Saffron Seeds Guide: Type,Cost,Material…
Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for saffron seeds
In today’s competitive landscape, international B2B buyers face the pressing challenge of sourcing high-quality saffron seeds that meet their specific agricultural and culinary needs. With saffron being one of the most sought-after spices globally, understanding the nuances of saffron seed procurement is crucial for maximizing both quality and profitability. This comprehensive guide delves into various aspects of saffron seed sourcing, including types of saffron seeds, their applications in culinary and medicinal contexts, and strategies for vetting reliable suppliers.
By equipping buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—particularly Saudi Arabia and Vietnam—with actionable insights, this guide empowers them to make informed purchasing decisions. It addresses key considerations such as cost factors, cultivation requirements, and market trends, ensuring that buyers can navigate the complexities of the saffron seed market effectively.
Whether you are a seasoned importer or new to the saffron business, understanding these elements will not only enhance your sourcing strategy but also enable you to capitalize on the growing demand for this luxurious spice. With the right knowledge, you can establish fruitful partnerships and secure a competitive edge in the saffron industry.
Understanding saffron seeds Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Saffron Crocus (Crocus sativus) | Produces the highest quality saffron; blooms in fall; requires specific climate conditions. | Culinary, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics | Pros: High yield of saffron per corm; premium quality. Cons: Requires careful climate management; can be costly to establish. |
| Persian Saffron | Renowned for its deep red color and strong flavor; harvested primarily in Iran. | Gourmet food markets, specialty shops | Pros: Highly sought after; commands premium prices. Cons: Limited supply; geopolitical factors may affect availability. |
| Spanish Saffron | Grown in Spain, characterized by a slightly different flavor profile; often less expensive than Persian saffron. | Culinary use, food processing | Pros: More accessible pricing; versatile in culinary applications. Cons: Slightly lower quality than Persian; may not meet all gourmet standards. |
| Kashmiri Saffron | Known for its distinctive aroma and vibrant color; cultivated in the Kashmir region. | Luxury food products, cosmetics | Pros: Unique flavor and color; high market demand. Cons: Vulnerable to climatic changes; limited growing regions. |
| Organic Saffron | Cultivated without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides; can be sourced from various regions. | Health-conscious markets, organic food sectors | Pros: Appeals to health-conscious consumers; environmentally friendly. Cons: Generally higher cost; may have lower yields. |
What are the Characteristics of Saffron Crocus (Crocus sativus)?
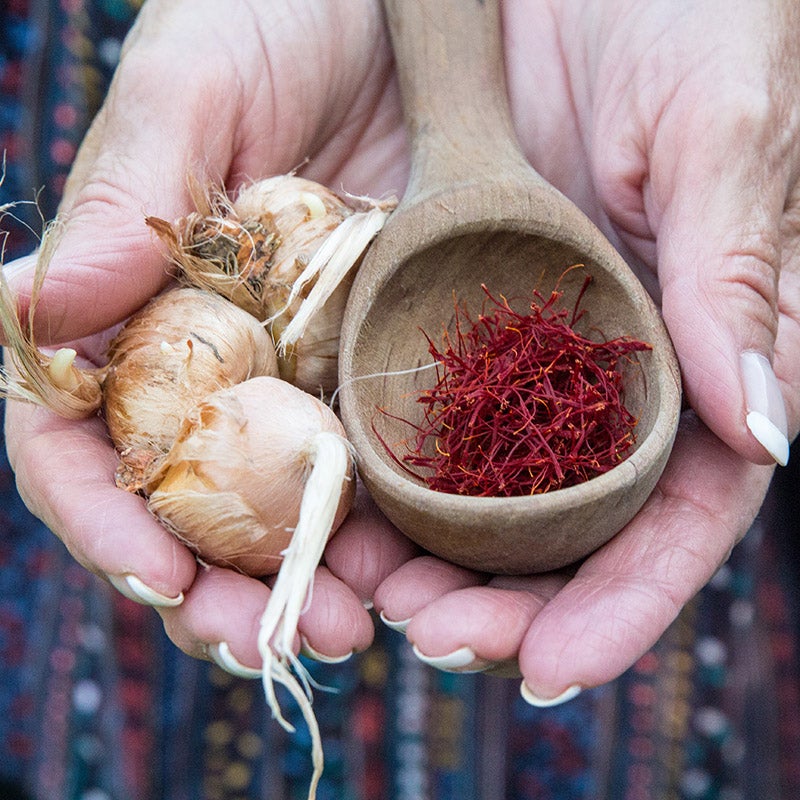
The Saffron Crocus, or Crocus sativus, is the primary source of saffron spice. It thrives in Mediterranean climates and blooms in the fall, producing striking flowers with vibrant red stigmas. Each corm can yield multiple flowers, and optimal cultivation requires well-drained soil and specific temperature ranges. For B2B buyers, investing in these corms can lead to high-quality saffron production, though careful climate management and initial investment are necessary to ensure successful growth.
Why is Persian Saffron Highly Valued in the Market?
Persian saffron is esteemed for its rich flavor and deep red color, primarily harvested in Iran. It is often considered the gold standard in saffron quality, making it highly sought after in gourmet culinary markets and specialty shops. B2B buyers should be aware of the geopolitical factors affecting supply and pricing, which can fluctuate significantly. This variety may command premium prices, but its exceptional quality can justify the investment for high-end culinary applications.
How Does Spanish Saffron Compare to Other Types?
Spanish saffron, cultivated primarily in the La Mancha region, offers a slightly different flavor profile than its Persian counterpart and is often available at a more accessible price point. This variety is popular in culinary use and food processing, making it a practical choice for restaurants and food manufacturers. While it may not reach the same gourmet status as Persian saffron, it provides a valuable alternative for buyers seeking quality saffron without the associated costs.
What Makes Kashmiri Saffron Unique?
Kashmiri saffron is distinguished by its potent aroma and vibrant color, making it a favorite among luxury food products and cosmetics. Its cultivation is limited to specific regions in Kashmir, which can make it vulnerable to climatic changes. B2B buyers should consider the high demand for this unique variety, which can command premium prices in the market. However, potential supply risks due to environmental factors should also be factored into purchasing decisions.
Why Choose Organic Saffron for Health-Conscious Markets?
Organic saffron is cultivated without synthetic fertilizers or pesticides, appealing to health-conscious consumers and sectors focused on organic products. This variety can be sourced from various regions, offering flexibility for B2B buyers. While organic saffron typically comes at a higher cost and may yield less than conventional options, its environmental benefits and growing consumer demand can make it a worthwhile investment for businesses targeting health-oriented markets.
Key Industrial Applications of saffron seeds
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of saffron seeds | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverage | Culinary use in gourmet restaurants | Enhances flavor and presentation, attracting premium customers | Quality assurance of saffron seeds for flavor potency |
| Pharmaceuticals | Extracts for medicinal formulations | Potential health benefits, catering to wellness trends | Compliance with health regulations and certifications |
| Cosmetics | Saffron-infused skincare products | Natural anti-aging properties, appealing to eco-conscious consumers | Sourcing sustainably grown saffron seeds |
| Agriculture | Cultivation for local markets | Supports local economies and reduces import dependency | Understanding local climate and soil conditions |
| Textile | Dye production for fabrics | Unique coloring properties, appealing to high-end textile markets | Ensuring consistency in seed quality for dye yield |
How Can Saffron Seeds Benefit the Food and Beverage Industry?
In the food and beverage industry, saffron seeds are essential for cultivating the saffron crocus, which produces the world-renowned spice. Gourmet restaurants utilize saffron to enhance the flavor and visual appeal of their dishes, thus attracting customers willing to pay a premium. Buyers must ensure the quality of saffron seeds, as the potency of flavor and aroma directly impacts the final product. Sourcing from reputable suppliers who provide quality assurance can help businesses maintain their culinary standards.
What Role Do Saffron Seeds Play in Pharmaceuticals?
Saffron seeds are increasingly used in pharmaceutical applications, where extracts from saffron are formulated into medicinal products. The spice is known for its potential health benefits, including antioxidant properties and mood enhancement, making it attractive in the wellness sector. For international buyers, compliance with health regulations and obtaining necessary certifications are critical when sourcing saffron seeds for medicinal use. This ensures that the products meet market standards and consumer safety requirements.
How Are Saffron Seeds Used in Cosmetics?
In the cosmetics industry, saffron seeds are sought after for their use in skincare formulations. Saffron is recognized for its natural anti-aging properties and ability to brighten skin tone, appealing to consumers looking for organic and effective beauty solutions. Sourcing sustainably grown saffron seeds is essential for businesses aiming to promote eco-friendly practices. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who can guarantee the ethical cultivation of saffron, aligning with the values of environmentally conscious consumers.
Why Is Saffron Important for Local Agriculture?
The agricultural sector can leverage saffron seeds to cultivate saffron crocus for local markets. This not only supports local economies but also reduces reliance on imported saffron, which can be costly and less fresh. Buyers interested in this application should understand the specific climate and soil conditions required for saffron cultivation in their region. Collaborating with local agricultural experts can help ensure successful cultivation and maximize yield.
How Do Saffron Seeds Contribute to the Textile Industry?
In the textile industry, saffron seeds are utilized for producing natural dyes. The unique coloring properties of saffron make it a desirable choice for high-end textiles, offering an organic alternative to synthetic dyes. For businesses in this sector, ensuring consistency in seed quality is crucial for achieving reliable dye yields. Buyers should seek suppliers who provide detailed information on the dyeing properties of their saffron seeds, enabling them to meet the specific requirements of their textile production processes.
3 Common User Pain Points for ‘saffron seeds’ & Their Solutions
Scenario 1: Navigating Saffron Seed Quality Issues
The Problem: B2B buyers often face significant challenges when it comes to ensuring the quality of saffron seeds. Poor quality seeds can lead to low germination rates, unhealthy plants, and ultimately, a disappointing saffron yield. Buyers may encounter suppliers who overstate the quality or fail to provide adequate information about the seeds’ origin and viability. This issue is particularly pressing for businesses in regions with stringent quality standards, where inferior products can jeopardize contracts and customer satisfaction.
The Solution: To mitigate quality concerns, buyers should prioritize sourcing saffron seeds from reputable suppliers who provide comprehensive product information. Look for suppliers that offer detailed specifications, including the origin of the seeds, germination rates, and cultivation practices. Establishing a relationship with suppliers who have a track record of quality assurance can also be beneficial. Additionally, consider requesting sample seeds for testing before placing bulk orders. Implementing a robust quality control process that includes inspecting seeds upon arrival can further ensure that only the best quality saffron seeds are utilized.
Scenario 2: Understanding Optimal Growing Conditions for Saffron Seeds
The Problem: Many B2B buyers are unaware of the specific growing conditions required for saffron seeds, leading to poor cultivation outcomes. Saffron crocus thrives in particular climates and soil types, and without this knowledge, buyers risk investing in seeds that may not flourish in their geographic regions. Factors such as soil drainage, light exposure, and temperature can significantly impact the success of saffron production, which can be especially problematic for buyers in less familiar markets.
The Solution: To address these challenges, it is crucial for buyers to conduct thorough research on the optimal growing conditions for saffron seeds. This includes understanding the specific climate zones (ideally between latitudes 30° and 50°) and soil preferences (well-drained, sandy soils with a pH of 6 to 8) of saffron crocus. Collaborating with local agricultural experts or agronomists can provide valuable insights tailored to specific regions. Buyers should also consider investing in soil testing and amendments to create an ideal growing environment. Utilizing cultivation guides and resources from experienced saffron producers can further equip buyers with the necessary knowledge to ensure successful growth.
Scenario 3: Managing Harvesting and Processing Challenges
The Problem: Harvesting saffron can be labor-intensive and time-sensitive, creating a logistical challenge for B2B buyers. The delicate nature of saffron flowers means that stigmas must be hand-harvested at the right moment, which can lead to labor shortages or timing issues, especially if the harvest coincides with other agricultural activities. Additionally, improper processing can degrade the quality of saffron, impacting its market value and the buyer’s reputation.
The Solution: To streamline the harvesting and processing of saffron, buyers should develop a well-planned harvesting strategy that includes training workers on the proper techniques for collecting and handling saffron flowers. Establishing a clear timeline for the harvest, based on local climatic conditions and flowering patterns, can help ensure that the flowers are picked at their peak. Additionally, investing in appropriate drying and storage facilities is essential to preserve the quality of the saffron after harvest. Buyers may also consider partnering with local processing facilities that specialize in saffron to ensure that the product is handled with expertise, thus maintaining its high market value.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for saffron seeds
What Are the Key Materials for Saffron Seed Production?
When selecting materials for saffron seed production, several options are commonly considered. Each material has its unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages that can significantly impact the cultivation and harvesting processes. Below, we analyze four prevalent materials used in the production of saffron seeds.
How Do Different Materials Affect Saffron Seed Production?
1. Crocus Corms
Crocus corms are the primary planting material for saffron cultivation. They are bulb-like structures that store nutrients and energy for the plant. Corms thrive in well-drained soil and require specific temperature conditions, ideally between 15°C and 20°C, for optimal growth.
- Pros: Corms are relatively easy to plant and maintain. They can multiply over time, providing a sustainable source for future harvests. Additionally, they are cost-effective compared to purchasing saffron threads from the market.
- Cons: Corms can be susceptible to rot if overwatered, and they require specific climatic conditions to thrive, limiting their cultivation to certain regions.
- Impact on Application: The quality of the corm directly impacts the yield and quality of saffron produced. Healthy corms will produce more flowers and, consequently, more saffron threads.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with local agricultural standards and import regulations. In regions like the Middle East and Europe, adherence to specific agricultural practices is crucial for successful cultivation.
2. Soil Amendments
Soil amendments, such as compost or organic fertilizers, play a vital role in enhancing soil quality for saffron cultivation. These materials improve nutrient availability and soil structure, which are essential for healthy corm development.
- Pros: Organic amendments are environmentally friendly and can significantly increase soil fertility, leading to better yields. They also improve water retention and drainage, which are critical for saffron.
- Cons: The initial cost of high-quality organic amendments can be substantial. Additionally, they may require time to decompose and integrate into the soil.
- Impact on Application: Proper soil amendments can lead to healthier plants and higher-quality saffron, making them a worthwhile investment for growers.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of local regulations regarding organic farming practices and certifications, especially in Europe, where strict standards apply.
3. Irrigation Systems
Efficient irrigation systems are crucial for saffron cultivation, particularly in arid regions. Drip irrigation is often preferred due to its efficiency in water usage and ability to deliver moisture directly to the root zone.
- Pros: Drip irrigation minimizes water wastage and reduces the risk of fungal diseases associated with overwatering. It also allows for precise control over water delivery.
- Cons: The installation and maintenance of drip irrigation systems can be costly and complex. They require a reliable water source and regular monitoring.
- Impact on Application: Proper irrigation directly affects the growth and flowering of saffron, impacting both yield and quality.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider local water availability and regulations regarding water use. In regions like Africa and the Middle East, water scarcity can significantly influence irrigation choices.
4. Harvesting Tools
Specialized harvesting tools, such as scissors or tweezers, are essential for the delicate process of collecting saffron threads. These tools must be designed to minimize damage to the flowers during harvesting.
- Pros: High-quality harvesting tools enhance efficiency and reduce labor costs by allowing workers to harvest more flowers in less time.
- Cons: The initial investment in specialized tools can be high, and they require proper maintenance to ensure longevity.
- Impact on Application: The quality of the tools directly affects the amount of saffron harvested and its overall quality.
- Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that tools meet local safety and quality standards, particularly in regions with stringent agricultural regulations.
Summary Table of Material Selection for Saffron Seeds
| Material | Typical Use Case for saffron seeds | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crocus Corms | Planting material for saffron cultivation | Sustainable source for future harvests | Susceptible to rot if overwatered | Medium |
| Soil Amendments | Enhancing soil quality | Environmentally friendly, improves fertility | Initial cost can be substantial | Medium |
| Irrigation Systems | Efficient water delivery | Minimizes water wastage | Installation can be costly | High |
| Harvesting Tools | Collecting saffron threads | Enhances efficiency and reduces labor costs | Initial investment can be high | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide aims to provide B2B buyers with actionable insights into the materials that significantly influence saffron seed production. Understanding these materials will help buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and regional conditions.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for saffron seeds
What Are the Main Stages in the Manufacturing Process of Saffron Seeds?
The manufacturing process of saffron seeds involves several critical stages that ensure the quality and viability of the product. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers assess suppliers effectively.
Material Preparation: What Are the Initial Steps?
Material preparation begins with the sourcing of high-quality saffron crocus bulbs (corms). Suppliers must ensure that these bulbs are disease-free and sourced from reputable growers. This involves inspecting the bulbs for any signs of rot or disease and ensuring they are stored under optimal conditions to prevent sprouting before planting. Key techniques in this stage include:
- Sorting and Grading: Bulbs are sorted by size and health, ensuring uniformity in planting and harvesting.
- Soil Preparation: The planting site is prepared with well-draining soil, as saffron crocus thrives in specific soil conditions. Proper pH levels and nutrient content must be maintained.
Forming: How Are the Bulbs Planted?
Once the bulbs are prepared, the next stage involves planting them in the designated fields. This is a critical step, as improper planting can affect yield and quality.
- Planting Techniques: Bulbs are typically planted 3-4 inches deep and spaced appropriately to allow for growth. Manual planting is often preferred to ensure careful placement and minimize damage.
- Watering and Fertilization: After planting, the bulbs require adequate watering, though overwatering must be avoided to prevent rot. Organic fertilizers may be applied to promote healthy growth.
What Are the Key Techniques in Harvesting Saffron?
Saffron harvesting is labor-intensive and requires meticulous care. The saffron flowers bloom in the fall, and the timing of the harvest is crucial.
- Hand-Harvesting: Flowers must be picked by hand before they fully open, as this preserves the quality of the stigmas. Each flower typically yields three red stigmas, which are the saffron threads.
- Drying Process: After harvesting, the stigmas must be air-dried carefully to maintain their flavor and color. This process involves spreading the stigmas on a clean, dry surface in a well-ventilated area.
What Are the Finishing Processes for Saffron Seeds?
After harvesting and drying, the saffron undergoes finishing processes that prepare it for market.
- Sorting and Packaging: The dried saffron threads are sorted for quality and packaged in airtight containers to preserve freshness. This stage is crucial for maintaining the product’s integrity during transport.
- Labeling and Certification: Products are labeled according to international standards, often including certifications such as ISO 9001, which assures buyers of quality management practices.
How is Quality Control Implemented in Saffron Manufacturing?
Quality control (QC) is essential in saffron seed production to ensure that the end product meets international standards and buyer expectations.
What Are the Relevant International Standards for Saffron Quality?
International standards such as ISO 9001 provide a framework for quality management systems. Additionally, industry-specific certifications may include:
- CE Marking: Indicates compliance with European health and safety standards.
- API Certification: For suppliers involved in pharmaceutical applications of saffron.
These certifications help B2B buyers verify that their suppliers adhere to stringent quality protocols.
What Are the QC Checkpoints Throughout the Manufacturing Process?
Quality control checkpoints are strategically placed throughout the manufacturing process to catch any defects early.
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This checkpoint involves inspecting the saffron bulbs upon arrival to ensure they meet quality standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During the planting and harvesting stages, periodic checks are conducted to monitor growth and health.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): After packaging, the final product undergoes testing for moisture content, color, and potency to ensure it meets buyer specifications.
What Common Testing Methods Are Used for Saffron Quality Assurance?
Testing methods for saffron quality can include:
- Spectrophotometry: Measures the color intensity of saffron, providing an indication of its quality.
- Moisture Analysis: Ensures that the saffron is dried to appropriate levels, preventing spoilage.
- Microbial Testing: Checks for contamination that could affect the safety and quality of the saffron.
How Can B2B Buyers Verify Supplier Quality Control?
B2B buyers can take several steps to verify the quality control processes of their saffron suppliers:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits allows buyers to assess the manufacturing processes and QC measures firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting regular quality reports can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to standards and any issues encountered during production.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent inspectors to evaluate the saffron quality can offer an unbiased assessment.
What Are the QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers?
International buyers, particularly from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, must navigate various regulations and standards that can differ significantly by market.
- Regional Regulations: Understanding the specific import regulations for saffron in different countries is crucial. For example, some countries may require phytosanitary certificates to ensure the saffron is free from pests and diseases.
- Cultural Preferences: Different markets may have unique quality expectations and preferences, which suppliers should be aware of to tailor their products accordingly.
Conclusion: The Importance of Quality Assurance in Saffron Seed Manufacturing
For international B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for saffron seeds is essential. By focusing on supplier practices, certifications, and QC checkpoints, buyers can ensure that they are sourcing high-quality saffron that meets their market demands and maintains their reputation in the industry.
Practical Sourcing Guide: A Step-by-Step Checklist for ‘saffron seeds’
To assist international B2B buyers in procuring saffron seeds effectively, this guide outlines essential steps to ensure a successful sourcing process. By following this checklist, buyers can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and establish reliable supplier relationships.
Step 1: Define Your Sourcing Requirements
Clearly outline your specific needs regarding saffron seeds, including quantity, quality, and intended use. Understanding your requirements helps in narrowing down potential suppliers who can meet your specifications. Consider factors such as the saffron variety, seed size, and growing conditions that align with your agricultural practices.
Step 2: Research Potential Suppliers
Conduct thorough research to identify reputable suppliers in the saffron industry. Look for suppliers who specialize in saffron seeds and have a solid market presence. Utilize online directories, industry associations, and trade shows to gather a list of potential vendors.
- Check for Experience: Suppliers with a proven track record are more likely to provide quality products and reliable service.
- Review Online Feedback: Explore customer reviews and testimonials to gauge supplier reliability.
Step 3: Evaluate Supplier Certifications
Before engaging with suppliers, verify their certifications and compliance with agricultural standards. Certifications ensure that the saffron seeds meet quality and safety regulations, which is particularly crucial for international trade.
- Seek Organic Certifications: If you require organic saffron seeds, confirm that the supplier has the necessary organic certifications.
- Check Export Certifications: Ensure the supplier is authorized to export to your region, as this can affect the import process.
Step 4: Request Samples
Always request samples before making a bulk purchase. Evaluating samples allows you to assess the quality of the saffron seeds firsthand, including germination rates and overall health.
- Test for Viability: Conduct germination tests to ensure the seeds are viable and suitable for your growing conditions.
- Assess Physical Characteristics: Examine the seeds for size, shape, and any signs of disease or damage.
Step 5: Negotiate Terms and Pricing
Once you have identified a suitable supplier, engage in negotiations regarding pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules. Establishing clear terms helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures both parties are aligned on expectations.
- Discuss Bulk Pricing: Inquire about discounts for larger orders to optimize your procurement budget.
- Clarify Payment Methods: Choose secure payment options that protect both parties during the transaction.
Step 6: Confirm Shipping and Logistics
Discuss shipping options and logistics to ensure timely delivery of the saffron seeds. Understanding the logistics involved is vital for maintaining your planting schedule and operational efficiency.
- Verify Shipping Times: Confirm estimated delivery dates to align with your planting timeline.
- Check for Import Regulations: Familiarize yourself with any import restrictions or regulations in your country to avoid delays.
Step 7: Establish a Long-term Relationship
Aim to build a long-term relationship with your chosen supplier. Continuous collaboration can lead to better pricing, priority service, and access to new product offerings.
- Communicate Regularly: Keep an open line of communication to address any issues that may arise.
- Provide Feedback: Share your experiences and feedback to help suppliers improve their offerings.
By following this checklist, B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of sourcing saffron seeds, ensuring a successful procurement process that meets their agricultural needs.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for saffron seeds Sourcing
What Are the Key Cost Components for Saffron Seeds Sourcing?
When evaluating the cost structure of saffron seeds, several key components must be considered to provide a comprehensive understanding for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include:
-
Materials: The cost of saffron crocus bulbs (corms) varies significantly based on quality and source. Prices can range from $7.95 to $21.95 per bulb depending on the supplier and the quality of the corms. High-quality bulbs yield better flowers and, consequently, more saffron threads.
-
Labor: The labor costs associated with saffron cultivation are substantial. Saffron is traditionally hand-harvested, which requires skilled labor for flower picking and stigma extraction. This labor-intensive process contributes to the high market price of saffron.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs related to facilities, utilities, and equipment used in the cultivation and processing of saffron. Efficient operations can help reduce these overhead costs, impacting the overall pricing structure.
-
Tooling: Investment in proper gardening tools and machinery for planting and harvesting saffron can also affect the cost. While initial investments may be high, they often lead to increased efficiency and lower long-term costs.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring the quality of saffron bulbs and harvested saffron is crucial. Implementing rigorous QC processes incurs additional costs but is essential for maintaining product standards, especially for buyers seeking certifications.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs play a vital role in the overall cost of saffron seeds. Factors such as distance, shipping methods, and customs regulations can significantly influence logistics expenses.
-
Margin: Supplier margins vary widely based on market demand, competition, and the buyer’s negotiation power. Understanding the supplier’s margin can provide insights into potential price flexibility.
How Do Price Influencers Affect Saffron Seeds Pricing?
Several factors can influence the pricing of saffron seeds, particularly for international buyers:
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Suppliers often provide discounts for larger orders. Buyers should consider their consumption needs and negotiate MOQs to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Buyers requiring specific varieties or certifications (e.g., organic, fair trade) may face higher costs. Customization can lead to additional charges, so understanding the supplier’s offerings is crucial.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Higher-quality corms or certified organic bulbs generally command higher prices. Buyers should weigh the benefits of quality against their budget constraints.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers with a track record of quality may charge more due to their perceived value.
-
Incoterms: The chosen Incoterms can impact costs significantly. For instance, FOB (Free On Board) terms might require buyers to manage transportation and insurance, while DDP (Delivered Duty Paid) includes those costs in the purchase price.
What Buyer Tips Can Help Optimize Saffron Seeds Sourcing?
International B2B buyers can leverage several strategies to optimize their saffron seeds sourcing:
-
Negotiation: Building strong relationships with suppliers can facilitate better negotiation outcomes. Understanding market rates and being prepared to discuss pricing openly can lead to more favorable terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Conduct a thorough analysis of the total cost of ownership (TCO), which includes not just the purchase price but also transportation, handling, and potential wastage costs. This approach helps in assessing the true value of the investment.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and import tariffs that may affect pricing. Engaging local suppliers or distributors can sometimes mitigate these costs.
-
Market Research: Keeping abreast of market trends, demand fluctuations, and emerging suppliers can provide buyers with leverage in negotiations and help identify the best sourcing opportunities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics of saffron seeds is essential for international B2B buyers. By analyzing key cost components, recognizing price influencers, and employing strategic sourcing tips, buyers can make informed decisions that align with their business objectives. While indicative prices can provide a starting point, it is crucial to consider the broader context of sourcing saffron seeds to achieve optimal results.
Alternatives Analysis: Comparing saffron seeds With Other Solutions
Understanding the Alternatives to Saffron Seeds
In the competitive landscape of culinary and agricultural products, saffron seeds stand out due to their unique flavor profile and high market value. However, B2B buyers may also consider alternative solutions that can either complement or replace saffron seeds. This section explores viable alternatives, comparing their performance, costs, ease of implementation, maintenance requirements, and best use cases.
| Comparison Aspect | Saffron Seeds | Alternative 1: Safflower Seeds | Alternative 2: Turmeric Powder |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High-quality flavor, vibrant color | Similar color, mild flavor | Distinct earthy flavor, strong color |
| Cost | High cost per gram | Lower cost per pound | Moderate cost, widely available |
| Ease of Implementation | Requires specific climate conditions | Easy to grow in various climates | Readily available, no growing needed |
| Maintenance | Moderate (requires care and timing) | Low (minimal care needed) | None (ready to use) |
| Best Use Case | Gourmet dishes, luxury culinary items | Cost-effective coloring agent | Health-focused dishes, herbal remedies |
In-Depth Look at Alternatives
1. Safflower Seeds
Safflower seeds are often hailed as a cost-effective alternative to saffron. They produce a vibrant yellow color and can be used as a natural dye or coloring agent in culinary applications. While the flavor is milder than saffron, safflower seeds are easier to cultivate and require less maintenance. They can thrive in a variety of climates, making them accessible to a broader range of growers. However, the trade-off lies in the flavor, which may not satisfy high-end culinary applications where saffron is preferred for its distinct taste.
2. Turmeric Powder
Turmeric is another popular alternative that offers a bright yellow hue and is renowned for its health benefits. Unlike saffron, which is primarily used for its flavor, turmeric serves both culinary and medicinal purposes. It is widely available and can be incorporated into various dishes, making it a versatile ingredient. The main disadvantage is that turmeric imparts a different flavor profile that may not be suitable for all recipes that traditionally use saffron. Additionally, turmeric is available in powdered form, eliminating the need for cultivation and maintenance.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business Needs
When considering alternatives to saffron seeds, B2B buyers should evaluate their specific needs and target markets. For businesses focused on gourmet culinary experiences, saffron remains unmatched in flavor and prestige. However, for those seeking cost-effective solutions or who operate in broader markets, safflower seeds and turmeric powder provide viable alternatives that can serve different purposes. Understanding the unique properties and applications of each option will enable buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals and market demands.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for saffron seeds
What are the Key Technical Properties of Saffron Seeds?
When considering saffron seeds for commercial cultivation, several technical properties are crucial for B2B buyers to understand. Here are some of the most critical specifications:
-
Corm Size and Quality
The size of saffron corms (bulb-like structures) significantly impacts the yield and quality of the saffron produced. Typically, corms should be at least 9 cm in diameter for optimal growth. Larger corms often produce more flowers and, consequently, more saffron threads. Buyers should prioritize high-quality, larger corms as they enhance profitability through better yields. -
Days to Maturity
Understanding the days to maturity is essential for planning harvest schedules. Saffron crocus typically blooms in the fall, and the time from planting to harvest can range from 6 to 12 months, depending on local climate conditions. This knowledge allows businesses to align their production timelines with market demand, ensuring optimal sales windows. -
Hardiness Zones
Saffron thrives in specific hardiness zones, primarily between 30° and 50° latitudes. This factor is critical for buyers in regions like Africa and the Middle East, as it determines whether saffron can be successfully cultivated in their area. Understanding hardiness zones helps businesses avoid investing in seeds that may not perform well in their climate. -
Photoperiod Sensitivity
The saffron crocus is sensitive to light conditions, requiring specific day lengths to trigger flowering. This sensitivity impacts planting schedules and cultivation practices. Buyers must consider local daylight hours and adjust their growing practices accordingly, which can influence the overall cost and success of saffron production. -
Yield Potential
Each corm can produce 2 to 4 flowers, with each flower yielding 3 stigmas (saffron threads). Understanding yield potential helps buyers calculate the expected output per hectare or acre, which is essential for financial planning and market positioning. This knowledge can assist in setting competitive pricing strategies.
What Trade Terminology Should B2B Buyers Know About Saffron Seeds?
Navigating the saffron seed market requires familiarity with specific trade terms. Here are some key jargon and their meanings:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
In the context of saffron seeds, OEM refers to companies that produce saffron corms for other brands or businesses. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers establish partnerships for bulk purchases or unique product offerings in their markets. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
This term specifies the least number of units a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is crucial for buyers to assess whether they can meet the supplier’s requirements without overcommitting resources. It can also impact cash flow and inventory management. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers asking for pricing and terms for specific quantities of saffron seeds. This process allows buyers to compare offers from different suppliers, ensuring they secure the best price and terms for their purchase. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
These are standard trade terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. Familiarity with Incoterms, such as FOB (Free On Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight), is essential for buyers to understand shipping costs, insurance responsibilities, and delivery points, ultimately impacting the total cost of procurement. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the period between placing an order and receiving the product. For saffron seeds, this can vary based on the supplier’s location and production capacity. Understanding lead times helps buyers plan their operations effectively, ensuring they have the necessary stock when required.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions when sourcing saffron seeds, ultimately enhancing their competitive edge in the market.
Navigating Market Dynamics and Sourcing Trends in the saffron seeds Sector
What Are the Current Market Dynamics and Key Trends Affecting Saffron Seeds?
The global saffron market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for high-quality, organic, and gourmet food products. As the world’s most expensive spice, saffron commands a premium price, which has led to a surge in interest among international B2B buyers looking to secure reliable sources. Key trends include the rise of online sourcing platforms, which facilitate direct connections between growers and buyers, reducing intermediaries and costs. Furthermore, innovations in agricultural technology, such as precision farming and climate-resilient cultivation techniques, are becoming essential for saffron producers, particularly in regions like the Middle East and South America, where climatic conditions can be challenging.
Emerging markets in Africa and Southeast Asia are also beginning to cultivate saffron, creating new opportunities for buyers seeking diverse sourcing options. For instance, countries like Morocco and Afghanistan are enhancing their production capabilities, which could lead to more competitive pricing. Additionally, as global trade networks expand, international buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who can demonstrate transparency and reliability in their operations. This shift is particularly pronounced in regions like Europe, where stringent quality standards and regulatory compliance are paramount.
How Is Sustainability and Ethical Sourcing Impacting the Saffron Seed Industry?
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor for B2B buyers in the saffron seeds sector, as environmental concerns rise globally. The cultivation of saffron can be resource-intensive, requiring careful management of water and soil health. Ethical sourcing practices are essential to minimize environmental impact and ensure the sustainability of saffron farming. Buyers are increasingly looking for suppliers who adhere to sustainable agricultural practices, such as organic farming, which avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers.
Moreover, certifications such as GlobalGAP and Fair Trade are gaining traction among saffron producers, providing buyers with assurance regarding the ethical treatment of workers and sustainable farming practices. By sourcing saffron seeds from certified growers, businesses can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for ethically produced goods. This trend is particularly relevant in Europe and North America, where consumers are increasingly willing to pay a premium for sustainably sourced products.
What Is the Historical Context of Saffron Cultivation and Its Relevance Today?
The history of saffron cultivation dates back over 3,000 years, with origins believed to be in regions of the Mediterranean and Persia. Traditionally valued for its culinary and medicinal properties, saffron has been a symbol of luxury and wealth throughout history. Today, the relevance of saffron in the global market continues to grow, fueled by its unique flavor profile and health benefits, including antioxidant properties.
Understanding the historical significance of saffron can provide B2B buyers with insights into its cultural value, informing marketing strategies and product positioning. As buyers seek to differentiate their offerings in a competitive marketplace, leveraging the rich heritage of saffron can enhance product appeal, particularly in regions like the Middle East, where saffron holds deep cultural significance. This historical context not only enriches the narrative around saffron but also aligns with the increasing consumer interest in authenticity and provenance in food products.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of saffron seeds
-
How do I choose the right saffron seed supplier for my business?
Selecting a reliable saffron seed supplier involves several key considerations. Start by researching potential suppliers, focusing on their reputation, customer reviews, and experience in the industry. Verify their certifications and compliance with international quality standards. It’s also crucial to request samples to assess the quality of the saffron seeds. Building a relationship through direct communication can help gauge their responsiveness and willingness to meet your needs. Finally, consider suppliers who offer transparent pricing and flexible terms to align with your business model. -
What are the ideal growing conditions for saffron seeds?
Saffron thrives in well-drained, loamy soil with a pH of 6-8. It requires full sun, needing at least 5-6 hours of direct sunlight daily. The optimal climate is Mediterranean, with cool, dry winters and hot, dry summers. Ensure that the planting area has good drainage to prevent corm rot. Saffron is sensitive to excessive moisture, so avoid waterlogged conditions. Understanding these requirements will help you select suitable regions for cultivation and maximize your yield. -
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for saffron seeds?
Minimum order quantities for saffron seeds can vary significantly among suppliers. Typically, MOQs range from 50 to 500 corms, depending on the supplier’s policies and the specific variety of saffron. When negotiating, discuss your projected needs and the potential for future orders to see if suppliers can accommodate smaller initial orders. Ensure that the MOQ aligns with your budget and planting plans, allowing for adequate testing of the supplier’s products before committing to larger purchases. -
What payment terms should I expect when purchasing saffron seeds internationally?
Payment terms for international saffron seed purchases can vary widely based on the supplier and your relationship with them. Common options include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and the balance upon delivery. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or escrow services for added security. It’s advisable to negotiate terms that suit your cash flow while ensuring the supplier feels secure in the transaction. Always confirm payment methods accepted, as these may differ by region. -
How can I ensure the quality of saffron seeds before purchasing?
To ensure quality, request documentation such as seed certification and laboratory test results from potential suppliers. Consider conducting your own tests on samples to evaluate germination rates and disease resistance. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s cultivation and harvesting practices, as these significantly impact seed quality. Building a relationship with suppliers who are transparent about their processes can also provide assurance of the quality you will receive. -
What logistics should I consider when importing saffron seeds?
When importing saffron seeds, consider shipping methods, customs regulations, and import duties that may apply in your country. Ensure that the supplier provides all necessary documentation, such as phytosanitary certificates, to facilitate smooth customs clearance. It’s also wise to work with a freight forwarder experienced in agricultural products to navigate logistics efficiently. Plan for potential delays and ensure your supply chain can accommodate these fluctuations to prevent disruptions in your operations. -
What are the common challenges in sourcing saffron seeds internationally?
Sourcing saffron seeds internationally can present challenges such as fluctuating prices, varying quality standards, and potential regulatory hurdles. Language barriers and time zone differences may complicate communication with suppliers. Additionally, geopolitical factors can affect trade routes and costs. To mitigate these risks, build relationships with multiple suppliers and stay informed about market trends. Establishing clear contracts can also help protect your interests and ensure compliance with local laws. -
How can I customize my saffron seed order to fit my specific needs?
Customization options for saffron seed orders may include selecting specific varieties, adjusting quantities, or requesting specific packaging. Discuss your requirements directly with potential suppliers to see if they can accommodate your needs. Some suppliers may offer tailored solutions, such as bulk purchasing or seed blends for specific growing conditions. Ensure that any customization aligns with your growth plans and operational capabilities, and confirm that the supplier can meet your timeline and quality expectations.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Top 9 Saffron Seeds Manufacturers & Suppliers List
1. Sow True Seed – Saffron Crocus Bulbs
Domain: sowtrueseed.com
Registered: 2010 (15 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Saffron Crocus Bulbs”, “price”: “$17.95”, “availability”: “Now available for pre-order! Quantity is limited, order early to secure your bulbs!”, “estimated_shipping_window”: “October 6th – October 24th, 2025”}
2. Renee’s Garden – Saffron Crocus Bulbs
Domain: reneesgarden.com
Registered: 1998 (27 years)
Introduction: {“product_name”: “Saffron Crocus Bulbs”, “regular_price”: “$21.95”, “sale_price”: “$21.95”, “unit_price”: “per”, “lifecycle”: “Perennial”, “availability”: “In stock”}
3. Johnny’s Selected Seeds – Saffron Crocus Corm
Domain: johnnyseeds.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Saffron Crocus – Crocus Corm from Johnny’s Selected Seeds. Free Standard Shipping for Orders Over $200. Saffron Crocus is a flower bulb known for producing saffron, a valuable spice. It is categorized under flowers and is part of the Crocus family.
4. Eden Bros Nursery – Saffron Bulbs
Domain: reddit.com
Registered: 2005 (20 years)
Introduction: Saffron is typically grown from bulbs (Crocus Sativus) rather than seeds. They are usually planted in late summer or early fall and will sprout and flower within 4-6 weeks. Reputable sellers will sell bulbs at the right time of year for your location. Some sources mentioned include Eden Bros Nursery and Etsy, where 5 bulbs can be purchased for about $16. Local independent garden centers may sell t…
5. Rare Seeds – Saffron Crocus Bulbs (25 Pack)
6. Kokopelli Semences – Organic Saffron Bulbs
Domain: kokopelli-semences.com
Registered: 2012 (13 years)
Introduction: Saffron bulb – Crocus sativus (calibre 9-11), Open-Pollinated and Heirloom Seeds, 100% Certified Organic, Availability: In stock, Shipping: 3 to 4 days within Europe.
7. Gurney’s – Saffron Crocus
Domain: gurneys.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: This company, Gurney’s – Saffron Crocus, is a notable entity in the market. For specific product details, it is recommended to visit their website directly.
8. Saffron Crocus – Key Product
Domain: ebay.com
Registered: 1995 (30 years)
Introduction: Key product details for Saffron Seeds on eBay include: 1. Common Name: Saffron Crocus 2. Types: Herb Seeds, Vegetable Seeds, Bulbs, Houseplant Seeds, Bamboo Seeds, Vine Seeds 3. Season of Interest: Fall, Spring, Summer, Winter 4. Color Options: Red, Purple, Yellow, White, Multicolor, Green, Pink, Blue, Black, Orange 5. Features: Flowering, Edible, Fast Growing, Cold Resistant, Drought Resistant, D…
9. Superseeds – Saffron Crocus Bulbs
Domain: superseeds.com
Registered: 1996 (29 years)
Introduction: Saffron Crocus, also known as Crocus sativus, is a perennial flowering plant that produces saffron spice. It thrives in well-drained soil and requires full sun. The bulbs should be planted in the fall, 4-6 inches deep, and spaced 6-8 inches apart. Saffron is harvested in the fall, and each flower produces three red stigmas that are collected by hand. This product is ideal for culinary uses, adding…
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for saffron seeds
What Are the Key Takeaways for Sourcing Saffron Seeds?
Strategic sourcing of saffron seeds is pivotal for businesses aiming to capitalize on the growing demand for this high-value spice. By understanding the unique cultivation requirements and market dynamics, international buyers can secure quality saffron crocus bulbs that yield optimal harvests. Recognizing the geographical constraints of saffron cultivation—primarily in temperate regions—enables buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to identify viable sourcing partners.
How Can Strategic Sourcing Enhance Your Business?
Investing in strategic sourcing not only ensures access to premium saffron seeds but also fosters relationships with suppliers who can provide ongoing support and insights into best practices. This approach can lead to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved product quality, ultimately enhancing your competitive edge in the marketplace.
What’s Next for International Buyers of Saffron Seeds?
As the global appetite for saffron continues to rise, now is the time for proactive B2B buyers to engage with reputable suppliers. By prioritizing strategic sourcing, you can ensure a sustainable supply chain that meets the demands of your customers. Embrace this opportunity to grow your saffron offerings and position your business for long-term success in a lucrative market.