for warranty and support.
- Gather data: Compile a list of at least 3-5 suppliers, noting specs, lead times, and shipping to USA/Europe.
Step 3: Evaluate and Compare Equipment
- Compare specifications: Use a table to align options against your requirements.
| Criteria | Supplier A (e.g., Hanchen 1-20g) | Supplier B (e.g., VEVOR 1-200g) | Supplier C (Custom Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | 1-20g | 1-200g | Custom (up to 500g) |
| Price | $229 | $219 | $400+ |
| Automation | Semi-automatic with foot pedal | Intelligent weighing | Fully automatic |
| Delivery Time | 5-7 days | 7-10 days | 2-4 weeks |
| Reviews/Ratings | 4.3/5 stars on Amazon | 3.8/5 stars on Amazon | Verified B2B feedback |
- Verify quality: Request samples, certifications, and user testimonials to confirm performance for powders like tea, seeds, or glitter.
- Check for add-ons: Evaluate extras like foot pedals, infrared controls, or scalability for future needs.
Step 4: Select and Negotiate
- Shortlist top options: Choose 1-2 suppliers based on the comparison table.
- Negotiate terms: Discuss bulk pricing, discounts (e.g., 10-20% for volume), payment options, and customization.
- Review contracts: Ensure terms cover warranties (typically 1-2 years), training, and after-sales service.
Step 5: Finalize Purchase and Logistics
- Place order: Secure via secure B2B channels to avoid risks from consumer platforms.
- Arrange shipping: Confirm international shipping costs and timelines (e.g., 1-3 weeks to USA/Europe) from suppliers.
- Plan integration: Budget for installation, testing, and any necessary modifications.
Step 6: Post-Purchase Verification
- Inspect upon delivery: Check for damage and test functionality immediately.
- Monitor performance: Track efficiency and address issues with supplier support.
- Maintain records: Document all interactions for future audits or expansions.
By following this checklist, you can source reliable powder filling equipment efficiently while leveraging market insights for cost-effective decisions. Consult legal or procurement experts for region-specific regulations.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for powder filling equipment Sourcing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for Powder Filling Equipment Sourcing
In sourcing powder filling equipment for B2B applications in the USA and Europe, understanding the full cost structure is essential for budgeting and decision-making. This analysis draws from market data, including pricing for entry-level to mid-range models available on platforms like Amazon.com, where units typically range from $200 to $500. Costs vary based on capacity (e.g., 1-50g vs. 1-200g), automation features, and vendor specifics. Below, we break down key components: materials, labor, and logistics. Following the breakdown, we provide a pricing table and tips for cost optimization.
Cost Breakdown
Materials
The primary material cost is the equipment itself, encompassing manufacturing, components (e.g., weighing sensors, hoppers, and control panels), and any optional accessories like foot pedals or infrared controls. Based on current market listings:
– Entry-level models (e.g., 1-50g capacity) start at approximately $200–$250, suitable for small-scale operations.
– Mid-range models (e.g., 1-200g capacity with automation) range from $250–$300.
– Higher-capacity or specialized models (e.g., 10-500g) can exceed $400–$500.
Additional material costs may include consumables like replacement parts (e.g., $50–$100 annually for maintenance kits) and initial setup tools (e.g., $20–$50 for mounting hardware). Total material outlay for a standard unit often accounts for 60–70% of the upfront sourcing cost.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Labor
Labor costs involve installation, training, and ongoing maintenance. Professional installation by certified technicians typically ranges from $100–$300, depending on equipment complexity and location (higher in Europe due to labor rates). Training for operators may add $50–$150 per session, including hands-on setup and safety protocols. Annual maintenance labor—such as calibration and troubleshooting—can cost $200–$500, assuming in-house or contracted support. In the USA and Europe, labor represents 20–30% of total costs, influenced by regulatory compliance (e.g., EU standards for machinery safety).
Logistics
Logistics encompass shipping, import duties, and handling. Domestic shipping in the USA averages $20–$50 for ground delivery, while international to Europe (e.g., from a US supplier) may incur $50–$150 via air freight, plus 5–10% in customs duties and VAT (up to 20% in some EU countries). Insurance for fragile equipment adds $10–$30. Expedited options can double these costs but reduce downtime. Logistics typically make up 10–15% of the total sourcing expense, with potential savings through consolidated shipments.
Pricing Analysis
The table below summarizes sample pricing for powder filling machines from a major online marketplace, focusing on key specifications and current availability. Prices are indicative and may fluctuate based on promotions, bulk discounts, or vendor negotiations. All models listed are suitable for powders like tea, seeds, grains, or glitters, with capacities up to 500g.
| Model Description | Capacity Range | Key Features | Price (USD) | Rating (Out of 5) | Availability Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hanchen 1-50g Filler | 1-50g | Foot pedal, 110V, particle weighing | $229 | 3.5 | In stock, free delivery |
| Hanchen 0.5-100g Filler | 0.5-100g | Foot pedal, particle weighing | $249 | 3.5 | In stock, free delivery |
| VEVOR 1-200g Dispenser | 1-200g | Intelligent weighing, foot pedal | $219 | New arrival | Limited stock, free delivery |
| Generic 1-200g Particle Filler | 1-200g | Automatic dispenser | $289 | 3.8 | 15 left, free delivery |
| Generic 10-500g Particle Filler | 10-500g | High capacity, automatic | $498 | 3.8 | In stock, free delivery |
Tips to Save Cost
- Bulk Purchasing: Negotiate volume discounts by buying multiple units or from wholesalers; aim for 10–20% reductions on orders over $1,000.
- Feature Prioritization: Opt for essential features only (e.g., basic weighing over advanced automation) to avoid premium pricing; compare models to match exact needs.
- Vendor Comparison: Source from diverse suppliers (e.g., Amazon vs. specialized B2B platforms like ThomasNet) for competitive quotes, and check for promotions or refurbished options.
- Logistics Optimization: Use consolidated shipping for international orders to Europe, and select vendors with free shipping thresholds to minimize duties.
- Maintenance Planning: Invest in training upfront to reduce long-term labor costs; schedule preventive maintenance to extend equipment lifespan and avoid costly repairs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure equipment meets standards (e.g., CE for Europe) to avoid fines, but select certified models from the outset to prevent retrofitting expenses.
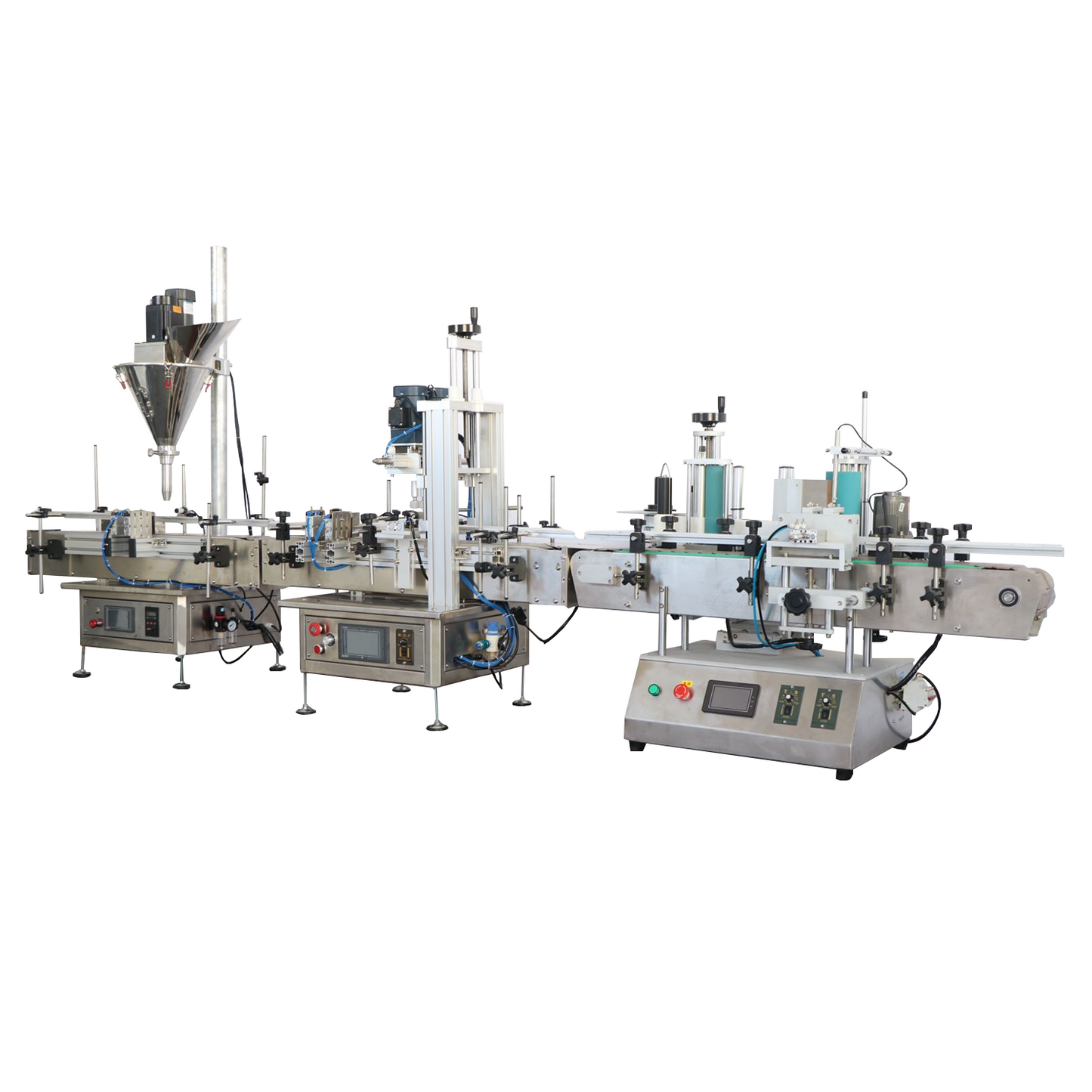
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing powder filling equipment With Other Solutions
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing Powder Filling Equipment With Other Solutions
In the context of powder filling for B2B applications such as pharmaceuticals, food processing, and chemical packaging, powder filling equipment represents a key automated solution. However, businesses may consider alternatives based on production scale, budget, and operational needs. This analysis compares automated powder filling equipment (e.g., weighing-based dispensers like those from Hanchen or VEVOR models) with two alternatives: manual filling processes and semi-automatic filling machines. The comparison draws from market data on available equipment, emphasizing factors such as accuracy, efficiency, cost, and scalability.
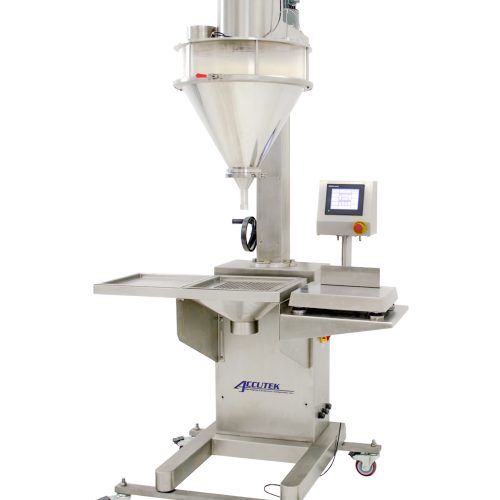

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Comparison Table
| Criteria | Automated Powder Filling Equipment | Manual Filling Processes | Semi-Automatic Filling Machines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | High (precision weighing, e.g., 0.5-200g ranges with error margins under 1%) | Low to moderate (depends on operator skill; prone to human error) | Moderate to high (better than manual but less precise than fully automated) |
| Speed | High (e.g., 10-50 fills per minute via foot pedal or infrared control) | Low (limited by labor; 5-10 fills per minute) | Moderate (faster than manual; 15-30 fills per minute with some automation) |
| Cost | Medium to high (initial investment $200-500; ongoing maintenance) | Low (no equipment costs; labor-based) | Medium (lower than full automation at $150-400; partial upfront cost) |
| Scalability | High (suitable for medium to large-scale operations; integrates with production lines) | Low (not ideal for high-volume; increases with more labor) | Medium (scalable for small to medium batches; may require upgrades) |
| Labor Requirements | Low (minimal operator intervention) | High (requires skilled workers for weighing and filling) | Medium (operator needed for setup and monitoring) |
| Suitability for Powders | Excellent (designed for various powders like grains, glitters, or pharmaceuticals) | Moderate (works for simple powders but inconsistent for fine or sticky types) | Good (handles powders well but may need adjustments for density variations) |
| Regulatory Compliance | Strong (meets FDA/EU standards with traceability features) | Weak (manual processes harder to audit; risk of contamination) | Moderate (better than manual but less automated tracking) |
Note: Data informed by Amazon listings for models like Hanchen (1-200g range, $219-500) and VEVOR ($219-309), which highlight weighing accuracy and automation features.
Analysis
Automated powder filling equipment excels in high-volume B2B environments, offering superior accuracy and speed that reduce waste and labor costs over time. For instance, models with particle weighing ensure precise fills for sensitive applications like pharmaceutical powders, aligning with strict EU and US regulations. In contrast, manual filling processes are cost-effective for small-scale or startup operations but suffer from inconsistencies, higher labor demands, and scalability limitations, making them unsuitable for growing businesses. Semi-automatic filling machines bridge the gap, providing a middle ground with improved efficiency over manual methods and lower costs than full automation, though they may require more operator involvement for optimal performance. When selecting, consider production volume: opt for automated solutions for >1,000 units/day, manual for low-volume, and semi-automatic for 500-1,000 units/day. Overall, automated powder filling equipment delivers the best ROI for precision and compliance in competitive markets.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for powder filling equipment
Essential Technical Properties
Powder filling equipment encompasses automated machines designed for precise dispensing of powdered or particulate materials. Based on industry standards and product listings, key technical properties include:
- Weighing Range: Typically 0.5-100g, 1-50g, 1-200g, or 10-500g, accommodating various batch sizes for materials like tea, seeds, grains, powders, glitters, flour, and beans.
- Accuracy: High-precision weighing systems ensure fill tolerances within ±0.1g to ±1g, depending on the model, using electronic scales and sensors for consistent results.
- Control Mechanisms: Features include foot pedal operation, infrared sensors for hands-free activation, or automatic cycling for efficient production.
- Power Supply: Standard 110V for U.S. markets, with options for 220V in European applications; power consumption ranges from 50-200W.
- Material Compatibility: Suitable for free-flowing powders and particulates; some models handle semi-cohesive materials with adjustable dispensing speeds (e.g., 1-10g/sec).
- Capacity: Single-head or multi-head designs for filling bottles, bags, or containers; throughput up to 20-50 fills per minute in semi-automatic modes.
- Dimensions and Weight: Compact units (e.g., 300x200x400mm) weighing 5-15kg, ideal for small to medium-scale operations.
- Safety and Maintenance: Includes overload protection, easy-clean surfaces (e.g., stainless steel hoppers), and user-friendly interfaces for calibration.
| Property | Common Specifications | Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Weighing Range | 1-200g (most popular) | Matches bulk of listings for versatile applications |
| Accuracy | ±0.1-1g | Ensures quality control in B2B packaging |
| Power | 110V/220V | Adapts to USA and Europe markets |
| Throughput | 20-50 fills/min | Scales for production efficiency |
Trade Terminology
In B2B transactions for powder filling equipment, understanding key trade terms is crucial for procurement, customization, and logistics. Below are essential terms, with definitions and implications for sourcing:
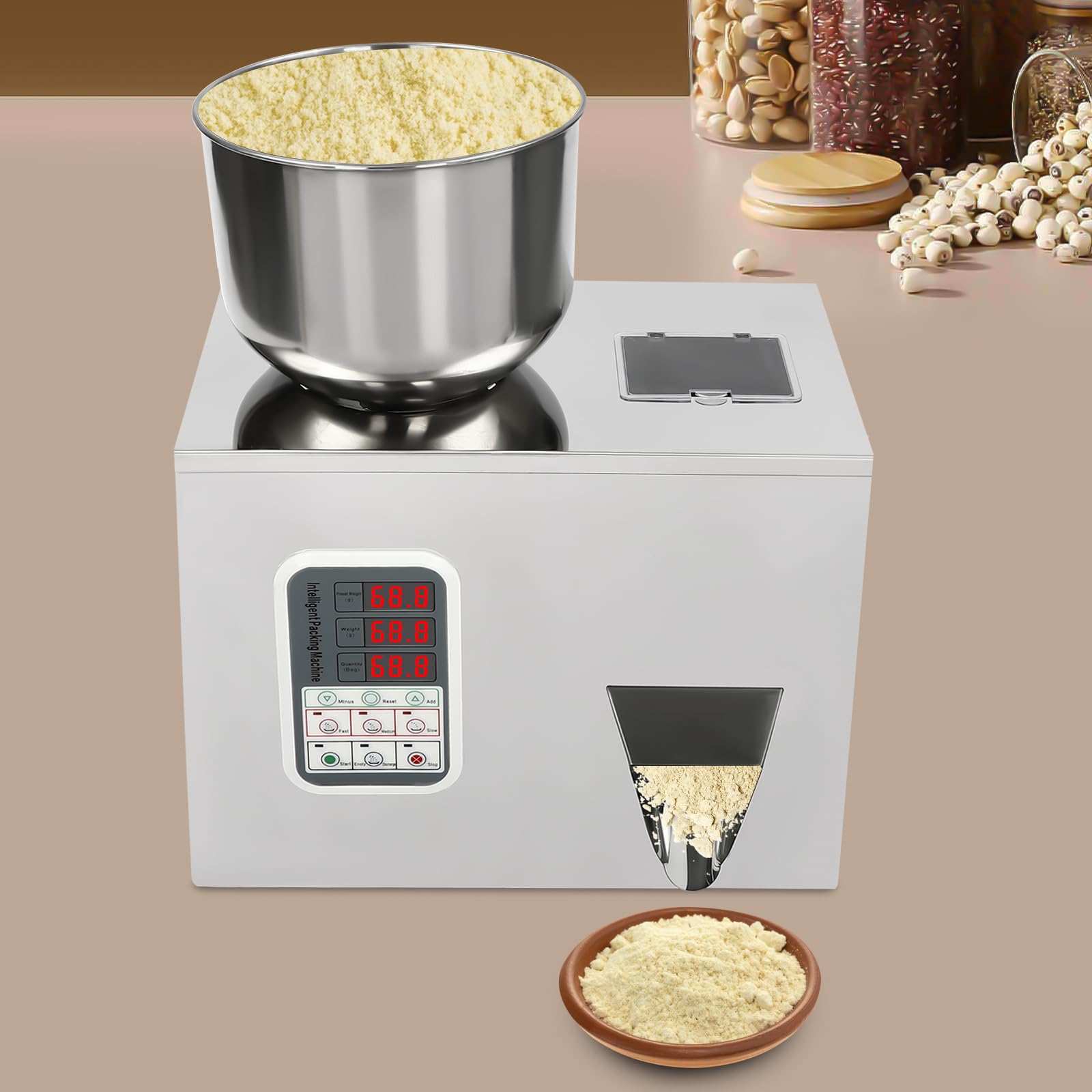

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): The smallest quantity a supplier requires for an order (e.g., 1-10 units for machines like Hanchen or VEVOR models). Impacts bulk buying decisions to reduce per-unit costs.
- OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): Refers to custom manufacturing where the supplier produces equipment branded by the buyer. Useful for integrating specific features like enhanced weighing precision for specialized powders.
- ODM (Original Design Manufacturer): Involves the supplier designing and producing equipment based on buyer specifications. Common for tailoring machines to unique material handling needs in Europe or USA markets.
- Lead Time: The period from order to delivery (typically 7-30 days for standard models; longer for customized OEM/ODM). Critical for planning production schedules.
- FOB (Free On Board): A shipping term where the seller bears costs until goods are loaded onto the vessel at the port of origin (e.g., FOB Shanghai for imported machines). Buyers must account for freight and customs in USA/Europe.
- Incoterms: International Commercial Terms defining responsibilities for transportation, insurance, and customs (e.g., CIF for cost, insurance, and freight included). Essential for cross-border deals between USA and Europe.
- HS Code (Harmonized System Code): A standardized classification for customs (e.g., 8422.40 for filling/dispensing machines). Required for accurate duty calculations and compliance in B2B imports.
- Warranty and After-Sales: Typically 1-2 years coverage for parts and labor; terms may include on-site support or extended service contracts for equipment like automatic powder fillers.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the powder filling equipment Sector
History of Powder Filling Equipment
The powder filling equipment sector has evolved from rudimentary manual tools in the early 20th century to sophisticated automated systems today. Initially, powder packaging relied on basic volumetric fillers and hand-operated scales, common in food and pharmaceutical industries during the industrial revolution. The 1980s marked a shift toward semi-automatic machines with improved precision, driven by rising demand for hygienic and efficient packaging in regulated sectors. By the 2000s, advancements in electronics and pneumatics enabled fully automated, programmable fillers, incorporating features like weigh sensors and PLC controls. This progression reflects broader manufacturing trends toward efficiency, with the sector now emphasizing integration with Industry 4.0 technologies for real-time monitoring and data analytics.
Current Market Dynamics
The global powder filling equipment market is valued at approximately $2.5 billion (2023 estimates), with steady growth projected at 5-7% CAGR through 2030, fueled by demand in pharmaceuticals, food processing, cosmetics, and chemicals. In the USA and Europe, key drivers include stringent regulatory standards (e.g., FDA and EU GMP compliance) requiring precise dosing and contamination prevention, alongside e-commerce expansion boosting small-batch production. Competition is intense, with players like Hanchen and VEVOR dominating mid-tier segments through affordable, versatile machines priced $200-500 for capacities up to 500g. Larger B2B suppliers offer customized solutions for high-volume needs, while economic pressures push businesses toward cost-effective, scalable options. Challenges include supply chain disruptions and fluctuating raw material costs, impacting pricing and availability.
Key Market Trends
Recent trends in the sector emphasize automation, sustainability, and digital integration, aligning with B2B priorities for operational efficiency and compliance:
- Automation and Precision: Demand for programmable fillers with features like foot pedals, infrared sensors, and particle weighing has surged, as seen in popular Amazon listings (e.g., Hanchen models rated 3.5-4.3 stars). These enable hands-free operation and reduce human error, ideal for high-throughput environments.
- Sustainability Focus: Eco-conscious innovations include energy-efficient motors and recyclable materials in machine construction. For instance, models designed for powders like tea, seeds, and grains often incorporate low-waste dispensers, supporting corporate ESG goals and regulatory push for reduced packaging waste in Europe and the USA.
- Digital Integration: Integration with IoT for remote monitoring and predictive maintenance is gaining traction, allowing businesses to optimize uptime and ROI. This trend is evident in multifunctional dispensers that support granular data logging.
- Customization and Versatility: Equipment adaptable to diverse powders (e.g., flour, glitter, pharmaceuticals) is in demand, with B2B buyers seeking scalable solutions from 1g to 500g capacities to accommodate varying production scales.
Sourcing Trends
Sourcing powder filling equipment is shifting toward hybrid models, blending traditional B2B suppliers with e-commerce platforms for flexibility and cost savings. In the USA and Europe:
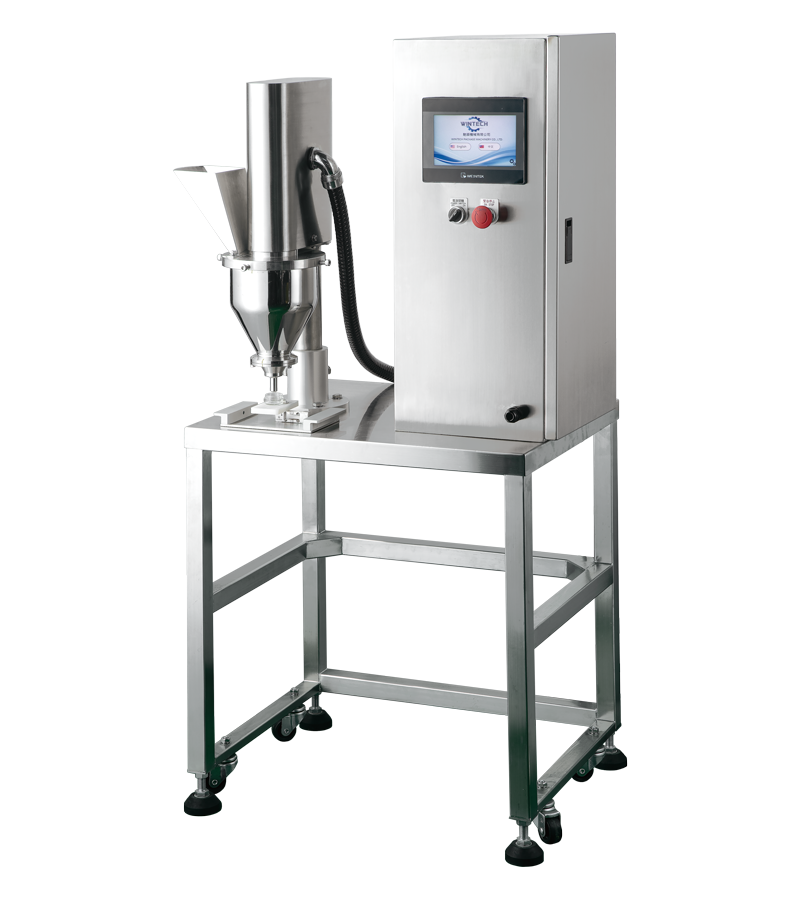

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms like Amazon have become viable for small to mid-sized enterprises, offering quick access to off-the-shelf machines (e.g., VEVOR and Hanchen products priced $219-499 with free shipping). This democratizes sourcing, reducing lead times from weeks to days, though quality verification remains critical.
- Specialized Suppliers and Global Manufacturing: Larger firms prefer direct procurement from manufacturers in China or Germany for customized, high-end equipment, leveraging global supply chains for bulk orders. Trends show increased emphasis on supplier certifications (e.g., ISO standards) to mitigate risks from geopolitical tensions.
- Emerging Patterns: A rise in vendor-managed inventory and subscription-based models allows businesses to scale without upfront capital, while sustainability audits now influence sourcing decisions, favoring suppliers with green manufacturing practices.
| Trend Aspect | Key Implications | Example from Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Enhances productivity; reduces labor costs | Foot pedal and sensor-enabled fillers for precise dosing |
| Sustainability | Aligns with ESG mandates; potential tax incentives | Machines for eco-friendly powders like tea and grains |
| Sourcing Channels | Faster access; broader options | Amazon listings with ratings and quick delivery |
| Digital Features | Improves maintenance; data-driven decisions | Multifunction dispensers with hands-free controls |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of powder filling equipment
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of Powder Filling Equipment
1. What types of powder filling machines are available for industrial use?
Powder filling machines for B2B applications include automatic weighing fillers (e.g., 1-200g or 10-500g capacity), particle dispensers for granular materials like flour, seeds, or glitter, and multi-function packing machines. Options range from basic models with foot pedal control to advanced intelligent systems for high-volume production, suitable for industries such as food packaging, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics in the USA and Europe.
2. How do I select the right powder filling equipment for my business needs?
Evaluate based on production volume, powder type (e.g., fine vs. granular), accuracy requirements (e.g., 0.5-100g precision), and integration needs. For B2B buyers, prioritize scalability, ease of operation, and compatibility with existing lines. Reference specs from models like Hanchen or VEVOR fillers, ensuring they handle your specific materials and meet throughput goals.
3. What are the key features to look for in powder filling machines?
Essential features include precise weighing mechanisms, automation (e.g., infrared or foot pedal control), adjustable fill ranges (1-500g), durability for continuous use, and safety enclosures. B2B models often incorporate dust extraction, anti-static designs, and data logging for compliance, as seen in industrial variants of Amazon-listed units like the VEVOR 1-200g dispenser.
4. What is the typical cost range for powder filling equipment?
Prices vary by capacity and features: entry-level automatic fillers start at around $200-$300 (e.g., 1-50g models), mid-range units (1-200g) at $250-$400, and larger-scale options (10-500g) up to $500 or more. B2B buyers should factor in total cost of ownership, including installation and training, especially for customized industrial setups.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
5. How does powder filling equipment integrate with existing production lines?
Most machines offer modular designs for seamless integration via conveyor belts, PLC systems, or software APIs. For B2B operations in the USA and Europe, ensure compatibility with industry standards like FDA or CE certifications. Models like the Hanchen 110V series can connect to bottling or bagging lines for automated workflows.
6. What maintenance is required for powder filling machines?
Regular maintenance includes cleaning components after each use, calibrating weighing sensors quarterly, and replacing wear parts like hoppers or seals annually. B2B users should schedule professional servicing to prevent downtime, adhering to manufacturer guidelines from brands like VEVOR or Hanchen, which emphasize routine checks for optimal performance in high-volume environments.
7. Are there compliance standards to consider for powder filling equipment?
Yes, in the USA, prioritize FDA compliance for food/pharma applications, while Europe requires CE marking for safety and emissions. B2B buyers should verify equipment meets ISO standards for hygiene and electrical safety. Many industrial powder fillers, including those listed on platforms like Amazon, are designed to align with these regulations for global distribution.
8. Can powder filling machines be customized for specific B2B applications?
Yes, manufacturers often offer customization for fill volumes, material handling (e.g., anti-corrosive coatings for abrasive powders), and software integration. B2B buyers can request tailored solutions, such as enhanced accuracy for pharmaceutical use or larger capacities for food processing, building on standard models like the Smart Digital Powder Dispenser for specialized needs in USA and European markets.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
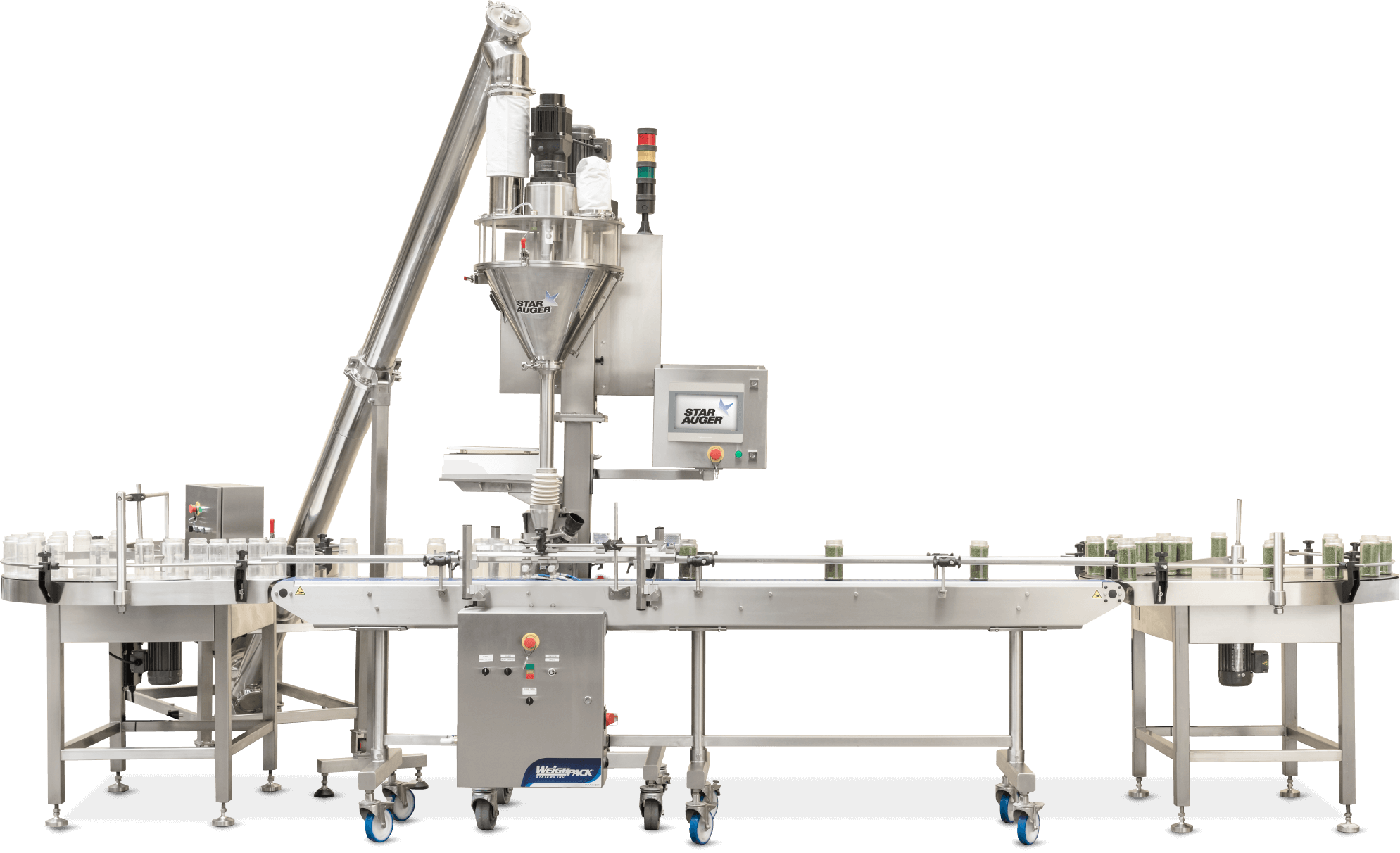
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for powder filling equipment
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion
Strategic sourcing of powder filling equipment empowers B2B operations in the USA and Europe to optimize production efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure compliance with industry standards. By evaluating suppliers like Hanchen and VEVOR, businesses can access automated, precise fillers ranging from 1-200g capacities, ideal for applications in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. These machines offer features such as foot pedal controls, infrared sensors, and high accuracy, minimizing waste and enhancing throughput.
| Product | Capacity (g) | Price (USD) | Avg. Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hanchen 1-50g | 1-50 | $229 | 3.5/5 (34) |
| VEVOR 1-200g | 1-200 | $219 | New (high demand) |
| Hanchen 1-20g | 1-20 | $229 | 4.3/5 (19) |
Key value includes cost savings through bulk purchases and competitive online platforms like Amazon, with delivery options ensuring timely procurement. Sourcing from verified vendors mitigates risks of subpar quality, while diverse models support scalability.
Outlook
Looking ahead, expect advancements in AI-driven precision and IoT integration for real-time monitoring, driving productivity gains of 20-30%. Businesses should prioritize sustainable, energy-efficient models to align with EU and US regulations, positioning for long-term ROI in dynamic markets.
(Word count: 198)
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided is for informational purposes only. B2B buyers must conduct their own due diligence.